A compact, fuel-powered device provides temporary electrical power to residential buildings. These units are typically employed during power outages caused by severe weather, grid failures, or in locations lacking permanent grid access. They offer a range of power outputs, enabling operation of essential household appliances and devices.
Backup power supplies are crucial for maintaining essential services during disruptions to the electrical grid. These disruptions can have significant impacts on safety, comfort, and the preservation of food and medication. The ability to power vital equipment such as refrigerators, sump pumps, heating systems, and medical devices can be life-saving. Historically, reliance on candles, oil lamps, and wood-burning stoves posed significant safety risks during extended power outages. The advent of compact power generation technologies has dramatically improved safety and quality of life during these events.
This article will explore the various types of compact, fuel-based residential generators, their selection criteria, safe operation procedures, maintenance requirements, and the benefits of incorporating them into a comprehensive home emergency preparedness plan.
Safety and Operational Tips for Portable Generators
Proper operation and safety procedures are crucial for maximizing the effectiveness and lifespan of a portable generator while mitigating potential hazards.
Tip 1: Operate Outdoors Only: Never operate a portable generator indoors, including garages, basements, or crawl spaces. Exhaust fumes contain carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and lethal gas. Ensure adequate ventilation around the unit.
Tip 2: Dry Location Required: Operate the generator on a dry, level surface away from rain and snow. Moisture can damage the unit and create electrical hazards.
Tip 3: Safe Refueling Practices: Turn off the generator and allow it to cool completely before refueling. Gasoline vapors are highly flammable. Store fuel in approved containers away from ignition sources.
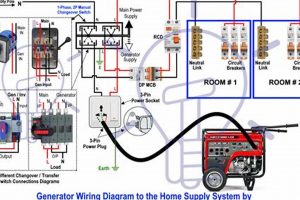
Tip 4: Proper Connection Procedures: Never connect a portable generator directly to household wiring. This can create dangerous backfeeding to the electrical grid, posing risks to utility workers. Use a transfer switch installed by a qualified electrician.
Tip 5: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Protection: Utilize extension cords equipped with GFCI protection for added safety against electrical shocks, especially in damp conditions.
Tip 6: Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance intervals, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement. Regular maintenance ensures reliable operation and extends the generator’s lifespan.
Tip 7: Load Management: Avoid overloading the generator. Calculate the total wattage of the devices being powered and operate within the generator’s specified wattage capacity.
Adherence to these guidelines promotes safe and efficient operation, extending the lifespan of the equipment and safeguarding against potential hazards.
By prioritizing safety and following recommended operational guidelines, homeowners can maximize the benefits of portable power generation during emergencies.
1. Power Output
A critical factor in selecting a portable generator for residential use is its power output, measured in watts. This specification dictates the number and type of appliances and devices the generator can power simultaneously. Understanding power output is essential for matching the generator to specific household needs and avoiding overload, which can damage both the generator and connected equipment.
- Starting Watts vs. Running Watts
Electrical devices require a surge of power to start, known as starting watts, which is significantly higher than the power required to maintain operation, known as running watts. Generators are rated with both values. For example, a refrigerator might require 2,000 starting watts but only 700 running watts. Selecting a generator with sufficient starting wattage is crucial to ensure appliances start correctly.
- Calculating Total Power Requirements
Determining the combined wattage requirements of essential appliances is vital for selecting a generator with adequate capacity. Adding the running watts of intended devices, and factoring in the highest starting wattage of any single appliance, provides the minimum required generator output. For instance, a household intending to power a refrigerator, sump pump, and several lights must sum the individual wattages to determine the appropriate generator size.
- Overload Protection
Most generators incorporate overload protection mechanisms, such as circuit breakers, to prevent damage from exceeding the rated power output. However, relying solely on these mechanisms is not recommended. Careful load management, prioritizing essential appliances and avoiding simultaneous operation of high-wattage devices, ensures optimal generator performance and longevity.
- Power Output and Fuel Consumption
Higher power output generally correlates with higher fuel consumption. While a larger generator offers greater versatility, it also necessitates more frequent refueling and incurs higher operating costs. Balancing power requirements with fuel efficiency is a crucial consideration when selecting a generator.
Matching the power output of a portable generator to the specific electrical demands of a household is fundamental for ensuring its effectiveness during power outages. Accurate calculation of power needs and careful load management optimize performance and prevent overload, extending the generator’s operational life and guaranteeing the reliable operation of essential household systems.
2. Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency represents a crucial consideration when selecting a gasoline-powered portable generator for residential use. It directly impacts operational costs and the frequency of refueling, particularly during extended power outages. A more fuel-efficient generator requires less gasoline to produce the same amount of power, translating to lower fuel expenses and reduced logistical burdens associated with fuel acquisition and storage. This is particularly important in emergency situations where gasoline availability may be limited.
Fuel efficiency in these generators is typically expressed in gallons per hour (GPH) at various load levels. Manufacturers often provide fuel consumption data at different percentages of the generator’s rated output. For example, a generator might consume 0.5 GPH at 25% load, 0.75 GPH at 50% load, and 1.0 GPH at full load. Understanding these varying consumption rates allows for more accurate estimation of fuel requirements based on anticipated load demands. Furthermore, technological advancements such as inverter technology contribute to improved fuel efficiency by adjusting engine speed to match the power demand, reducing fuel consumption during periods of lower power usage. Choosing a generator with a larger fuel tank capacity can also extend the runtime between refueling sessions, but this must be balanced against considerations of portability and storage space.
Careful consideration of fuel efficiency is essential for optimizing the cost-effectiveness and logistical practicality of operating a portable generator. Evaluating fuel consumption data at various load levels, understanding the impact of technological advancements, and selecting an appropriately sized fuel tank contribute to a more informed purchasing decision and more efficient operation during power outages. This ultimately reduces the financial and logistical burden associated with powering essential household systems during emergencies.
3. Runtime
Runtime represents a critical factor influencing the practical utility of a gasoline-powered portable generator for residential applications. It signifies the duration a generator can operate continuously on a single tank of fuel at a given load. This duration directly impacts the generator’s ability to provide uninterrupted power during extended outages. The interplay between fuel tank capacity and fuel consumption rate determines the overall runtime. A larger fuel tank generally allows for longer operation, while a more fuel-efficient engine extends runtime by consuming less gasoline per hour. For instance, a generator with a 5-gallon tank consuming 0.5 gallons per hour at 50% load will offer a 10-hour runtime. Understanding runtime characteristics is essential for matching the generator to specific needs and outage scenarios.
Runtime considerations become particularly salient during prolonged power outages where refueling may be difficult or impossible. A longer runtime minimizes the frequency of refueling, reducing logistical challenges and ensuring continuous power for critical systems. For example, during a multi-day power outage caused by a severe storm, a generator with a longer runtime can power essential appliances overnight without requiring refueling, enhancing safety and comfort. Conversely, a generator with a short runtime might necessitate frequent refueling, potentially disrupting sleep and increasing the risk of operating the generator in hazardous conditions during the night. Therefore, accurate assessment of anticipated outage duration and corresponding power needs is crucial for selecting a generator with appropriate runtime capabilities. Balancing runtime against fuel tank size and portability is also an important consideration, as larger tanks increase weight and storage requirements.
In summary, runtime serves as a key performance indicator for gasoline-powered portable generators in residential settings. A thorough understanding of runtime characteristics, including the interplay of fuel tank capacity, fuel consumption rate, and load demands, is essential for effective generator selection. Prioritizing adequate runtime based on anticipated outage durations and power needs ensures uninterrupted operation of critical household systems during emergencies, enhancing safety and mitigating disruptions to daily life. This understanding, combined with considerations of fuel efficiency and power output, allows for informed decision-making and optimal generator utilization.
4. Noise Levels
Noise levels represent a significant consideration when selecting and operating a gasoline-powered portable generator for residential use. Excessive noise can disrupt household activities, disturb neighbors, and violate local noise ordinances. Understanding the factors influencing generator noise levels and available mitigation strategies is essential for responsible and considerate operation.
- Decibel Levels and Human Perception
Generator noise is typically measured in decibels (dB). A higher dB value indicates a louder sound. Prolonged exposure to high dB levels can cause hearing damage. Furthermore, the human ear perceives certain frequencies as more intrusive than others. Generators often produce noise in a frequency range that is particularly noticeable and potentially irritating. Understanding the dB output of a generator and how it translates to perceived loudness is crucial for assessing its suitability for residential environments.
- Factors Influencing Noise Output
Several factors contribute to a generator’s noise output, including engine design, load level, and enclosure design. Generators with larger engines tend to produce more noise. Operating a generator at higher loads typically increases noise levels. Some generators feature sound-attenuating enclosures or mufflers designed to minimize noise output. Considering these factors during generator selection can help minimize noise pollution.
- Mitigation Strategies
Various strategies can mitigate generator noise. Placing the generator on a sound-absorbing surface, such as a rubber mat, can reduce noise transmission. Constructing a sound barrier around the generator using noise-reducing materials can further dampen sound propagation. Maintaining a sufficient distance between the generator and living spaces also minimizes noise impact. Adhering to manufacturer recommendations for proper maintenance, such as ensuring adequate lubrication and proper muffler function, can also contribute to minimizing noise levels.
- Local Regulations and Considerations
Many municipalities have noise ordinances restricting the permissible noise levels at certain times of day. Operating a generator in violation of these ordinances can result in fines or other penalties. Considerate operation, including minimizing nighttime operation and informing neighbors of anticipated generator use, fosters positive community relations and minimizes potential conflicts. Selecting a quieter generator model can also contribute to compliance with local regulations.
Minimizing noise pollution from portable generators is crucial for maintaining a peaceful home environment and fostering positive relationships with neighbors. Careful consideration of noise levels during generator selection, combined with effective mitigation strategies and adherence to local regulations, ensures responsible and considerate operation, reducing the impact on both the household and the surrounding community. Understanding the interplay between decibel levels, operating conditions, and mitigation techniques empowers homeowners to make informed decisions and operate their generators in a manner that balances power needs with noise considerations.
5. Safety Features
Safety features are paramount in gasoline-powered portable generators designed for residential use. These features mitigate inherent risks associated with gasoline and electricity, safeguarding users and property. A comprehensive understanding of these safety mechanisms is essential for informed generator selection and safe operation. The consequences of neglecting safety features can range from equipment damage and electrical shocks to carbon monoxide poisoning and fire hazards.
Key safety features include low-oil shutoff sensors, which automatically turn off the generator when oil levels drop below a critical threshold, preventing engine damage. Overload protection mechanisms, such as circuit breakers, prevent damage to the generator and connected appliances by interrupting power flow in overload situations. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) on outlets protect against electrical shocks, especially in damp conditions, by detecting current imbalances and rapidly cutting off power. Spark arrestors prevent the escape of sparks from the exhaust, reducing fire hazards in dry or flammable environments. Properly designed fuel caps prevent spills and leaks, minimizing fire risks and environmental contamination. Well-ventilated enclosures promote safe heat dissipation, preventing overheating and reducing fire hazards while also minimizing noise output. Clearly marked operating instructions and safety labels provide essential guidance for safe operation and maintenance procedures.
The absence or malfunction of these safety features can have serious consequences. For instance, operating a generator without a functional low-oil shutoff can lead to catastrophic engine failure. Overloading a generator without proper overload protection can damage both the generator and connected appliances. Using a generator without GFCI protection in wet conditions increases the risk of fatal electrical shocks. Ignoring spark arrestor maintenance elevates the risk of fire, especially near dry vegetation. Therefore, regular inspection and maintenance of these safety features are crucial for ensuring reliable operation and minimizing potential hazards. Prioritizing safety features during generator selection and adhering to safe operating practices are essential for protecting life and property when utilizing portable generators for residential power supply.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, operation, and maintenance of gasoline-powered portable generators for residential use. Clear and concise answers provide practical guidance for homeowners considering or currently utilizing these devices for backup power.
Question 1: What size generator is needed to power a typical house?
Determining the appropriate generator size requires calculating the total wattage of essential appliances. Consider starting and running wattage requirements. A qualified electrician can assist with accurate load calculations and safe generator connection.
Question 2: How long can a portable generator run continuously?
Runtime depends on fuel tank capacity, fuel efficiency, and load. Consult manufacturer specifications for runtime estimates at various load levels. Fuel efficiency and tank size influence overall runtime duration.
Question 3: Is it safe to operate a portable generator indoors or in an attached garage?
Never operate a portable generator indoors or in attached spaces. Exhaust fumes contain carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and lethal gas. Operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas.
Question 4: How should a portable generator be connected to a house?
Never connect a generator directly to household wiring. This can cause dangerous backfeeding to the electrical grid. A qualified electrician should install a transfer switch for safe connection.
Question 5: What type of maintenance does a portable generator require?
Regular maintenance includes oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement. Consult the owner’s manual for specific maintenance intervals and procedures. Proper maintenance ensures reliable operation and extends generator lifespan.
Question 6: What safety precautions should be taken when operating a portable generator?
Operate generators outdoors on a dry, level surface. Allow the generator to cool before refueling. Use GFCI-protected extension cords. Store fuel in approved containers away from ignition sources.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of portable generator operation contributes to informed decision-making and safe usage. Consulting qualified professionals for installation and maintenance ensures optimal performance and mitigates potential risks.
The next section explores various fuel types and their respective advantages and disadvantages for portable generator operation.
Gasoline Portable Generators for Residential Use
This exploration of gasoline-powered portable generators for residential applications has highlighted key factors influencing their selection, operation, and maintenance. Critical aspects such as power output, fuel efficiency, runtime, noise levels, and safety features have been examined in detail. Understanding these factors is crucial for homeowners seeking reliable backup power solutions. Safe operating procedures, proper connection methods, and regular maintenance requirements have been emphasized to ensure user safety and prolong generator lifespan. The potential risks associated with improper generator use, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire hazards, and electrical shocks, underscore the importance of adhering to established safety guidelines. Careful consideration of these elements empowers informed decision-making and responsible generator operation.
Reliable access to backup power is paramount in an increasingly unpredictable world. Portable generators offer a crucial lifeline during grid outages, enabling the continuity of essential household services and enhancing safety and well-being. Investing in a properly sized and maintained gasoline-powered portable generator provides peace of mind and preparedness for unforeseen disruptions to the electrical grid. Diligent research and adherence to safety guidelines ensure the effective and responsible utilization of this valuable technology, safeguarding homes and families during times of critical need. Further exploration of alternative fuel sources and emerging technologies may yield even more efficient and sustainable backup power solutions in the future.