Safe and effective generator operation for residential purposes involves careful planning and execution. This encompasses selecting a generator with appropriate wattage for essential appliances, connecting appliances directly to the generator or through a properly installed transfer switch, and adhering to manufacturer instructions for safe fueling and operation. For example, a homeowner might power a refrigerator, a few lights, and a furnace during a power outage using a portable generator.
Residential generator use offers crucial backup power during outages, ensuring the continuity of essential services and enhancing safety. This capability becomes particularly vital in areas prone to severe weather or unreliable grid infrastructure. Historically, generators served primarily industrial purposes. However, technological advancements and increased affordability have made them increasingly common in residential settings, significantly improving homeowner resilience.
The following sections will delve into the specifics of generator selection, safe operation procedures, connection options, and essential maintenance practices for optimal performance and longevity.
Safe and Effective Portable Generator Operation for Home Use
Proper generator operation is crucial for safety and efficiency. The following tips provide guidance for safe and effective portable generator use in residential settings.
Tip 1: Calculate Power Needs: Determine the wattage requirements of essential appliances intended for generator power. This ensures the generator can handle the load without overloading. Consult appliance manuals for wattage information.
Tip 2: Select the Right Generator: Choose a generator with sufficient wattage to cover the calculated load, with a slight buffer for safety. Consider fuel type and runtime based on anticipated outage durations.
Tip 3: Safe Placement: Operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from doors, windows, and air intakes. Never operate a generator indoors, including garages, due to carbon monoxide risks.
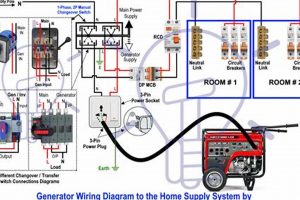
Tip 4: Proper Connection: Connect appliances directly to the generator using heavy-duty extension cords rated for the appropriate wattage, or utilize a professionally installed transfer switch for seamless integration with household circuits.
Tip 5: Safe Refueling: Allow the generator to cool completely before refueling. Store fuel in approved containers in a safe location away from the generator.
Tip 6: Regular Maintenance: Follow manufacturer recommendations for maintenance, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Tip 7: Grounding: Ensure the generator is properly grounded according to manufacturer instructions to prevent electrical shocks.
Adherence to these guidelines ensures safe and reliable backup power during outages, safeguarding both individuals and property.
By understanding these essential tips, homeowners can effectively utilize portable generators for safe and reliable backup power, enhancing their preparedness for unexpected power disruptions.
1. Safety First
Safe operation is paramount when utilizing portable generators for residential power. Negligence can lead to severe consequences, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire hazards, and electrocution. Understanding and implementing safety protocols is therefore essential for protecting life and property.
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Prevention
Generators produce carbon monoxide, an odorless, colorless, and lethal gas. Never operate a generator indoors, including garages, basements, or crawl spaces. Adequate ventilation is crucial, even outdoors. Position the generator away from windows, doors, and vents to prevent exhaust fumes from entering the home. Installing carbon monoxide detectors provides an additional layer of protection.
- Fire Hazard Mitigation
Fuel spillage and improper storage pose significant fire risks. Allow the generator to cool completely before refueling. Store fuel in approved, sealed containers away from the generator and any ignition sources. Keep flammable materials clear of the generator’s operating area.
- Electrical Safety
Incorrect electrical connections can result in electrocution or equipment damage. Avoid overloading the generator by calculating the total wattage of connected appliances. Use heavy-duty, outdoor-rated extension cords designed for the specific amperage and wattage. A properly installed transfer switch is the safest way to connect a generator to a home’s electrical system, preventing backfeeding, which can endanger utility workers.
- Safe Operation Practices
Dry hands are essential when operating a generator. Never touch the generator during rain or wet conditions. Ground the generator according to manufacturer instructions. Regularly inspect the generator for damage, including frayed cords and loose connections. Turn off the generator and allow it to cool before storing.
Prioritizing these safety measures ensures the effective and responsible use of portable generators for home backup power. Careful planning and adherence to safety guidelines mitigate potential hazards, enabling safe and reliable power generation during outages.
2. Proper Connection
Safe and effective power delivery from a portable generator relies heavily on proper connection methods. Incorrect connections can lead to appliance damage, generator overload, or even electrocution. Understanding connection options and their implications is therefore crucial for safe generator operation within a residential setting.
- Direct Connection to Appliances
This method involves connecting individual appliances directly to the generator using heavy-duty extension cords. Each cord must be rated for the specific amperage and wattage of the appliance it powers. This approach is generally suitable for powering a limited number of essential appliances. For example, a refrigerator and a few lamps could be powered directly. However, managing multiple cords can be cumbersome, and care must be taken to avoid overloading the generator.
- Transfer Switch Connection
A transfer switch, professionally installed by a qualified electrician, offers a safer and more convenient connection method. The transfer switch isolates the generator power from the utility grid, preventing backfeeding, a dangerous condition that can harm utility workers. It also allows for seamless switching between generator and utility power. This method enables powering selected household circuits, providing a more comprehensive power solution during an outage. A transfer switch might power a kitchen circuit, a living room circuit, and a bedroom circuit, ensuring broader coverage.
- Understanding Wattage and Amperage
Calculating the total wattage and amperage draw of the connected appliances is crucial for avoiding generator overload. Exceeding the generator’s capacity can damage the generator and appliances. Consult appliance manuals for wattage and amperage information. Adding these values determines the total load, ensuring the generator is appropriately sized. For example, connecting a 1500-watt space heater to a 1000-watt generator will overload the generator.
- Extension Cord Safety
When using extension cords, ensure they are heavy-duty, outdoor-rated, and designed for the specific amperage and wattage of the connected appliances. Avoid using damaged or frayed cords, as they pose a fire hazard. Proper cord management is essential to prevent tripping hazards. Using appropriately sized cords ensures safe and efficient power delivery. A 12-gauge cord might be suitable for a small appliance, while a 10-gauge cord would be necessary for a larger appliance.
Correct connection practices form the foundation of safe and efficient generator operation for home use. Whether through direct connection or a transfer switch, understanding wattage limitations, using appropriate extension cords, and prioritizing safety ensures reliable backup power during outages.
3. Load Calculation
Accurate load calculation is fundamental to safe and effective portable generator use for residential applications. Selecting a generator with insufficient capacity leads to overloads and potential damage, while an oversized generator represents unnecessary expense and potential inefficiency. Understanding power requirements ensures appropriate generator selection and prevents operational issues during outages.
- Identifying Essential Appliances
Determining which appliances require generator power during an outage is the first step in load calculation. Critical appliances might include refrigerators, freezers, sump pumps, furnaces, and essential lighting. Non-essential appliances, such as entertainment systems and non-essential lighting, can be excluded to minimize the required generator capacity. For example, a homeowner might prioritize powering a refrigerator over a television during a power outage.
- Determining Wattage Requirements
Each appliance has a specific wattage requirement, indicating its power consumption. This information is typically found on an appliance’s data plate or in its owner’s manual. Wattage represents the amount of power the appliance consumes during operation. For instance, a refrigerator might require 150 watts to run and 500 watts to start.
- Calculating Total Load
Summing the wattage requirements of all intended appliances provides the total load the generator must handle. It’s crucial to consider both the running wattage and the starting wattage, as some appliances, such as refrigerators and air conditioners, require a surge of power upon startup. Adding these values provides the maximum power demand the generator must meet. For example, if the total running wattage is 800 watts and the highest starting wattage is 500 watts, the generator should handle at least 1300 watts.
- Safety Margin
Adding a safety margin to the calculated total load is recommended. This margin, typically 10-20%, accounts for potential fluctuations in power demand and ensures the generator operates within its safe operating range. This precaution prevents overloading and potential damage. For a calculated load of 1300 watts, a 10% safety margin would suggest selecting a generator with a minimum capacity of 1430 watts.
Accurate load calculation is therefore essential for matching generator capacity to power requirements, ensuring efficient and reliable power delivery during outages. This process enables informed generator selection, preventing overloads and maximizing the generator’s operational effectiveness within the context of residential power backup.
4. Fuel Management
Proper fuel management is integral to the safe and effective operation of portable generators for home use. Incorrect handling or storage of fuel can lead to hazardous situations, including fires and environmental contamination. Effective fuel management encompasses fuel selection, storage, handling, and efficient usage, contributing significantly to the overall success of generator operation during power outages.
- Fuel Type Selection
Generators typically operate on gasoline, propane, or diesel. Gasoline is common due to its availability, but it has a limited shelf life and requires stabilizer for long-term storage. Propane offers a longer shelf life and cleaner burning but requires larger, more specialized tanks. Diesel offers high efficiency and long run times but can be more expensive and may gel in cold temperatures. The chosen fuel type influences generator maintenance and operational requirements.
- Safe Fuel Storage
Fuel should be stored in approved, sealed containers specifically designed for flammable liquids. These containers must be stored in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources, such as appliances, pilot lights, and electrical equipment. Proper storage prevents hazardous fumes and minimizes the risk of accidental fires. Rotating fuel stock ensures fuel remains usable and prevents degradation, especially important for gasoline.
- Refueling Procedures
Generators should be turned off and allowed to cool completely before refueling. This precaution prevents accidental ignition of fuel vapors. Refueling should occur outdoors or in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Spilled fuel should be cleaned up immediately to minimize fire hazards and environmental contamination. Using a funnel during refueling minimizes spills and ensures accurate fuel delivery.
- Efficient Fuel Usage
Monitoring fuel consumption and adjusting generator load can optimize fuel efficiency. Avoid overloading the generator, as this increases fuel consumption and can damage the unit. Properly maintaining the generator, including regular air filter and spark plug changes, contributes to efficient fuel usage. Operating the generator at the appropriate load for the required appliances maximizes fuel economy. Running only essential appliances during an outage helps conserve fuel and extend generator runtime.
Effective fuel management is therefore essential for the safe, efficient, and responsible use of portable generators for home backup power. Careful consideration of fuel type, storage, handling, and efficient usage practices ensures reliable generator operation during outages and minimizes potential hazards associated with fuel handling.
5. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for the safe, efficient, and long-term operation of portable generators used in residential settings. Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to decreased performance, increased fuel consumption, unexpected breakdowns, and potential safety hazards. A well-maintained generator provides reliable power during outages, while a neglected one can become a liability. For instance, failing to change the oil can lead to engine seizure, rendering the generator useless during a critical power outage.
Specific maintenance tasks vary depending on the generator model and manufacturer recommendations, but several key procedures apply universally. Regular oil changes, typically every 50-100 hours of operation, ensure proper lubrication and prevent premature engine wear. Air filter cleaning or replacement prevents dust and debris from restricting airflow, which can affect engine performance and fuel efficiency. Spark plug replacement, typically annually or as recommended by the manufacturer, ensures reliable ignition and efficient combustion. Fuel system maintenance, including draining old fuel and adding stabilizer, prevents fuel degradation and carburetor issues. For example, a homeowner operating a generator frequently during extended outages might need to change the oil more frequently than someone using it only occasionally for short durations.
Implementing a consistent maintenance schedule, adhering to manufacturer guidelines, and proactively addressing potential issues ensures the generator remains a reliable power source during emergencies. This proactive approach minimizes downtime, extends the generator’s lifespan, and contributes to safe and efficient operation, ultimately maximizing the value and dependability of the investment in home backup power. Ignoring these procedures can lead to costly repairs, reduced performance, and potential safety risks, undermining the very purpose of having a generator for emergency preparedness.
6. Placement and Ventilation
Proper placement and ventilation are paramount for safe and effective portable generator operation in residential settings. These considerations directly impact the mitigation of carbon monoxide poisoning, a serious and potentially fatal hazard associated with generator exhaust. Correct placement and ventilation practices ensure user safety and prevent the accumulation of toxic fumes within the home. Ignoring these crucial aspects can have severe consequences, jeopardizing the well-being of occupants and undermining the intended purpose of backup power generation.
- Outdoor Placement
Generators must always be operated outdoors, far from any enclosed structures. This includes garages, sheds, and other outbuildings, even if doors and windows are open. Exhaust fumes can accumulate rapidly in confined spaces, posing significant health risks. Placing the generator a safe distance from the home, ideally 20 feet or more, minimizes the risk of fumes entering through windows, doors, or ventilation systems. For instance, positioning a generator near an open window, even on a seemingly breezy day, can allow exhaust to infiltrate the home.
- Distance from Openings
Maintaining a significant distance between the generator and any openings in the home, such as windows, doors, and vents, is crucial. Exhaust fumes can be drawn into the home through these openings, even if the generator is placed outdoors. The further the generator is from the home, the lower the risk of fume infiltration. Even seemingly small gaps or cracks can allow dangerous levels of carbon monoxide to enter the home.
- Elevated Surfaces
Placing the generator on a stable, elevated surface, such as a dry concrete pad or a sturdy platform, helps prevent contact with moisture and debris. This protects the generator from damage and ensures stable operation. Elevating the generator also minimizes the risk of exhaust fumes accumulating at ground level, further reducing the potential for inhalation. For example, operating a generator directly on wet ground can damage the unit and create electrical hazards.
- Wind Direction Consideration
Considering prevailing wind direction when placing the generator is essential. Positioning the generator downwind of the home minimizes the likelihood of exhaust fumes being carried towards the residence. Monitoring wind direction during operation ensures fumes are directed away from occupied areas, further enhancing safety. Ignoring wind direction can inadvertently direct exhaust fumes towards the home, even if the generator is placed a safe distance away.
Proper placement and ventilation are therefore inextricably linked to the safe use of portable generators for home backup power. Prioritizing these safety measures ensures that the benefits of backup power are not overshadowed by the potentially fatal consequences of carbon monoxide poisoning. Careful consideration of these factors protects occupants, maintains a safe environment, and allows for the effective and responsible use of portable generators during power outages.
Frequently Asked Questions about Portable Generator Use for Home Backup Power
This FAQ section addresses common inquiries regarding the safe and effective utilization of portable generators for residential backup power. Understanding these frequently asked questions helps homeowners make informed decisions and operate generators responsibly.
Question 1: How does one determine the correct generator size for home use?
Generator size is determined by calculating the total wattage of appliances intended for generator power during an outage. Summing the running wattage of each appliance and adding the highest starting wattage of any single appliance provides the minimum generator capacity required. Adding a safety margin of 10-20% is recommended. Consulting an electrician can provide further guidance.
Question 2: What are the primary safety concerns associated with portable generator operation?
Carbon monoxide poisoning is the most significant safety concern. Generators produce this odorless, colorless, and lethal gas. Generators must always be operated outdoors, far from any enclosed structures, including garages and sheds. Additional safety concerns include fire hazards from fuel spills and electrical shocks from improper connections.
Question 3: Can a portable generator be connected directly to a home’s electrical system?
Direct connection to a home’s electrical system is strongly discouraged unless done through a properly installed transfer switch. Direct connection without a transfer switch can lead to backfeeding, energizing downed power lines and posing a lethal threat to utility workers. A qualified electrician should install a transfer switch for safe and code-compliant connection.
Question 4: What type of fuel is best for a portable generator used for home backup?
The optimal fuel type depends on individual circumstances. Gasoline is readily available but has a limited shelf life. Propane offers a longer shelf life and cleaner burning but requires larger tanks. Diesel provides high efficiency and long run times but can gel in cold weather. Fuel choice involves considering availability, storage capacity, and generator compatibility.
Question 5: How often should a portable generator be maintained?
Maintenance frequency depends on usage and manufacturer recommendations. General guidelines include oil changes every 50-100 hours of operation, air filter cleaning or replacement as needed, and spark plug replacement annually or as recommended. Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and prolongs the generator’s lifespan.
Question 6: Where should a portable generator be placed during operation?
Generators should be placed outdoors on a stable, level surface, at least 20 feet from the home and any openings, such as windows, doors, and vents. The generator should be positioned downwind of the home to prevent exhaust fumes from entering the residence. Proper placement is crucial for carbon monoxide safety.
Careful consideration of these frequently asked questions enables informed decision-making regarding generator selection, operation, and maintenance, ensuring safe and reliable backup power during outages.
For further information and specific guidance, consulting qualified electricians and reviewing manufacturer recommendations is advised.
Safe and Effective Portable Generator Operation for Residential Use
Effective utilization of portable generators for home backup power requires careful consideration of several key factors. Safe operation necessitates prioritizing proper placement, ventilation, and adherence to carbon monoxide safety guidelines. Appropriate generator selection relies on accurate load calculation, matching generator capacity to the anticipated power demands of essential appliances. Proper connection procedures, whether through direct connection or a transfer switch, are crucial for both safety and efficient power delivery. Regular maintenance, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement, ensures optimal performance and prolongs generator lifespan. Effective fuel management, encompassing safe storage, handling, and efficient usage, contributes significantly to reliable operation during outages.
Residential generator use provides crucial backup power during unforeseen outages, contributing significantly to household resilience and safety. Understanding and implementing the principles of safe operation, proper connection, accurate load calculation, routine maintenance, and effective fuel management ensures reliable performance and mitigates potential hazards. Proactive planning and responsible generator operation empower homeowners to safeguard their households during power disruptions, maintaining essential services and enhancing overall safety and well-being.