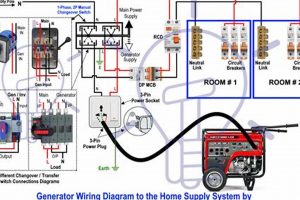
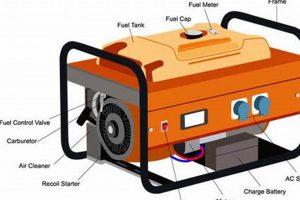
A top-tier mobile power source capable of supplying electricity to an entire residence during outages represents a significant investment in preparedness and comfort. Such a device offers a comprehensive solution for powering essential appliances, lighting, and HVAC systems, ensuring continuity of household operations during emergencies or grid disruptions. For instance, a properly sized unit can sustain critical functions like refrigeration, sump pumps, and medical equipment, mitigating potential losses and safeguarding well-being.
The value of reliable backup power extends beyond convenience. In regions prone to severe weather events or areas with aging infrastructure, a readily available power supply provides crucial peace of mind and can even be life-saving. Historically, homeowners relied on smaller, less powerful portable generators for limited backup power, necessitating careful load management and prioritizing essential circuits. Advancements in generator technology have led to more powerful and portable options, enabling whole-home coverage without sacrificing mobility.
Understanding the nuances of selecting and operating a robust and mobile residential power solution requires careful consideration of power output, fuel type, runtime, noise levels, and safety features. The following sections will delve into these crucial aspects, offering guidance on choosing the most appropriate unit for individual needs and circumstances, as well as safe operation and maintenance practices.
Tips for Selecting and Utilizing a Robust Mobile Power Solution
Choosing and operating a high-capacity portable generator requires careful planning and consideration. The following tips offer guidance for maximizing the benefits and ensuring safe operation.
Tip 1: Accurate Power Needs Assessment: Calculate the total wattage required to run essential appliances and systems. Consider both starting wattage (the initial surge of power required to start a motor) and running wattage (the power needed to sustain operation). Overestimating power needs is recommended to avoid overloading the generator.
Tip 2: Fuel Type Considerations: Evaluate available fuel options (gasoline, propane, dual-fuel) based on accessibility, storage capacity, and cost. Propane offers longer shelf life and cleaner burning, while gasoline is more readily available in emergencies.
Tip 3: Runtime and Fuel Efficiency: Assess the generator’s runtime at various load levels. Longer runtimes minimize refueling frequency. Fuel efficiency is a crucial factor impacting operating costs.
Tip 4: Noise Level Evaluation: Generator noise can be a significant concern. Consider models with lower decibel ratings, particularly if operating in close proximity to neighbors or during nighttime hours. Sound-dampening enclosures can further mitigate noise pollution.
Tip 5: Safety Features and Certifications: Prioritize models equipped with safety features like automatic shutoff for low oil levels and overload protection. Look for certifications from recognized testing organizations to ensure compliance with safety standards.
Tip 6: Professional Installation and Maintenance: Engage qualified professionals for proper installation, including transfer switch setup and grounding. Regular maintenance, including oil changes and air filter cleaning, is essential for optimal performance and longevity.
Tip 7: Adherence to Operational Guidelines: Carefully review and follow the manufacturer’s operating instructions. Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
By adhering to these guidelines, individuals can harness the full potential of their portable power investment, ensuring reliable backup power during critical situations while prioritizing safety and efficiency.
Informed decision-making and responsible operation are key to maximizing the long-term value and safety of a mobile whole-house power source.
1. Power Output
Power output, measured in watts or kilowatts (kW), represents a critical factor in selecting a mobile power source for residential use. Appropriate power output ensures the generator can handle the combined electrical load of essential appliances and systems during an outage. Understanding power requirements and generator capabilities is paramount for effective backup power planning.
- Starting vs. Running Watts
Electrical devices, particularly those with motors (refrigerators, air conditioners), require a higher surge of power to start, known as starting wattage. Once running, the power demand stabilizes to a lower level, termed running wattage. Generators must accommodate both starting and running wattages of intended appliances. Accurately calculating these values prevents overloading and ensures reliable operation.
- Sizing for Specific Needs
Homes vary significantly in their power requirements. Smaller homes with essential appliances may require a generator with lower output, while larger residences with multiple high-power devices necessitate a higher capacity unit. Conducting a comprehensive power audit, including both starting and running wattages of all intended devices, informs proper generator sizing. A slightly oversized generator provides a buffer for unexpected loads or future additions.
- Impact on Runtime
Power output directly influences runtime, the duration a generator can operate on a given fuel supply. Higher power output generally corresponds to shorter runtime at full load. Balancing power needs with desired runtime is essential. Larger fuel tanks or selecting a fuel-efficient model can mitigate the impact of higher power output on runtime.
- Relationship to Physical Size and Cost
Higher power output generators tend to be larger and heavier, impacting portability and storage requirements. Increased power output typically correlates with higher purchase cost. Balancing power needs with portability and budget constraints requires careful consideration. Prioritizing essential appliances and systems helps optimize power output requirements and manage costs.
Selecting a generator with adequate power output ensures effective operation of essential household systems during power outages. Careful assessment of power needs, consideration of starting vs. running wattages, and balancing power output with runtime, portability, and budget constraints leads to informed decision-making and a reliable backup power solution.
2. Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency represents a critical factor in the evaluation of mobile whole-house power sources. Efficient fuel consumption directly impacts operational costs and logistical considerations during extended outages. A fuel-efficient generator minimizes the frequency of refueling, reducing inconvenience and expense. This characteristic becomes particularly crucial during prolonged grid disruptions when fuel availability may be limited. For instance, a generator consuming less fuel per kilowatt-hour (kWh) produced extends the runtime on a given fuel supply, potentially mitigating the need for frequent refueling trips under challenging conditions. Conversely, a less fuel-efficient model may necessitate more frequent refueling, adding complexity and cost, especially in emergency scenarios.
Several factors influence generator fuel efficiency. Engine design, load size, and operating conditions all play a role. Modern generators often incorporate advanced engine technologies and control systems to optimize fuel consumption. Operating the generator at the optimal load level, typically between 50% and 75% of its rated capacity, often yields the highest fuel efficiency. Overloading or underloading the generator can decrease efficiency. Furthermore, regular maintenance, including air filter cleaning and spark plug replacement, contributes to optimal fuel consumption. Understanding these influencing factors empowers informed decision-making and efficient generator operation.
Prioritizing fuel efficiency translates to tangible benefits. Reduced fuel consumption lowers operating costs, minimizes environmental impact, and enhances operational convenience during outages. Evaluating fuel consumption rates, considering generator technologies that promote efficiency, and adhering to recommended operating practices contribute to a more cost-effective and sustainable backup power solution. The interplay between fuel efficiency and generator performance underscores its significance in achieving reliable and cost-effective whole-house power backup.
3. Portability/Size
The portability and size of a whole-house power source significantly influence its practicality and suitability for various applications. Balancing power output with manageable size and weight is crucial for ease of transport, storage, and deployment. Optimal portability ensures the generator can be readily positioned and utilized when and where needed, enhancing its overall value as a backup power solution.
- Physical Dimensions and Weight
Physical dimensions and weight directly impact maneuverability. Compact designs and lighter weight facilitate easier transport and positioning, particularly for individuals operating the generator independently. Bulkier, heavier units may require assistance or specialized equipment for movement, limiting their practicality in certain situations. Manufacturers often provide detailed specifications regarding dimensions and weight, enabling consumers to assess suitability for their specific needs and physical capabilities.
- Wheel Design and Mobility Features
Integrated wheel designs and other mobility features, such as folding handles and ergonomic grips, contribute significantly to ease of transport. Never-flat tires and sturdy frames enhance maneuverability over uneven terrain. Well-designed mobility features minimize strain and effort during generator relocation, promoting safe and convenient operation. Assessing the robustness and practicality of these features is crucial for ensuring long-term usability.
- Storage Considerations
Storage footprint is a key consideration, particularly for those with limited storage space. Compact designs minimize required storage area, while larger units demand more dedicated space. Evaluating storage dimensions and planning for appropriate storage location ensures the generator remains readily accessible when needed without encroaching on valuable space.
- Impact on Power Output
Portability often involves trade-offs with power output. While highly portable generators offer convenience, they may have limited power output, potentially insufficient for powering all household systems simultaneously. Larger, more powerful generators often compromise portability due to increased size and weight. Balancing power requirements with desired portability is essential for selecting a unit that meets specific backup power needs without sacrificing practicality.
Careful consideration of portability and size ensures the selected generator aligns with individual needs and circumstances. Evaluating physical dimensions, weight, mobility features, and storage requirements in conjunction with power output capabilities empowers informed decision-making and maximizes the practicality of the chosen backup power solution. A well-balanced approach to portability and power ensures the generator remains a valuable and readily deployable asset during power outages.
4. Noise Levels
Noise levels represent a critical consideration when selecting a mobile whole-house power source. Excessive noise can disrupt daily life, irritate neighbors, and violate local noise ordinances. A quieter generator contributes to a more peaceful environment during outages, enhancing overall quality of life. Understanding the factors influencing generator noise and available noise-reduction technologies empowers informed decision-making.
- Decibel Ratings and Perceived Loudness
Generator noise is typically measured in decibels (dB). Lower dB ratings indicate quieter operation. Perceived loudness is not solely determined by dB level; frequency content also plays a role. Some generators emit high-frequency noise, perceived as more intrusive than low-frequency sounds at the same dB level. Comparing dB ratings and considering manufacturer specifications regarding frequency content helps assess potential noise impact.
- Operating Conditions and Load
Noise output varies depending on operating conditions and load. Generators typically produce more noise under heavy load compared to lighter loads. Ambient temperature and air circulation also influence noise levels. Understanding these factors helps anticipate and manage noise output in different scenarios. Operating the generator at the optimal load and ensuring adequate ventilation can minimize noise production.
- Noise Reduction Technologies
Manufacturers employ various noise reduction technologies to mitigate generator noise. Mufflers, sound-dampening enclosures, and advanced engine designs contribute to quieter operation. Evaluating available noise reduction features and comparing noise levels across different models allows for informed selection of a quieter unit. Investing in a generator with advanced noise reduction technology can significantly enhance user experience and minimize neighborhood disturbance.
- Placement and Mitigation Strategies
Strategic generator placement and implementation of noise mitigation strategies further minimize noise impact. Positioning the generator away from living areas and neighboring properties reduces noise exposure. Utilizing sound-absorbing barriers or constructing purpose-built enclosures can further attenuate noise. Careful planning and implementation of these strategies create a more peaceful environment during generator operation.
Prioritizing lower noise levels enhances the overall usability and acceptance of a whole-house power solution. Evaluating dB ratings, understanding the factors influencing noise output, exploring available noise reduction technologies, and implementing strategic placement and mitigation strategies contribute to a more peaceful and neighborly experience during power outages. Selecting a quieter generator minimizes disruption and enhances the quality of life for both the user and the surrounding community.
5. Runtime
Runtime, representing the duration a portable generator can operate continuously on a single fuel tank, constitutes a critical factor in evaluating whole-house power solutions. Extended runtime translates directly to prolonged backup power availability, reducing the frequency of refueling during outages. This characteristic assumes paramount importance during extended grid disruptions, where access to fuel may be limited or challenging. For instance, a generator capable of sustained operation for 12 hours at 50% load provides significantly greater operational flexibility and peace of mind compared to a unit requiring refueling every few hours. The interplay between runtime, fuel capacity, and load determines the practical utility of a generator during prolonged power outages. A larger fuel tank generally extends runtime, but fuel efficiency also plays a crucial role. A more fuel-efficient generator extracts greater runtime from a given fuel volume, optimizing operational efficiency.
Practical implications of runtime extend beyond mere convenience. Consider a scenario involving a multi-day power outage due to a severe weather event. A generator with limited runtime necessitates frequent refueling, potentially exposing individuals to hazardous conditions or disrupting essential tasks. Conversely, extended runtime minimizes disruptions, allowing for uninterrupted operation of critical appliances, lighting, and communication systems. This sustained power availability can be essential for maintaining safety, comfort, and connectivity during emergencies. Furthermore, extended runtime reduces the logistical burden of fuel management, conserving valuable time and resources during critical situations.
Careful consideration of runtime requirements is integral to selecting a suitable whole-house power solution. Evaluating fuel capacity, fuel efficiency, and anticipated load requirements informs appropriate runtime estimations. Prioritizing extended runtime enhances preparedness and mitigates potential disruptions during unforeseen power outages. Understanding the interplay between runtime, fuel management, and operational continuity empowers informed decision-making and contributes to a more robust and reliable backup power strategy. A generator with ample runtime provides sustained power, enhancing resilience and peace of mind during challenging circumstances.
6. Safety Features
Safety features represent paramount considerations when evaluating portable whole-home generators. A “best” designation necessitates prioritizing safety mechanisms that protect both users and connected equipment. These features mitigate potential hazards associated with generator operation, ensuring reliable and secure power delivery during outages. For instance, a critical safety feature like carbon monoxide (CO) detection and automatic shutoff prevents dangerous CO buildup in enclosed spaces. CO poisoning poses a significant threat during generator operation, and robust CO safety mechanisms are essential for safeguarding occupants. Similarly, overload protection prevents damage to the generator and connected appliances by automatically shutting down the unit in case of excessive electrical load. This feature prevents potential electrical fires and equipment damage, preserving the generator’s longevity and protecting valuable household electronics.
Further enhancing safety, features such as low-oil shutdown prevent engine damage by automatically turning off the generator when oil levels drop below critical thresholds. This proactive protection extends the generator’s lifespan and prevents costly repairs. Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) provide additional electrical safety by detecting ground faults and immediately interrupting power flow, mitigating the risk of electrical shock. These examples illustrate the practical significance of integrated safety features in portable generators. Choosing a generator equipped with comprehensive safety mechanisms safeguards users, protects connected appliances, and ensures reliable operation during critical situations.
A comprehensive approach to generator safety encompasses not only the presence of these features but also user education and adherence to safe operating practices. Understanding the function and importance of each safety feature, combined with diligent maintenance and adherence to manufacturer guidelines, maximizes safety and ensures reliable performance. Ultimately, prioritizing safety features distinguishes a truly “best” portable whole-home generator, providing not only reliable power but also peace of mind during emergencies.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding high-capacity portable generators suitable for residential use. Clear and concise responses aim to provide practical guidance for informed decision-making.
Question 1: How is the necessary generator size determined for a specific residence?
Generator sizing requires calculating the total wattage of essential appliances and systems intended for backup power. Consider both running wattage (power consumed during operation) and starting wattage (higher initial surge). Online resources and qualified electricians can assist with accurate load calculations. Slightly oversizing the generator is recommended to accommodate potential future needs.
Question 2: What differentiates inverter generators from conventional generators?
Inverter generators produce cleaner, more stable power suitable for sensitive electronics. They adjust engine speed based on load, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and quieter operation compared to conventional generators. Conventional generators operate at a fixed speed, often leading to higher fuel consumption and noise levels.
Question 3: What fuel types are commonly used in portable whole-house generators?
Common fuel types include gasoline, propane, and dual-fuel (capable of using both gasoline and propane). Gasoline offers widespread availability but requires more frequent refueling and has a shorter shelf life. Propane offers longer storage life and cleaner burning but may be less readily available during emergencies. Dual-fuel models offer flexibility.
Question 4: What safety precautions are essential when operating a portable generator?
Operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from windows and doors, to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. Never refuel a hot generator. Ensure proper grounding and utilize a transfer switch for safe connection to household circuits. Consult the owner’s manual for detailed safety instructions specific to the chosen model.
Question 5: What maintenance is typically required for a portable generator?
Regular maintenance ensures optimal performance and longevity. Change oil and air filters according to manufacturer recommendations. Inspect spark plugs and fuel lines periodically. Store fuel properly to prevent degradation. Consult the owner’s manual for model-specific maintenance schedules and procedures.
Question 6: What are the typical costs associated with owning and operating a portable whole-house generator?
Costs vary based on generator size, fuel type, and usage frequency. Initial purchase price, fuel costs, and ongoing maintenance contribute to overall ownership expenses. Conducting a thorough cost analysis, considering both initial investment and long-term operating expenses, informs budgetary planning.
Careful consideration of these frequently asked questions, combined with thorough research and consultation with qualified professionals, empowers informed decisions regarding portable whole-house generator selection and operation. Prioritizing safety, understanding operational requirements, and planning for long-term maintenance ensure a reliable and valuable backup power solution.
The next section will delve into specific generator models and comparative analyses to further assist in the selection process.
Conclusion
Selecting a top-tier mobile residential power source requires careful evaluation of numerous interconnected factors. Power output, fuel efficiency, portability, noise levels, runtime, and safety features all contribute to the overall suitability of a specific unit for individual needs and circumstances. A comprehensive understanding of these elements empowers informed decision-making, ensuring a reliable and effective backup power solution during grid disruptions. Prioritizing essential power needs, balancing performance characteristics with budgetary constraints, and adhering to safe operating practices maximize the value and longevity of the investment.
Reliable access to backup power provides essential peace of mind and can even be life-saving during emergencies. Investing in a robust and well-suited mobile power solution represents a significant step towards enhanced preparedness and resilience in the face of unforeseen power outages. Thorough research, careful planning, and responsible operation ensure that the chosen unit delivers dependable performance when needed most, safeguarding comfort, security, and continuity of essential household operations.