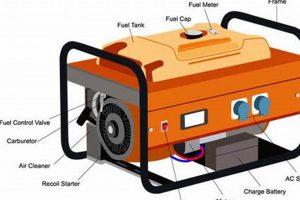
Connecting a portable generator to a home’s electrical system involves establishing a safe and effective power transfer during outages. This typically requires a transfer switch, a device that isolates the home’s circuits from the utility grid and connects them to the generator’s output. Alternative methods, like using extension cords for individual appliances, exist but pose safety risks and are not recommended for powering an entire house.
Reliable backup power is crucial for maintaining essential functions during grid failures. Uninterrupted power can prevent food spoilage, maintain comfortable temperatures, and power critical medical equipment or communication devices. Planning ahead and ensuring proper generator installation safeguards against the disruption and potential dangers associated with power loss. The increased reliance on electricity in modern homes highlights the growing importance of readily available backup solutions.
Successfully integrating a portable generator involves careful planning and execution. The following sections will cover crucial safety considerations, the necessary equipment, and step-by-step connection procedures, offering a comprehensive guide to establishing a reliable backup power source.
Tips for Portable Generator Connection
Safe and effective generator integration requires careful attention to detail. These tips provide crucial guidance for proper connection procedures.
Tip 1: Consult a qualified electrician. Professional guidance is essential for safe generator installation, particularly for integrating a transfer switch. Electrical codes and regulations vary, and professional expertise ensures compliance and mitigates potential hazards.
Tip 2: Select the appropriate generator size. Generator capacity should match the power requirements of the appliances intended for backup power. Calculating wattage needs accurately ensures sufficient power delivery.
Tip 3: Utilize a transfer switch for whole-house connections. Transfer switches prevent backfeeding, a dangerous phenomenon that can energize downed power lines and pose risks to utility workers. They also simplify the connection process.
Tip 4: Position the generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area. Generator exhaust contains carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and deadly gas. Adequate ventilation is crucial to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
Tip 5: Allow the generator to cool before refueling. Hot engine components and spilled fuel can ignite. Allowing sufficient cooling time before refueling minimizes fire hazards.
Tip 6: Regularly inspect and maintain the generator. Routine maintenance, including oil changes and spark plug replacements, ensures reliable operation during power outages.
Tip 7: Store fuel safely in approved containers. Proper fuel storage prevents leaks and minimizes fire risks. Store fuel away from ignition sources and in a well-ventilated area.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures safe and efficient generator operation, providing a reliable power source during outages. Careful planning and execution are crucial for maximizing generator effectiveness and minimizing potential hazards.
By understanding these crucial steps, individuals can equip themselves with the knowledge needed for successful portable generator integration, thereby ensuring a safe and reliable backup power solution.
1. Safety First
Safe operation is paramount when connecting a portable generator. Overlooking safety protocols can lead to serious consequences, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire hazards, and electrical shocks. Understanding and implementing safety measures is crucial for protecting individuals and property.
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Prevention
Generator exhaust contains carbon monoxide, an odorless, colorless, and lethal gas. Generators should always be operated outdoors in a well-ventilated area, far from windows, doors, and vents. Never operate a generator indoors, in garages, or in enclosed spaces. Carbon monoxide detectors should be installed and tested regularly.
- Fire Hazard Mitigation
Fuel spills and hot engine components pose significant fire risks. Allow the generator to cool completely before refueling. Store fuel in approved containers away from ignition sources. Keep flammable materials away from the generator’s operating area. A fire extinguisher rated for gasoline fires should be readily available.
- Electrical Shock Prevention
Proper grounding is essential to prevent electrical shocks. Ensure the generator is properly grounded according to manufacturer instructions and local electrical codes. Avoid contact with water or wet surfaces while operating the generator. Damaged power cords should be replaced immediately.
- Safe Connection Procedures
Using a transfer switch is the safest method for connecting a generator to a home’s electrical system. Transfer switches prevent backfeeding, which can energize downed power lines and pose a lethal threat to utility workers. Never connect a generator directly to a wall outlet.
Prioritizing safety during generator connection is not merely a recommendation; it is a necessity. Implementing these safety measures ensures the well-being of individuals and prevents potential damage to property. Adherence to safety guidelines allows for safe and reliable backup power during outages.
2. Transfer Switch
Transfer switches play a critical role in safely connecting a portable generator to a home’s electrical system. They serve as the central point for managing power flow, ensuring the generator powers the house safely without backfeeding onto the utility grid. Understanding the functionality of a transfer switch is essential for proper generator integration.
- Preventing Backfeeding
A primary function of a transfer switch is preventing backfeeding, a dangerous condition where electricity flows from the generator back onto the utility grid. This can energize downed power lines, posing a lethal threat to utility workers. Transfer switches isolate the home’s circuits from the utility lines during generator operation, eliminating this risk. Neglecting a transfer switch significantly compromises safety.
- Types of Transfer Switches
Several types of transfer switches are available, each designed for specific applications. Manual transfer switches require user intervention to switch between utility and generator power. Automatic transfer switches detect power outages and automatically engage the generator. Selecting the appropriate type depends on individual needs and budget. Manual switches offer a more affordable option, while automatic switches provide greater convenience.
- Installation Considerations
Transfer switch installation requires professional expertise. An electrician will assess the home’s electrical system, determine the appropriate transfer switch capacity, and ensure compliance with local electrical codes. Proper installation is crucial for safe and effective operation. Incorrect installation can lead to malfunctions, safety hazards, and potential damage to appliances.
- Impact on Appliance Usage
Transfer switches dictate which circuits receive power from the generator. Homeowners can choose to power essential circuits or the entire house, depending on the generator’s capacity and the transfer switch configuration. This allows for prioritized power distribution during outages. Understanding circuit management is essential for effective power allocation during emergencies.
The transfer switch is an integral component of safe and effective generator integration. Its role in preventing backfeeding, the different types available, proper installation procedures, and its impact on appliance usage are crucial factors for homeowners to consider. Proper understanding and implementation of a transfer switch ensure a reliable and safe backup power solution during utility outages.
3. Proper Grounding
Proper grounding is a critical safety aspect of portable generator connection. It provides a low-resistance path for fault currents to flow to the earth, protecting individuals and equipment from electrical shocks. Without proper grounding, a generator can become energized, posing a lethal hazard. A grounded generator ensures that any unintended electrical flow is directed safely away, preventing potentially fatal shocks. For instance, a faulty appliance connected to an ungrounded generator could energize the generator’s metal casing, creating a shock hazard for anyone who touches it. Conversely, a properly grounded generator would divert the fault current to the earth, minimizing the risk of shock.
Grounding a portable generator typically involves connecting a grounding wire from the generator’s grounding terminal to a grounding rod driven into the earth. The grounding rod must be of sufficient length and diameter to provide an effective ground. Local electrical codes dictate specific grounding requirements, and adherence to these regulations is paramount. Using inadequate grounding materials or improper installation methods can compromise the safety of the generator, rendering the grounding system ineffective. In practical applications, grounding is crucial for outdoor use where moisture and debris can create conductive paths. A grounded generator minimizes the risk of shocks, especially in wet conditions, ensuring operator safety.
Neglecting proper grounding presents substantial risks, including electrical shocks, equipment damage, and fire hazards. Grounding safeguards against these dangers by providing a designated path for stray electrical currents. Ensuring a reliable grounding system is an essential step in safe generator operation, reducing the likelihood of accidents and enhancing overall safety. Understanding and implementing proper grounding techniques is therefore indispensable for anyone operating a portable generator.
4. Fuel Management
Fuel management is integral to safe and efficient portable generator operation. Incorrect fuel handling poses significant fire hazards and can damage the generator, potentially leading to malfunctions or complete failure. Effective fuel management encompasses proper storage, correct fuel type selection, and careful refueling procedures. For instance, using contaminated fuel can clog the carburetor and prevent the generator from starting, while storing fuel in unsuitable containers can lead to leaks and hazardous fumes.
Appropriate fuel selection is crucial for preventing engine damage. Generators require specific fuel types, as indicated in the manufacturer’s instructions. Using the wrong fuel can lead to performance issues, engine damage, and increased emissions. Gasoline generators, for example, typically require unleaded gasoline with a specific octane rating. Using diesel fuel in a gasoline generator would cause significant damage. Further, fuel stabilizers prevent deterioration during storage, ensuring reliable starting after prolonged periods of non-use, especially crucial for emergency backup power situations.
Safe refueling procedures minimize fire risks. Generators should be turned off and allowed to cool completely before refueling. This prevents hot engine components from igniting spilled fuel. Refueling should occur in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Properly sealing fuel containers prevents leaks and minimizes the risk of accidental fires. Understanding these procedures and adhering to safety precautions ensures reliable generator operation and mitigates potential hazards associated with fuel handling. Neglecting these practices can not only compromise the generator’s function but also endanger lives and property.
5. Load Calculation
Accurate load calculation is fundamental to selecting and operating a portable generator effectively. Understanding the power demands of intended appliances ensures the generator can handle the required load without overloading, preventing potential damage to both the generator and connected devices. Incorrect load calculation can lead to insufficient power supply or generator overload, jeopardizing the functionality of essential appliances during outages and potentially shortening the generator’s lifespan.
- Wattage Assessment
Determining the wattage requirements of each appliance intended for generator power is the first step in load calculation. Appliance wattage is typically found on a label affixed to the device or in the owner’s manual. Adding the wattages of all intended appliances provides the total power demand the generator must meet. For example, a refrigerator might require 1500 watts at startup and 700 watts during continuous operation. Accurately assessing these values is crucial for precise load calculation.
- Starting vs. Running Watts
Appliances with electric motors, such as refrigerators and air conditioners, require a surge of power upon startup, known as starting wattage. This surge is typically higher than the wattage needed for continuous operation (running wattage). Load calculations must account for both starting and running wattages to ensure the generator can handle the initial surge without overloading. Failure to account for starting wattage can lead to the generator stalling when appliances are switched on.
- Generator Capacity Selection
Once the total load is determined, selecting a generator with sufficient capacity is essential. The generator’s rated wattage should exceed the calculated load to provide a safety margin and accommodate potential future needs. Choosing a generator with inadequate capacity will lead to overloads, potentially damaging the generator and connected appliances. Conversely, an oversized generator wastes fuel and increases operating costs. Careful selection ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
- Load Management
Effective load management involves prioritizing essential appliances during generator operation. Powering all appliances simultaneously might exceed the generator’s capacity. Prioritizing critical appliances like refrigerators, medical equipment, and lighting ensures essential functions are maintained during outages. Load management maximizes generator run time and prevents overloads, optimizing power distribution during emergencies.
Accurate load calculation is therefore inextricably linked to the successful integration and operation of a portable home generator. Understanding wattage requirements, differentiating between starting and running watts, selecting appropriately sized generators, and implementing load management strategies are all crucial steps in ensuring a reliable and safe backup power solution. These considerations optimize generator performance and protect both the generator and connected appliances, maximizing the effectiveness of the backup power system during utility outages.
6. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the reliable and safe operation of a portable generator, especially crucial when it serves as a backup power source. Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to performance issues, reduced lifespan, and potentially hazardous situations during power outages. Proper maintenance ensures the generator functions optimally when needed most, providing consistent power and minimizing the risk of malfunctions. A well-maintained generator is a reliable generator.
- Oil Changes
Regular oil changes are fundamental to engine health and longevity. Oil lubricates moving parts, reducing friction and heat. Over time, oil degrades and loses its lubricating properties, increasing engine wear. Following the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals ensures optimal engine performance and prolongs the generator’s lifespan. For example, failing to change the oil can lead to overheating, increased fuel consumption, and ultimately, engine failure.
- Air Filter Cleaning/Replacement
Clean air filters are crucial for proper engine combustion. Dirty air filters restrict airflow, reducing engine efficiency and increasing fuel consumption. Regularly cleaning or replacing the air filter, as specified in the manufacturer’s instructions, maintains optimal airflow, ensuring efficient fuel combustion and maximizing generator output. A clogged air filter can lead to reduced power output, increased emissions, and potential engine damage.
- Spark Plug Inspection/Replacement
Spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine cylinder. Worn or fouled spark plugs can cause misfires, reducing engine performance and increasing fuel consumption. Regular inspection and replacement of spark plugs, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, ensures reliable ignition and optimal engine performance. Worn spark plugs can lead to difficulty starting, rough running, and decreased fuel efficiency.
- Fuel System Maintenance
Proper fuel system maintenance prevents fuel-related issues that can affect generator performance. This includes draining the fuel tank and carburetor during periods of prolonged storage to prevent fuel degradation and gumming. Inspecting fuel lines for leaks and cracks ensures safe operation. Using fuel stabilizers helps prevent fuel degradation during storage, maintaining fuel quality and ensuring reliable starting. Neglecting fuel system maintenance can lead to starting problems, reduced performance, and potential fuel leaks, creating fire hazards.
Regular maintenance is therefore integral to the safe and reliable operation of a portable generator. By adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, homeowners can ensure their generator is ready to provide essential power during outages. This preventative approach minimizes the risk of malfunctions, extends the generator’s lifespan, and provides peace of mind during emergencies. Proper maintenance, in essence, transforms the process of hooking up a portable generator from a simple task into a sustainable and reliable backup power solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common inquiries regarding portable generator connection clarifies crucial aspects of safe and effective operation. Understanding these points ensures proper usage and mitigates potential risks.
Question 1: Is professional installation necessary for a portable generator?
While connecting a generator to individual appliances via extension cords can be done independently, integrating a transfer switch requires professional electrical expertise. Professional installation ensures compliance with electrical codes and maximizes safety.
Question 2: How is the correct generator size determined?
Generator size selection depends on the total wattage of the appliances intended for backup power. Calculating the combined running wattage and considering starting wattage requirements for motor-driven appliances ensures the generator can handle the load. Consulting an electrician can assist with accurate load calculations.
Question 3: What are the hazards of backfeeding?
Backfeeding occurs when electricity flows from the generator back onto the utility grid, potentially energizing downed power lines and creating lethal hazards for utility workers. Transfer switches prevent backfeeding, ensuring the safety of utility personnel.
Question 4: Where should a portable generator be operated?
Generators should always be operated outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from windows, doors, and vents. Generator exhaust contains carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and deadly gas. Operating a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces poses significant health risks.
Question 5: What type of maintenance does a portable generator require?
Regular maintenance is crucial for reliable generator performance. This includes regular oil changes, air filter cleaning or replacement, spark plug inspection and replacement, and fuel system maintenance. Adhering to the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule ensures optimal generator performance and longevity.
Question 6: How should generator fuel be stored?
Fuel should be stored in approved, sealed containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Proper fuel storage minimizes fire risks and prevents fuel degradation. Never store fuel indoors or near heat sources.
Understanding these frequently asked questions provides essential knowledge for safe and effective portable generator operation. Prioritizing safety, adhering to proper procedures, and performing regular maintenance ensure reliable backup power during outages.
For further information and specific guidance, consulting qualified electricians and referring to the generator manufacturers instructions is highly recommended.
Connecting a Portable Generator Safely and Effectively
Establishing a reliable backup power source requires a thorough understanding of safe connection procedures. This exploration has highlighted the crucial steps involved in connecting a portable generator, emphasizing the importance of safety precautions, proper equipment utilization, and adherence to established guidelines. Key aspects covered include the critical role of transfer switches in preventing backfeeding, the significance of proper grounding for electrical safety, the importance of accurate load calculation for optimal generator performance, and the necessity of regular maintenance for reliable operation. Fuel management and adherence to manufacturer specifications were also underscored as essential elements of safe and effective generator use.
Reliable backup power is paramount in today’s increasingly electrified world. Investing time and effort in understanding proper generator connection procedures safeguards against the disruptions and potential hazards associated with power outages. Careful planning, professional guidance when necessary, and adherence to safety protocols ensure a secure and dependable backup power solution, providing peace of mind during unforeseen power disruptions and contributing to enhanced home safety and preparedness.