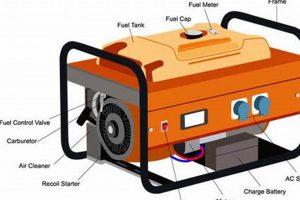
A top-tier, transportable power source designed for residential use during outages provides critical backup electricity for essential appliances and devices. For instance, during a power outage caused by a severe storm, such a unit could power refrigerators, sump pumps, and essential medical equipment. This ensures safety and maintains a degree of normalcy during disruptive events.
Reliable backup power is increasingly vital in a world facing more frequent and intense weather events. Having a readily available source of electricity safeguards against food spoilage, protects property from flooding, and ensures continued access to necessary medical devices. Historically, homeowners relied on less convenient and environmentally friendly options like gasoline-powered pumps or simply endured outages. Modern advancements in portable generator technology offer significantly quieter, cleaner, and more efficient solutions, enhancing preparedness and peace of mind.
The following sections delve into key considerations for selecting an appropriate unit, including power output requirements, fuel types, noise levels, and essential safety precautions.
Essential Tips for Portable Generator Use
Proper planning and operation are critical for maximizing the effectiveness and safety of a portable generator during emergencies. Careful consideration of the following tips will ensure reliable performance and prevent hazards.
Tip 1: Calculate Power Needs: Accurately assess the wattage requirements of essential appliances and devices that will need to be powered during an outage. This total wattage informs the necessary generator capacity.
Tip 2: Choose the Right Fuel Type: Generators are commonly fueled by gasoline, propane, or diesel. Each fuel type presents advantages and disadvantages regarding availability, storage, and environmental impact. Careful consideration of these factors is recommended.
Tip 3: Prioritize Safety: Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces. Adequate ventilation is paramount to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. Placement outdoors, away from windows and doors, is crucial.
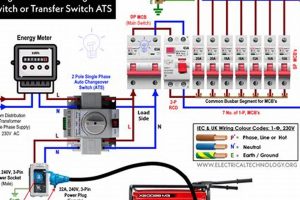
Tip 4: Connection Procedures: Utilize a properly rated transfer switch for safe connection to home circuits. Direct connection to household wiring is unsafe and can damage appliances and pose significant electrocution risks.
Tip 5: Maintenance is Key: Regular maintenance, including oil changes and air filter cleaning, ensures optimal performance and extends the generator’s lifespan. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule is vital.
Tip 6: Proper Storage: Store fuel safely and in accordance with local regulations. Fuel should be kept in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources.
Tip 7: Test Regularly: Periodically test the generator to ensure it starts and operates correctly. This practice identifies potential issues early on and confirms readiness for an actual power outage.
By adhering to these guidelines, homeowners can harness the power of portable generators safely and efficiently, mitigating the disruption and inconvenience caused by unexpected power outages.
Equipped with this essential information, the concluding section offers final recommendations for selecting the ideal portable generator and ensuring its safe and effective use.
1. Power Output
A crucial factor in selecting a suitable emergency generator is its power output, measured in watts. Understanding power requirements ensures the generator can handle the anticipated load during an outage. Insufficient power can lead to overloaded circuits and generator failure, while excessive capacity results in unnecessary fuel consumption.
- Running Watts vs. Starting Watts
Running watts represent the continuous power a generator can supply, while starting watts refer to the surge of power needed to start motor-driven appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners. Starting watts are typically higher than running watts. For example, a refrigerator might require 1,000 starting watts but only 200 running watts. Therefore, the generator must accommodate both the starting and running wattage needs of all intended appliances.
- Calculating Total Wattage Requirements
To determine the necessary generator capacity, calculate the combined running wattage of all essential devices and the highest starting wattage of any single appliance. This calculation ensures the generator can handle the initial surge when starting appliances. For instance, a household might need to power a refrigerator, sump pump, and several lights, requiring a combined wattage exceeding the sum of their individual running wattages.
- Matching Generator Capacity to Load
Choosing a generator with adequate power output is essential for reliable operation. A generator with insufficient capacity will struggle to power the required devices, while an excessively large generator consumes more fuel and is less cost-effective. Matching the generator’s capacity to the calculated load ensures efficient and reliable power delivery.
- Power Output and Fuel Consumption
Generator power output directly correlates with fuel consumption. Higher power output generally means higher fuel consumption. Selecting a generator with the appropriate power output for the anticipated load minimizes fuel usage and extends runtime. This consideration is especially important during extended outages.
Careful consideration of power output ensures the selected generator can reliably power essential appliances during an outage. Accurately assessing wattage needs and matching them to the generator’s capacity prevents overloads and optimizes fuel efficiency. This informed approach ensures preparedness and peace of mind during emergencies.
2. Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a critical factor in selecting a portable generator for home emergencies. A fuel-efficient generator reduces operating costs and minimizes the frequency of refueling during extended power outages, maximizing its practicality and minimizing environmental impact.
- Fuel Consumption Rate
Generators consume fuel at varying rates, typically measured in gallons per hour (GPH). A lower GPH indicates better fuel efficiency. This factor directly impacts the runtime on a given amount of fuel. For example, a generator consuming 0.5 GPH will run twice as long on a single tank compared to a generator consuming 1.0 GPH, assuming identical fuel tank capacities. This extended runtime is crucial during prolonged outages.
- Engine Technology and Efficiency
Modern generator engines incorporate technologies designed to improve fuel efficiency. Features like inverter technology and advanced combustion systems optimize fuel usage without compromising power output. Inverter generators, in particular, adjust engine speed based on the load, resulting in significant fuel savings compared to traditional generators running at a constant speed.
- Fuel Type and Availability
The choice of fuel type gasoline, propane, or diesel influences both efficiency and logistical considerations. Propane, for example, burns cleaner than gasoline and can be stored for extended periods without degradation, making it a practical choice for emergency preparedness. However, propane generators may have slightly lower energy density compared to gasoline equivalents, potentially affecting runtime.
- Load Management and Fuel Savings
Managing the electrical load placed on the generator can significantly impact fuel consumption. Prioritizing essential appliances and avoiding unnecessary power usage reduces the load and extends the generator’s runtime on a given amount of fuel. Power management strategies, such as using energy-efficient appliances and staggering usage, further enhance fuel efficiency.
Prioritizing fuel efficiency in generator selection translates to significant long-term cost savings, reduced environmental impact, and extended operation during critical power outages. Choosing a model that balances power output with efficient fuel consumption ensures reliable performance when needed most.
3. Noise Levels
Noise levels are a crucial consideration when selecting a portable generator, especially for residential use. Excessive noise can disrupt daily life, irritate neighbors, and violate local noise ordinances. A quieter generator enhances comfort during extended outages and minimizes disturbance to the surrounding environment. For example, some communities enforce nighttime noise restrictions, making a low-decibel generator essential for overnight power supply.
Generator noise levels are typically measured in decibels (dB). Lower dB ratings signify quieter operation. Manufacturers often provide noise level specifications at a specific distance, usually 7 meters. Comparing these ratings across different models helps consumers make informed decisions. Furthermore, technological advancements, such as inverter technology and sound-dampening enclosures, contribute to significantly quieter operation in modern generators. The practical implication is that users can operate these generators without causing undue noise pollution.
Understanding the impact of generator noise levels is vital for both user convenience and community harmony. Choosing a quieter generator demonstrates consideration for neighbors and ensures compliance with local regulations. This factor, alongside power output and fuel efficiency, contributes significantly to the overall quality and suitability of a portable generator for home emergency use.
4. Runtime
Runtime, the duration a portable generator can operate continuously on a single fuel tank, is a critical factor influencing its suitability for emergency home use. Extended runtime translates to uninterrupted power supply during prolonged outages, ensuring essential appliances and systems remain functional. This capability is paramount for maintaining safety, preserving food, and powering critical medical devices. For instance, during a multi-day power outage caused by a severe winter storm, a generator with a longer runtime provides sustained power for heating systems, preventing pipe freezing and potential property damage. Conversely, a generator with limited runtime necessitates frequent refueling, potentially posing logistical challenges and safety risks during hazardous conditions.
Several factors influence generator runtime, including fuel tank capacity, engine efficiency, and power demand. Larger fuel tanks generally provide longer runtimes, but also increase the generator’s size and weight. Fuel-efficient engines maximize runtime on a given amount of fuel, while minimizing operating costs and environmental impact. Power demand directly affects runtime; higher power consumption reduces the duration of operation on a single tank. Consequently, balancing power needs with desired runtime is crucial when selecting a generator. Operating a smaller number of essential appliances extends the available runtime, while powering numerous devices simultaneously depletes the fuel supply more rapidly.
Understanding the interplay between runtime, fuel capacity, engine efficiency, and power demand is crucial for selecting a generator that effectively meets specific emergency preparedness needs. A generator with adequate runtime provides a reliable source of power during extended outages, minimizing disruptions and maximizing safety and comfort. This consideration, alongside factors such as power output and noise levels, defines a “best” option for home emergency power solutions.
5. Portability
Portability is a defining characteristic of emergency generators designed for residential use, directly impacting their practicality and ease of deployment during critical situations. The ability to easily move and position the generator influences its usability in various scenarios, from powering a home during a widespread outage to providing temporary power for outdoor events. A generator’s portability features must align with individual needs and the anticipated use cases to ensure optimal functionality and convenience.
- Weight and Dimensions
The physical size and weight of a portable generator dictate its maneuverability. Lighter, more compact units are easier to transport and position, while heavier models may require assistance or specialized equipment for movement. For example, a compact, lightweight generator can be easily moved by a single person from storage to the desired operating location, while a larger, heavier unit might necessitate a wheeled dolly or multiple individuals for safe transport. The weight and dimensions should be carefully considered based on individual physical capabilities and storage limitations.
- Wheels and Handles
Integrated features like wheels and handles significantly enhance portability. Durable, well-designed wheels facilitate smooth movement across various terrains, while ergonomically designed handles provide a secure and comfortable grip during transport. A generator equipped with never-flat wheels can be easily rolled over uneven ground, while a folding handle minimizes storage space requirements. These features are essential for users who anticipate needing to move the generator frequently or over longer distances.
- Compact Design
A compact design minimizes the generator’s footprint, simplifying storage and transportation. Units with a smaller form factor are easier to fit into vehicles or store in limited spaces, increasing their versatility and practicality. A compact generator can be stored in a garage or shed without consuming excessive space, while its smaller size simplifies transport in the back of a truck or SUV. This attribute is particularly advantageous for individuals with limited storage space or those who anticipate needing to transport the generator to different locations.
- Ease of Setup
Beyond physical portability, the ease with which a generator can be set up and operational influences its overall usability. Simplified setup procedures, clear instructions, and readily accessible controls minimize the time and effort required to initiate power generation. A generator with a straightforward starting mechanism and clearly labeled connection points can be quickly deployed during an emergency, minimizing downtime and maximizing its effectiveness. This aspect of portability is crucial for users who may need to quickly deploy the generator in stressful or time-sensitive situations.
The portability of a home emergency generator is intrinsically linked to its overall value and practicality. A truly portable generator seamlessly integrates factors such as weight, dimensions, integrated features, and ease of setup to provide a versatile and readily deployable power solution. Careful consideration of these elements ensures the selected generator aligns with individual needs and the anticipated usage scenarios, maximizing its effectiveness during critical power outages.
6. Safety Features
Safety features are paramount in defining a “best” home emergency portable generator. These features protect users, connected appliances, and the surrounding environment from potential hazards associated with generator operation. Generators produce electricity and potentially harmful exhaust gases, necessitating robust safety mechanisms. A generator lacking essential safety features presents significant risks, potentially leading to injuries, property damage, or even fatalities. For instance, a generator without automatic carbon monoxide shut-off could expose users to lethal levels of this odorless, colorless gas, especially during enclosed or poorly ventilated operation.
Critical safety features in a high-quality portable generator include automatic carbon monoxide shut-off, overload protection, low-oil shutdown, and properly grounded outlets. Carbon monoxide detectors automatically shut down the generator if dangerous levels of this gas are detected, preventing potential poisoning. Overload protection prevents damage to the generator and connected appliances by automatically shutting down the unit if the electrical load exceeds its capacity. Low-oil shutdown protects the engine from damage by automatically shutting down the generator when oil levels drop below a safe operating threshold. Properly grounded outlets minimize the risk of electrical shock. These features collectively mitigate potential risks associated with generator operation, safeguarding users and their property.
Prioritizing safety features in generator selection ensures reliable and hazard-free operation during emergencies. Choosing a generator equipped with these essential safety mechanisms protects users and their property from potential harm. Understanding the function and importance of each safety feature empowers informed decision-making and ultimately contributes to the selection of a truly “best” home emergency portable generator. This informed approach aligns with the core principle of emergency preparedness: mitigating risks and ensuring safety during critical situations.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection and utilization of portable generators for home emergency preparedness. Clear and concise answers provide practical guidance for consumers navigating the complexities of generator technology.
Question 1: What size generator is needed to power a typical home?
Generator sizing depends on the specific power requirements of essential appliances. Calculating the combined running wattage of necessary devices, including refrigerators, sump pumps, and lighting, determines the appropriate generator capacity. Consulting a qualified electrician can provide a precise assessment of household power needs.
Question 2: How long can a portable generator run continuously?
Runtime varies depending on fuel tank capacity, engine efficiency, and power demand. Generators with larger fuel tanks and more efficient engines offer extended runtimes. Managing the electrical load by prioritizing essential appliances can also maximize runtime.
Question 3: What type of fuel is best for a portable generator?
Common fuel types include gasoline, propane, and diesel. Gasoline is readily available but has a limited shelf life. Propane offers extended storage stability and cleaner burning. Diesel provides high efficiency but can be more expensive. Fuel choice depends on individual needs and storage capabilities.
Question 4: Where should a portable generator be placed during operation?
Generators should always be operated outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from windows, doors, and other openings. This placement prevents carbon monoxide buildup and minimizes noise pollution. Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces.
Question 5: Is a transfer switch necessary for connecting a portable generator?
A transfer switch is highly recommended for safe and proper connection to home circuits. Direct connection to household wiring is unsafe and can damage appliances. A transfer switch isolates the generator’s power supply, preventing backfeeding into the utility grid, which poses significant risks to utility workers.
Question 6: How often should a portable generator be maintained?
Regular maintenance, as outlined in the manufacturer’s instructions, is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Typical maintenance tasks include oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement. Adhering to the recommended maintenance schedule ensures reliable operation during emergencies.
Understanding these key aspects of generator selection and usage ensures informed decision-making and promotes safe and efficient operation during power outages. Investing time in researching and understanding these factors provides homeowners with the knowledge necessary to choose the most suitable generator for their specific needs.
The following section provides concluding remarks and final recommendations for selecting the ideal portable generator for home emergency preparedness.
Best Home Emergency Portable Generator
Selecting a top-tier portable generator for emergency home use requires careful evaluation of several crucial factors. Power output must align with anticipated load requirements. Fuel efficiency impacts operational costs and runtime. Noise levels affect both user comfort and neighborhood harmony. Portability influences ease of use and storage. Robust safety features are non-negotiable for user protection. A comprehensive understanding of these interconnected elements empowers informed decision-making, ensuring the chosen unit effectively meets individual needs and provides reliable power during critical outages. Investing in a high-quality portable generator represents a significant step towards enhanced emergency preparedness.
Reliable access to electricity is essential for maintaining safety and well-being during unforeseen disruptions. Portable generators offer a practical solution for mitigating the impact of power outages, ensuring critical systems remain operational. Diligent research and careful consideration of the factors discussed herein empower homeowners to select the best portable generator for their specific circumstances. This proactive approach ensures preparedness and peace of mind in the face of unpredictable events. A well-chosen portable generator represents a valuable investment in resilience and self-sufficiency.