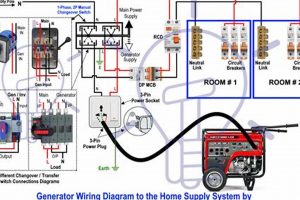
Compact, independent power sources fueled by diesel provide electricity during outages or in locations lacking grid access. These units offer a reliable backup solution for residences, powering essential appliances and devices when primary power is unavailable. For instance, during a power outage, such a unit can operate refrigerators, lighting, and heating systems, maintaining critical home functions.
Residential power solutions using this technology offer homeowners increased resilience against power disruptions, ensuring continuity of vital services and enhancing safety. Historically, reliance on centralized power grids has left homes vulnerable to blackouts caused by weather events or grid failures. These independent power sources mitigate this vulnerability, providing peace of mind and safeguarding against potential disruptions to daily life. Their availability contributes significantly to home safety and comfort, particularly in emergency situations.
The following sections will explore the various aspects of these power solutions in greater detail, encompassing topics such as sizing, fuel efficiency, noise levels, maintenance, and safety considerations.
Tips for Selecting and Operating a Standby Power System
Careful consideration of several factors ensures optimal performance and safety when utilizing a standby power system for residential applications. These tips offer guidance for homeowners seeking reliable backup power.
Tip 1: Accurate Power Assessment: Determine the wattage requirements of essential appliances and devices intended for operation during a power outage. Account for starting wattage, which can be significantly higher than running wattage for some appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners.
Tip 2: Proper Unit Sizing: Select a unit with sufficient power output to meet calculated wattage needs. Opting for slightly more capacity offers flexibility for future power demands.
Tip 3: Strategic Placement: Position the unit outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from windows and doors. Ensure adequate clearance for exhaust dissipation and maintenance access.
Tip 4: Routine Maintenance: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, including oil changes, filter replacements, and general inspections. Regular maintenance ensures reliable operation and prolongs the unit’s lifespan.
Tip 5: Safe Fuel Handling: Store diesel fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Exercise caution when refueling the unit to prevent spills and ensure proper ventilation.
Tip 6: Professional Installation: Consider professional installation for proper connection to the home’s electrical system. This ensures compliance with safety regulations and minimizes the risk of electrical hazards.
Tip 7: Load Management: Prioritize essential appliances during an outage to avoid overloading the unit. Power management maximizes runtime and prevents potential damage.
Tip 8: Regular Testing: Periodically test the unit to verify proper operation and identify any potential issues. Regular testing ensures readiness during an actual power outage.
By adhering to these guidelines, homeowners can ensure the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of their standby power system, providing crucial support during power disruptions.
Following these recommendations enables informed decisions regarding standby power system selection, installation, and operation, maximizing benefits and contributing to household preparedness.
1. Power Output
Power output, measured in watts or kilowatts (kW), represents a critical factor in selecting a portable diesel generator for home use. Matching generator output to anticipated power demands ensures effective operation of essential appliances and devices during power outages. Understanding power output nuances facilitates informed generator selection and optimal performance.
- Running Watts vs. Starting Watts
Running watts refer to the power required for continuous operation of an appliance, while starting watts, often significantly higher, represent the surge of power needed to initially start certain appliances (e.g., refrigerators, air conditioners). Accurately calculating both running and starting wattage requirements for intended appliances prevents generator overload and ensures reliable operation. For example, a refrigerator might require 700 running watts but 2,100 starting watts.
- Sizing for Household Needs
Proper generator sizing involves summing the wattage requirements of all appliances planned for simultaneous use. Overestimating power needs slightly provides a safety margin for future appliance additions or unexpected power demands. Underestimating can lead to overloaded circuits and potential generator damage. A household prioritizing essential appliances might only need a smaller generator, whereas a household intending to power multiple large appliances simultaneously requires a larger output.
- Power Output and Fuel Consumption
Generally, higher power output correlates with higher fuel consumption. Balancing power needs with fuel efficiency optimizes runtime and minimizes operational costs. Selecting a generator with appropriate power outputneither excessively high nor too lowcontributes to responsible resource management. A larger generator operating at a low load can be less fuel-efficient than a smaller, appropriately sized generator.
- Generator Capacity and Appliance Types
Different appliances have varying power requirements. Sensitive electronics require stable power output, while heavy-duty appliances may tolerate minor fluctuations. Understanding these nuances and the generator’s capacity to deliver stable power across various appliance types ensures safe and reliable operation. Generators with inverter technology offer cleaner power, suitable for sensitive electronics.
Careful consideration of power output, including running watts, starting watts, and overall household demands, ensures appropriate generator selection for reliable home backup power. Balancing power requirements with fuel efficiency and appliance compatibility optimizes performance and contributes to long-term cost savings.
2. Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency represents a critical operational parameter for portable diesel generators intended for residential applications. Efficient fuel consumption reduces operating costs, extends runtime during power outages, and minimizes environmental impact. Understanding the factors influencing fuel efficiency enables informed generator selection and responsible resource management.
- Load Factor and Efficiency
Generators operate most efficiently at a specific load percentage, typically around 75% of their rated capacity. Operating a significantly oversized generator at a low load reduces fuel efficiency. Conversely, overloading a generator can also decrease efficiency and potentially damage the unit. Matching generator size to actual power demands optimizes fuel consumption.
- Engine Design and Technology
Modern diesel engines incorporate advanced technologies like direct injection and turbocharging to enhance fuel efficiency. These technologies optimize combustion and power output, resulting in lower fuel consumption for a given power level. Selecting a generator with a technologically advanced engine contributes to long-term fuel savings.
- Maintenance and Fuel Efficiency
Regular maintenance, including air filter replacements, fuel filter changes, and oil changes, directly impacts fuel efficiency. Clean filters and fresh oil ensure optimal engine performance, contributing to lower fuel consumption. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule maximizes fuel economy.
- Fuel Quality and Storage
Using high-quality diesel fuel and proper storage practices contributes to optimal fuel efficiency and prevents engine problems. Contaminated or degraded fuel can reduce engine performance and increase fuel consumption. Storing fuel in approved containers in a cool, dry place minimizes degradation and maintains fuel quality.
Optimizing fuel efficiency in portable diesel generators for home use involves selecting appropriately sized units, utilizing advanced engine technologies, adhering to maintenance schedules, and employing proper fuel handling practices. These considerations contribute to lower operating costs, extended runtime, and reduced environmental impact, maximizing the benefits of residential standby power.
3. Noise Levels
Noise levels represent a significant consideration when selecting and operating portable diesel generators for residential use. These units produce noise during operation, which can impact both the homeowner and the surrounding neighborhood. Understanding the factors influencing noise levels and available mitigation strategies promotes harmonious coexistence and informed generator selection.
Several factors contribute to generator noise output. Engine design, load level, and exhaust system configuration all play a role. Larger engines generally produce more noise than smaller engines. Higher load levels correlate with increased noise output. Poorly designed or maintained exhaust systems can amplify noise. For instance, a generator operating at full load will typically produce more noise than one operating at a lower load. Direct injection engines, while generally more fuel-efficient, can also contribute to higher noise levels compared to indirect injection engines. The enclosure design also plays a crucial role; some generators feature sound-attenuating enclosures that significantly reduce noise output.
Managing generator noise involves a multifaceted approach. Selecting a generator with a lower decibel rating is a primary consideration. Strategic placement of the unit away from living spaces and neighboring properties minimizes noise impact. Constructing noise barriers or utilizing sound-absorbing materials further reduces noise propagation. Regular maintenance, including muffler inspection and replacement, helps maintain optimal noise control. Furthermore, local ordinances often regulate permissible noise levels, particularly during nighttime hours. Adhering to these regulations ensures compliance and promotes positive community relations. Ultimately, understanding and addressing generator noise levels contributes to a more peaceful and considerate operating environment.
4. Portability
Portability represents a defining characteristic of certain diesel-powered generators designed for residential use. This feature significantly influences their practicality and applicability in various scenarios. Understanding the nuances of portability enhances informed generator selection and effective utilization.
- Physical Dimensions and Weight
Physical dimensions and weight directly impact the ease of transporting and maneuvering a portable generator. Compact designs and lighter weights facilitate movement and positioning, particularly in challenging terrains or confined spaces. For instance, a smaller, lighter unit proves easier to transport to a remote cabin compared to a larger, heavier model. Wheel kits and lifting handles further enhance maneuverability.
- Mobility Features
Integrated features like wheel kits, folding handles, and compact frames enhance portability. These features simplify transport and storage, making the generator more user-friendly and adaptable to diverse situations. A generator equipped with never-flat tires performs better on uneven terrain than one with standard pneumatic tires. Folding handles reduce storage footprint.
- Placement Flexibility
Portability allows for flexible placement of the generator to optimize power delivery and minimize noise disruption. Positioning the unit closer to the required power source reduces cable length and voltage drop. Siting the generator further from living areas minimizes noise impact. For example, during a camping trip, a portable generator can be positioned to power recreational equipment while minimizing disturbance to nearby campers.
- Storage Considerations
Portability impacts storage requirements. Compact designs minimize storage space needs, crucial for homeowners with limited storage capacity. Lightweight units are easier to lift and store in elevated locations. A generator with a smaller footprint fits more easily in a garage or shed, maximizing available storage space.
Portability in residential diesel generators encompasses physical dimensions, mobility features, placement flexibility, and storage considerations. Careful consideration of these factors ensures selection of a generator that aligns with individual needs and usage scenarios, maximizing its practicality and overall utility.
5. Maintenance
Maintenance constitutes a critical aspect of owning and operating a portable diesel generator for residential applications. Regular maintenance ensures reliable performance, prolongs the generator’s lifespan, and optimizes fuel efficiency. Neglecting maintenance can lead to performance degradation, premature failure, and increased operating costs. A well-maintained generator provides consistent power during outages, while a neglected unit may fail when needed most. For example, neglecting regular oil changes can lead to increased engine wear and reduced efficiency, potentially resulting in costly repairs or even engine failure.
Several key maintenance tasks contribute to optimal generator performance. Regular oil changes, typically every 50-200 hours of operation depending on the model, ensure proper lubrication and prevent excessive engine wear. Air filter replacement, crucial for efficient combustion, should be performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations or more frequently in dusty environments. Fuel filter replacement prevents contaminants from entering the fuel system and causing damage. Inspecting and cleaning spark plugs ensures reliable ignition. Battery maintenance, including checking electrolyte levels and ensuring proper connections, guarantees starting reliability. For instance, a clogged air filter restricts airflow to the engine, reducing combustion efficiency and increasing fuel consumption. Regularly inspecting and cleaning or replacing the air filter maintains optimal airflow and fuel efficiency.
A comprehensive maintenance schedule, tailored to the specific generator model and operating conditions, ensures consistent reliability and performance. Consulting the owner’s manual provides detailed maintenance instructions and recommended service intervals. Maintaining detailed service records helps track maintenance tasks and identify potential issues. Proactive maintenance minimizes downtime and extends the operational lifespan of the generator, providing reliable backup power for years to come. Failure to adhere to a regular maintenance schedule can void warranties and lead to costly repairs. By prioritizing maintenance, homeowners ensure the continued reliability and longevity of their portable diesel generators, safeguarding against power disruptions and providing peace of mind.
6. Safety Features
Safety features represent critical components of portable diesel generators designed for residential use. These features mitigate potential hazards associated with generator operation, protecting users and property. Careful consideration of these safety features ensures safe and responsible power generation during outages or off-grid scenarios. Overlooking safety features can expose users to risks such as carbon monoxide poisoning, fire hazards, and electrical shock. A generator equipped with comprehensive safety features contributes significantly to a secure operating environment.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO) Detectors and Shut-off Systems
Carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and poisonous gas produced during fuel combustion, poses a significant health hazard. Generators equipped with CO detectors automatically shut down the unit if dangerous CO levels are detected. This feature prevents CO buildup in enclosed spaces, protecting users from potential poisoning. A CO detector acts as a critical safeguard, mitigating the risk of CO exposure during generator operation. For example, if a generator is operating in a poorly ventilated area, the CO detector will activate and shut down the unit, preventing potential harm.
- Automatic Shut-off for Low Oil Levels
Low oil levels can cause severe engine damage. Generators with automatic low-oil shutoff systems prevent engine damage by automatically shutting down the unit when oil levels fall below a critical threshold. This feature protects the engine from damage and extends its operational lifespan. For example, if a generator develops an oil leak, the low-oil shutoff system will activate, preventing catastrophic engine failure.
- Overload Protection
Overloading a generator by exceeding its rated power output can damage the unit and pose a fire hazard. Overload protection circuits automatically shut down the generator in overload conditions, preventing damage to the unit and mitigating fire risks. This feature safeguards the generator and connected appliances from potential damage caused by excessive power demands. Connecting too many appliances or appliances with high starting wattage can trigger overload protection, preventing damage to the generator and the electrical system.
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI)
GFCI outlets protect against electrical shock. These outlets detect imbalances in electrical current flow, indicating a potential ground fault, and quickly interrupt the circuit, preventing electrical shock hazards. GFCI protection is particularly important in outdoor environments where moisture increases the risk of electrical shock. For example, if a power cord is damaged and contacts a wet surface, the GFCI outlet will immediately trip, preventing potential electrocution.
Prioritizing safety features in portable diesel generators for home use mitigates potential hazards, contributing to a secure operating environment. CO detectors, low-oil shutoff systems, overload protection, and GFCI outlets represent critical safety components that protect users and property. Selecting generators equipped with these features and adhering to safe operating practices ensures responsible and secure power generation during outages and off-grid scenarios. Understanding and utilizing these safety features maximizes the benefits of portable power while minimizing potential risks.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, operation, and maintenance of portable diesel generators for residential applications.
Question 1: How is the appropriate generator size determined for a specific home?
Generator sizing involves calculating the total wattage required to power essential appliances and devices during an outage. Consider both running watts (continuous power consumption) and starting watts (initial surge power). Consulting an electrician can assist in accurately assessing power requirements.
Question 2: What are the key maintenance requirements for a diesel generator?
Essential maintenance includes regular oil changes, fuel filter replacements, air filter cleaning or replacement, and periodic inspections of spark plugs and battery connections. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Question 3: Where should a portable diesel generator be placed during operation?
Generators should be operated outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from windows, doors, and air intakes. Adequate clearance around the unit allows for proper ventilation and heat dissipation. Positioning the generator on a stable, level surface prevents accidental tipping.
Question 4: What type of fuel is recommended for diesel generators?
High-quality diesel fuel, stored in approved containers and treated with fuel stabilizer as needed, ensures optimal engine performance and longevity. Avoid using contaminated or degraded fuel, which can cause engine problems and reduce efficiency.
Question 5: What safety precautions should be observed during generator operation?
Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Ensure adequate ventilation around the unit. Avoid refueling a hot generator. Allow the unit to cool down completely before refueling to prevent fire hazards.
Question 6: How can generator noise be minimized?
Selecting a generator with a lower decibel rating helps minimize noise pollution. Strategic placement of the unit, use of sound-dampening enclosures or barriers, and regular maintenance of the exhaust system contribute to noise reduction. Adhering to local noise ordinances ensures compliance and promotes neighborhood harmony.
Addressing these common questions provides a foundation for informed decision-making regarding portable diesel generator selection, operation, and maintenance for residential applications. Understanding these aspects contributes to safe, reliable, and efficient power generation during outages or off-grid scenarios.
The subsequent section delves further into specific generator models and their respective features.
Portable Diesel Generators for Home Use
Portable diesel generators offer a crucial safeguard for residences against power disruptions, ensuring the continuity of essential services and enhancing safety. Careful consideration of factors such as power output, fuel efficiency, noise levels, portability, maintenance requirements, and safety features is essential for effective selection and utilization. Understanding these elements allows homeowners to make informed decisions, maximizing the benefits of reliable backup power while mitigating potential risks. From sizing calculations to operational guidelines and maintenance best practices, a comprehensive understanding promotes responsible generator ownership and operation.
Reliable access to power underpins modern life. Portable diesel generators provide an essential layer of resilience against power grid vulnerabilities, contributing to household preparedness and peace of mind. Investing in a properly sized and maintained generator empowers homeowners to navigate power outages effectively, ensuring the safety and well-being of their households. As power grid reliability remains a concern, portable diesel generators stand as valuable resources, enabling households to maintain essential functions and navigate unforeseen power disruptions with confidence.