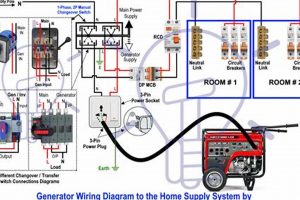
Providing backup power during outages involves safely integrating a mobile electricity source with a residential electrical system. This typically requires specialized equipment like a transfer switch to isolate the home’s circuits from the utility grid and prevent dangerous backfeeding. An example setup might involve a gasoline-powered unit connected to a transfer switch installed near the main electrical panel. This allows selected circuits, such as lighting, refrigeration, and heating, to be powered independently during a grid failure.
Ensuring uninterrupted power supply during emergencies safeguards essential household functions and enhances safety. Historically, homes relied on candles and fireplaces during power disruptions. Modern solutions offer improved comfort and security, powering critical appliances like medical equipment, sump pumps, and communication devices. This capability can be especially crucial in areas prone to severe weather or unreliable grid infrastructure.
The following sections will delve into specific aspects of safe and effective power backup integration, covering topics such as transfer switch selection and installation, generator sizing, grounding procedures, and operational safety guidelines. Understanding these elements is crucial for a reliable and secure backup power solution.
Safety and Effectiveness Tips for Backup Power Integration
Proper setup and operation are essential for safe and effective backup power. These tips provide critical guidance for a secure and reliable system.
Tip 1: Consult a qualified electrician. Electrical work presents significant hazards and requires professional expertise. A qualified electrician can assess specific needs, recommend appropriate equipment, and ensure safe installation conforming to local codes.
Tip 2: Select the correct transfer switch. Transfer switches safely isolate the home’s electrical system from the utility grid, preventing dangerous backfeeding. Choosing the right switch depends on the generator’s capacity and the number of circuits requiring backup power.
Tip 3: Size the generator appropriately. Generators must be sized to handle the electrical load of the connected appliances. Calculating wattage requirements for essential circuits ensures adequate power supply during outages.
Tip 4: Ground the generator effectively. Proper grounding protects against electrical shock. Follow manufacturer instructions and local codes for safe grounding procedures.
Tip 5: Operate the generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area. Generators produce carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and deadly gas. Operating the generator outdoors, away from windows and doors, prevents dangerous buildup.
Tip 6: Allow the generator to cool before refueling. Gasoline spills on a hot engine can ignite. Allowing sufficient cooling time before refueling minimizes fire hazards.
Tip 7: Regularly inspect and maintain the generator. Regular maintenance, including oil changes and spark plug replacements, ensures reliable operation during emergencies.
Adherence to these guidelines enhances safety and ensures the reliable performance of backup power systems. Careful planning and execution are crucial for protecting homes and families during power disruptions.
By following these precautions and seeking professional assistance when necessary, homeowners can confidently establish robust and secure backup power solutions.
1. Transfer Switch
Transfer switches play a critical role in safely connecting a portable generator to a home’s electrical system. They serve as a vital safety disconnect, isolating the house wiring from the utility power grid during generator operation. This isolation prevents backfeeding, a dangerous phenomenon where electricity flows from the generator back into the utility lines, potentially electrocuting utility workers. Without a transfer switch, the generator effectively energizes the entire neighborhood’s power lines, creating a significant hazard. For instance, during a widespread outage, a lineman working to restore power might be unaware of a homeowner’s operating generator, leading to a potentially fatal shock if backfeeding occurs. Transfer switches eliminate this risk.
Furthermore, transfer switches streamline the process of powering essential circuits. Instead of manually plugging individual appliances into the generator using extension cords, a transfer switch allows pre-selected circuits to be powered directly. This pre-selection typically includes crucial systems such as refrigerators, freezers, sump pumps, and lighting. Consider a scenario where a homeowner experiences a multi-day power outage due to a severe storm. A properly installed transfer switch enables seamless operation of critical appliances, maintaining food preservation and preventing basement flooding. This functionality significantly enhances safety and comfort during extended outages.
In conclusion, the transfer switch is not merely a convenient component but a fundamental safety and operational necessity for integrating a portable generator. Its ability to prevent backfeeding and facilitate efficient power delivery to essential circuits underscores its crucial role in safeguarding both homeowners and utility workers. Understanding its function and importance is paramount for anyone considering backup power solutions. While manual transfer switches offer a more budget-friendly option, automatic transfer switches provide enhanced convenience and safety by automatically detecting power outages and activating the generator. Proper selection and installation, often requiring professional electrical expertise, ensure the efficacy and safety of the entire backup power system.
2. Proper Grounding
Safe operation of a portable generator connected to a home requires meticulous attention to grounding. This critical safety measure protects against electrical shock and equipment damage, mitigating potentially lethal hazards associated with faulty electrical systems. A properly grounded generator provides a low-resistance path for stray electrical currents to flow safely into the earth, preventing dangerous voltage buildup.
- Preventing Electrical Shock
Grounding safeguards individuals from electric shock by providing an alternate path for fault currents. Without proper grounding, a person touching a faulty generator or appliance could become part of the electrical circuit, resulting in serious injury or death. For example, if a generator’s frame becomes energized due to an internal fault, a grounded system directs the current into the earth, minimizing the risk of shock to anyone in contact with the generator.
- Protecting Equipment
Proper grounding protects sensitive electronic equipment connected to the generator. Surges or faults can generate high voltages that damage or destroy electronic components. A ground connection provides a path for these surges to dissipate harmlessly, safeguarding appliances and electronics. For instance, a lightning strike near a power line can induce a voltage spike that travels through the electrical system. Grounding helps divert this surge, protecting connected devices.
- Stabilizing Voltage
Grounding contributes to voltage stabilization within the electrical system. It provides a common reference point for voltage potential, preventing erratic fluctuations that can damage equipment or disrupt operation. This stability ensures consistent and reliable performance of appliances and electronics powered by the generator. In areas with unstable grid power, grounding helps maintain consistent voltage levels during generator operation, protecting sensitive electronics.
- Meeting Safety Codes
Adherence to electrical codes and regulations mandates proper grounding for all electrical installations, including portable generators. These codes are designed to ensure public safety and prevent electrical hazards. Failure to comply with grounding requirements can result in fines, legal liabilities, and invalidation of insurance claims. Building inspectors typically verify proper grounding during inspections, ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Neglecting proper grounding when connecting a portable generator introduces significant risks. Effective grounding provides essential protection against electrical shock, safeguards connected equipment, and ensures stable voltage, contributing to a safe and reliable backup power system. Compliance with established safety codes through proper grounding is not merely a recommendation but a critical requirement for protecting lives and property.
3. Outlet Compatibility
Outlet compatibility is a crucial factor when connecting a portable generator to a home. Mismatched connections can lead to equipment damage, safety hazards, and ineffective power delivery. Generators produce electricity with specific voltage and amperage characteristics, and these must align with the outlets and appliances intended for connection. For example, attempting to power a 120-volt appliance with a 240-volt generator output can result in immediate and irreversible damage to the appliance. Conversely, connecting a 240-volt appliance to a 120-volt generator output will likely result in insufficient power, preventing the appliance from functioning correctly and potentially overheating the generator. Therefore, careful consideration of outlet compatibility is paramount for safe and effective generator usage.
Furthermore, various generator models offer different outlet configurations, including standard household outlets (120V), RV-style outlets (30A/125V), and higher-voltage outlets for larger appliances (240V). Understanding these configurations and their compatibility with household appliances is essential. Using adapters can sometimes bridge the gap between incompatible outlets, but this must be done with caution. Incorrect adapter usage can lead to overheating, fire hazards, and equipment damage. For instance, using a lightweight extension cord designed for low-power devices with a high-wattage appliance connected to a generator can cause the cord to overheat, potentially leading to a fire. Therefore, selecting the correct gauge and amperage rating for extension cords and adapters is crucial for safe operation.
In summary, ensuring outlet compatibility is not merely a technical detail but a fundamental safety and operational requirement when connecting a portable generator to a home. Careful matching of voltage and amperage between the generator’s output and the connected appliances, coupled with the correct use of appropriately rated adapters and extension cords, ensures efficient and safe power delivery, preventing equipment damage and potential hazards. Overlooking this critical aspect can compromise the entire backup power system, rendering it ineffective and potentially dangerous. Consulting the generator’s owner’s manual and seeking professional electrical advice are recommended steps to ensure proper and safe outlet compatibility.
4. Wattage Requirements
Accurately assessing household wattage requirements is paramount for successfully connecting a portable generator. Generator capacity must align with the combined power demands of intended appliances to ensure safe and effective operation. An undersized generator risks overload, potentially damaging both the generator and connected devices. Conversely, an oversized generator represents unnecessary expense and fuel consumption. Therefore, precise wattage calculations are essential for selecting the appropriately sized generator.
- Starting vs. Running Watts
Electrical devices often require a higher surge of power to start than to maintain operation. Starting watts, significantly higher than running watts, represent this initial surge. Generators must accommodate both. For example, a refrigerator might require 1,200 starting watts but only 200 running watts. Overlooking starting wattage requirements can lead to generator overload and failure to start essential appliances.
- Calculating Total Wattage Needs
Determining total wattage requirements involves summing the running watts of all intended appliances and adding the highest starting wattage among them. This calculation provides a realistic estimate of the generator capacity needed. For instance, a household intending to power a refrigerator (200 running watts), a sump pump (800 running/1,200 starting watts), and several lights (150 total running watts) would require a generator capable of handling at least 1,350 watts (1,150 running + 1,200 starting). Accurate calculations prevent overloading and ensure sufficient power supply.
- Prioritizing Essential Appliances
During outages, prioritizing essential appliances is crucial, especially with limited generator capacity. Critical needs, such as refrigeration, heating, and medical equipment, take precedence over less essential items. Creating a prioritized list helps determine which appliances to connect to the generator, ensuring essential functions are maintained. For example, during a winter storm, powering a furnace may take priority over a television, maximizing available generator power for essential needs.
- Generator Capacity and Fuel Efficiency
Generator capacity directly impacts fuel consumption. Larger generators consume more fuel, even when powering smaller loads. Matching generator capacity to actual wattage requirements optimizes fuel efficiency and minimizes operating costs. Choosing a generator significantly larger than necessary results in increased fuel consumption and unnecessary expense. A properly sized generator balances power delivery with fuel economy.
Understanding wattage requirements forms the foundation for safely and effectively connecting a portable generator. Accurate calculations, consideration of starting vs. running watts, prioritizing essential appliances, and aligning generator capacity with actual needs ensure reliable power delivery during outages while optimizing fuel efficiency. Neglecting these crucial factors can compromise the entire backup power system, leading to equipment damage, safety hazards, and ineffective power delivery. Careful planning and accurate assessment of wattage requirements are essential for a successful and safe backup power solution.
5. Extension Cord Safety
Safe connection of a portable generator to a home necessitates careful consideration of extension cord safety. Using improper extension cords presents significant fire and electrocution hazards. The electrical load from connected appliances dictates the required extension cord capacity. Undersized cords overheat, potentially igniting flammable materials. For example, using a lightweight, indoor-rated extension cord to power a high-wattage appliance like a refrigerator significantly increases the risk of fire. The cord’s inadequate current-carrying capacity leads to excessive heat buildup, potentially melting the insulation and igniting surrounding combustibles. Selecting heavy-duty, outdoor-rated extension cords with appropriate amperage and wattage ratings is crucial for safe operation.
Further emphasizing safety, extension cords should never be run through windows or doors where they can become pinched or damaged. Such damage compromises insulation, exposing live wires and increasing the risk of electrocution or fire. Similarly, cords should not be covered with rugs or furniture, as this traps heat and accelerates potential fire hazards. Proper cord placement, away from high-traffic areas and potential damage sources, is essential. For instance, running an extension cord across a driveway creates both a tripping hazard and a risk of vehicle damage to the cord, potentially exposing live wires. Careful planning and execution of cord routing mitigate these risks. Additionally, using multiple interconnected extension cords should be avoided as this can lead to voltage drops, reducing appliance efficiency and potentially overheating the cords.
In conclusion, extension cord safety is not a peripheral concern but an integral component of safely connecting a portable generator to a home. Selecting appropriate heavy-duty, outdoor-rated cords with adequate capacity, coupled with careful placement and routing, minimizes fire and electrocution risks. Overlooking these critical safety considerations can have severe consequences, undermining the entire purpose of backup power and jeopardizing safety. Prioritizing extension cord safety ensures reliable and secure generator operation during power outages, protecting both the home and its occupants. Regular inspection of extension cords for damage, fraying, or exposed wires is also essential for maintaining a safe electrical system.
6. Fuel Type and Storage
Safe and efficient operation of a portable generator integrated with a home electrical system critically depends on proper fuel selection and storage. Fuel type influences generator performance, maintenance requirements, and environmental impact. Storage practices directly impact safety, preventing fire hazards and ensuring fuel longevity. Neglecting these aspects can compromise the entire backup power system, creating risks and reducing effectiveness.
- Fuel Options and Generator Compatibility
Portable generators typically utilize gasoline, propane, or diesel. Generator design dictates fuel compatibility; using incorrect fuel damages the engine. Gasoline offers widespread availability but requires stabilizer for long-term storage. Propane, while less readily available, stores indefinitely without degradation. Diesel provides higher efficiency but requires specific engine designs. Matching fuel type to generator specifications is crucial for proper function and longevity. For instance, using gasoline in a diesel generator can cause severe engine damage, rendering the generator unusable. Consulting the manufacturers recommendations is essential.
- Safe Storage Practices for Fuels
Flammable fuels necessitate careful storage to mitigate fire hazards. Approved containers, stored away from ignition sources and in well-ventilated areas, are essential. Gasoline, particularly volatile, requires extra precautions. Storing fuel in a detached shed, away from the home and other structures, minimizes fire risks. For example, storing gasoline containers near a water heater or furnace pilot light creates a significant fire hazard. Proper ventilation prevents vapor buildup, further reducing fire risks.
- Fuel Stability and Longevity
Fuel degrades over time, impacting generator performance. Gasoline, especially susceptible, benefits from stabilizers to extend shelf life. Rotating fuel stock, using older fuel first, prevents deterioration and ensures reliable generator operation. Propane, inherently stable, avoids these concerns. Proper storage practices and fuel rotation maintain fuel quality, maximizing generator reliability during outages. For instance, using stale gasoline can clog carburetors and hinder generator performance.
- Environmental Considerations
Fuel choice influences environmental impact. Propane burns cleaner than gasoline, producing fewer emissions. Diesel, while efficient, emits particulates. Local regulations may restrict fuel types. Understanding environmental considerations promotes responsible generator operation and minimizes ecological footprint. For example, some jurisdictions may prohibit or limit the use of gasoline-powered generators due to air quality concerns. Adhering to local regulations is paramount.
Appropriate fuel selection and storage are integral aspects of safely and effectively connecting a portable generator to a home. Understanding fuel compatibility, adhering to safe storage practices, maintaining fuel stability, and considering environmental impacts ensure reliable generator operation during power outages while minimizing risks. These elements contribute significantly to a robust and secure backup power solution, safeguarding the home and promoting responsible energy usage.
7. Professional Installation
Integrating a portable generator with a home’s electrical system necessitates professional installation for safety and code compliance. Incorrect wiring can lead to hazardous backfeeding, endangering utility workers and damaging appliances. Furthermore, improper grounding increases electrocution risks. A licensed electrician understands local electrical codes, ensuring the installation meets safety standards and legal requirements. For instance, an improperly installed transfer switch can energize the utility grid during generator operation, posing a lethal threat to linemen working on downed power lines. Professional installation mitigates such risks.
Beyond safety, professional installation ensures system efficacy. Electricians calculate load requirements, ensuring the generator adequately powers essential circuits. They select appropriate wiring and components, optimizing power delivery and preventing voltage drops. Consider a scenario where a homeowner attempts DIY installation, underestimating load requirements. The generator may overload during operation, damaging connected appliances and potentially causing a fire. Professional expertise avoids such pitfalls, maximizing system reliability.
In summary, professional installation is crucial for safely and effectively connecting a portable generator to a home’s electrical system. It mitigates safety hazards like backfeeding and electrocution risks while ensuring system functionality and code compliance. While seemingly an added expense, professional installation represents a vital investment in safety and long-term system reliability, protecting both the homeowner and the wider community. Attempting to bypass professional installation for short-term cost savings can have significant long-term consequences, jeopardizing safety and potentially incurring higher repair costs in the future. Prioritizing professional installation ensures a secure, compliant, and reliable backup power solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding safe and effective portable generator integration with home electrical systems. Clarity on these points promotes informed decision-making and safe operation.
Question 1: Is professional installation necessary for connecting a portable generator?
Professional installation is strongly recommended. Licensed electricians ensure safe and code-compliant integration, minimizing hazards like backfeeding and improper grounding. Their expertise safeguards both homeowners and utility workers.
Question 2: What is a transfer switch, and why is it important?
A transfer switch isolates the home’s electrical system from the utility grid during generator operation. This prevents backfeeding, a dangerous phenomenon that can energize downed power lines, posing a lethal threat to utility workers.
Question 3: How is the correct generator size determined for a home?
Generator size depends on the wattage requirements of the appliances intended for connection. Calculating total running watts and factoring in the highest starting wattage of any single appliance determines the necessary generator capacity.
Question 4: What safety precautions are essential when operating a portable generator?
Generators produce carbon monoxide, a deadly gas. Operation must occur outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from windows and doors. Allowing the generator to cool before refueling is crucial to prevent fire hazards.
Question 5: Can any extension cord be used to connect appliances to a generator?
Using heavy-duty, outdoor-rated extension cords with appropriate wattage and amperage ratings is crucial. Undersized cords overheat, creating fire hazards. Cords should never be run through windows, doors, or under rugs.
Question 6: What type of fuel is best for a portable generator?
Generator design dictates fuel type (gasoline, propane, or diesel). Each fuel has advantages and disadvantages regarding availability, storage, and environmental impact. Consult the generator’s manual for the correct fuel type.
Prioritizing safety and code compliance through professional installation and adherence to safe operating procedures ensures reliable and effective backup power during outages. Careful consideration of these factors contributes significantly to a robust and secure home power solution.
For further guidance on specific installation requirements and local electrical codes, consult a qualified electrician and relevant regulatory authorities.
Connecting a Portable Generator to a Home
Safe and effective integration of a portable generator with a residential electrical system requires careful planning and execution. Key considerations include professional installation, proper grounding, transfer switch usage, outlet compatibility, wattage requirement calculations, extension cord safety, fuel selection and storage, and adherence to safety guidelines. Overlooking these critical aspects can lead to safety hazards, equipment damage, and ineffective power delivery. Professional guidance ensures adherence to electrical codes and best practices, mitigating risks and maximizing system reliability.
Reliable backup power provides essential support during outages, safeguarding critical household functions and enhancing safety. Investment in a properly installed and maintained generator system offers significant long-term value, ensuring preparedness for unforeseen power disruptions and promoting peace of mind. Thorough understanding of the technical and safety considerations surrounding portable generator integration empowers homeowners to make informed decisions, creating resilient and secure power solutions for their homes.