Operating a portable generator for residential purposes involves a series of carefully executed steps, from initial setup and connection to safe operation and proper shutdown procedures. A typical setup includes connecting appliances via extension cords or through a transfer switch for a more permanent solution, ensuring the generator is placed outdoors in a well-ventilated area away from windows and doors. Fueling and starting the generator, followed by careful load management, are key aspects of successful operation.
Reliable backup power during outages ensures critical systems like heating, refrigeration, and medical equipment remain functional. This capability offers peace of mind and significantly enhances safety and comfort during emergencies. Historically, access to reliable backup power was primarily limited to larger, permanently installed systems. Portable generator technology has democratized access to emergency power, providing a more affordable and flexible solution for homeowners.
Understanding the detailed procedures for safe and effective operation is paramount. The following sections will cover essential topics, including generator safety precautions, step-by-step starting and shutdown instructions, proper connection methods, recommended maintenance practices, and troubleshooting tips.
Operating a Portable Generator
Safe and efficient operation requires adherence to specific guidelines. The following tips provide crucial insights for maximizing the effectiveness and lifespan of a portable generator while ensuring user safety.
Tip 1: Consult the Owner’s Manual: Before operating any portable generator, thorough review of the manufacturer’s instructions is crucial. This document provides model-specific guidance on safe operation, maintenance procedures, and troubleshooting.
Tip 2: Prioritize Outdoor Placement: Generators produce carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and deadly gas. Operation must always occur outdoors in a well-ventilated area, positioned away from windows, doors, and air intakes.
Tip 3: Ensure Proper Grounding: Grounding the generator protects against electrical shock. Consult a qualified electrician for proper grounding procedures and adherence to local electrical codes.
Tip 4: Manage Electrical Loads: Avoid overloading the generator. Calculate the total wattage of connected appliances and ensure it remains within the generator’s rated capacity. Prioritize essential appliances during outages.
Tip 5: Allow the Generator to Cool: Before refueling, allow the generator to cool down completely. Hot engine components and fuel can create a fire hazard.
Tip 6: Store Fuel Safely: Store fuel in approved, sealed containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Never refuel a running or hot generator.
Tip 7: Perform Regular Maintenance: Routine maintenance, such as oil changes and air filter cleaning, as outlined in the owner’s manual, will prolong the generator’s life and ensure reliable operation.
Adhering to these operational guidelines ensures safe, reliable, and efficient power generation during emergencies. Proper usage not only maximizes the generator’s lifespan but also safeguards users from potential hazards.
By understanding and implementing these recommendations, individuals can confidently utilize portable generators as a dependable source of backup power.
1. Safety First
Safe operation of a portable generator is paramount. Prioritizing safety mitigates risks associated with improper usage, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire hazards, and electrical shock. Understanding and implementing safety procedures is essential before, during, and after operation.
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Prevention
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and lethal gas produced during generator operation. Fatal CO poisoning can occur quickly in enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces. Operating the generator outdoors, far from windows, doors, and air intakes, is crucial for preventing CO buildup and ensuring user safety. CO detectors should be installed and regularly tested.
- Fire Hazard Mitigation
Generators utilize flammable fuel. Spilled fuel combined with hot engine components presents a significant fire risk. Allowing the generator to cool completely before refueling is essential. Storing fuel in approved containers, away from ignition sources, further minimizes fire hazards.
- Electrical Shock Prevention
Improper grounding or faulty electrical connections can lead to electrical shock. Ensuring proper grounding of the generator and utilizing appropriate extension cords rated for the intended load minimizes the risk of electrocution. Consulting a qualified electrician for guidance on safe electrical practices is recommended.
- Safe Refueling Practices
Refueling a hot generator poses a severe fire hazard. Gasoline vapors can ignite when exposed to hot surfaces or sparks. Always allow the generator to cool down completely before refueling. Avoid spilling fuel and never refuel indoors or near open flames.
Integrating these safety practices into every stage of generator operation, from setup to shutdown, significantly reduces risks and ensures user well-being. Neglecting these precautions can lead to serious or fatal consequences. Prioritizing safety is not merely a recommendation but a critical requirement for responsible generator usage.
2. Placement Outdoors
Outdoor placement is a non-negotiable requirement for safe portable generator operation. Combustion engines produce carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas. CO accumulates rapidly in enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces, posing a severe health risk, including fatality. Positioning the generator outdoors, away from buildings, ensures adequate ventilation and prevents dangerous CO buildup. This practice safeguards occupants from potential exposure and adheres to established safety guidelines.
Selecting a suitable outdoor location involves careful consideration of prevailing wind direction and proximity to open windows, doors, and air intakes. Directing exhaust fumes away from occupied areas minimizes the risk of CO infiltration. Placing the generator on a stable, level surface prevents tipping and fuel spills. Further considerations include adequate distance from flammable materials and protection from inclement weather, such as rain or snow, using a generator cover or canopy while ensuring adequate ventilation.
Failure to place the generator outdoors can have dire consequences. Numerous incidents of CO poisoning have been reported due to improper generator placement, sometimes resulting in fatalities. Understanding the critical link between outdoor placement and safe operation is fundamental to responsible generator use. Adherence to this crucial safety precaution protects lives and prevents preventable tragedies.
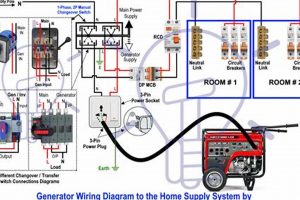
3. Connection Methods
Connecting appliances to a portable generator requires careful consideration to ensure both safety and proper functionality. Selecting the appropriate connection method depends on the specific needs and the complexity of the electrical setup. Understanding the available optionsdirect connection via extension cords and the installation of a transfer switchis crucial for effective and safe generator usage.
- Direct Connection via Extension Cords
This method involves connecting individual appliances directly to the generator using heavy-duty extension cords rated for the appliance’s wattage. This approach is generally suitable for powering a limited number of essential devices. For example, during a power outage, one might connect a refrigerator, a few lights, and a critical medical device. While convenient for short-term needs, this method requires careful load management and carries a slightly higher risk of mishaps if cords are not properly rated or maintained. Users must ensure each cord’s capacity exceeds the connected appliance’s wattage.
- Transfer Switch Installation
A transfer switch offers a more permanent and sophisticated connection method. Installed by a qualified electrician, a transfer switch connects the generator to the home’s electrical panel. This allows for convenient power restoration to selected circuits during an outage. This method avoids the need for numerous extension cords and simplifies the process of powering multiple devices. A transfer switch also prevents backfeeding, a dangerous phenomenon where electricity flows from the generator back into the power grid, posing a risk to utility workers. While requiring professional installation, a transfer switch offers enhanced safety and convenience for frequent or prolonged generator usage.
- Inlet Box Connection
An inlet box provides a dedicated connection point for the generator, often located on the exterior of the house. This eliminates the need to run extension cords through windows or doors, improving safety and convenience. The inlet box typically connects to a transfer switch or a dedicated circuit breaker in the electrical panel. This method offers a more organized and permanent solution, especially for frequently used generators.
- Adapter Cords (For Smaller Appliances)
Smaller appliances and electronics often use standard household plugs. Adapter cords can connect these devices directly to the generator’s outlets, provided the generator’s output matches the appliance’s requirements. This method is practical for charging phones, powering laptops, or running small fans. It is essential to monitor the cumulative load connected through adapters to avoid exceeding the generator’s capacity.
Selecting the appropriate connection method significantly impacts the safety and efficiency of generator operation. While direct connection via extension cords offers a simple solution for short-term needs, a transfer switch provides enhanced safety and convenience for more complex setups. Inlet boxes further streamline the process, and adapter cords cater to smaller devices. Understanding these methods empowers users to effectively utilize their portable generators while adhering to safety guidelines and maximizing power distribution efficiency.
4. Starting Procedure
The starting procedure represents a critical phase in portable generator operation, directly influencing safe and effective power generation. A properly executed starting procedure ensures the generator functions as intended, minimizing potential damage and maximizing its operational lifespan. Ignoring prescribed steps can lead to mechanical failure, reduced efficiency, and safety hazards. The starting procedure acts as the foundational element in the broader context of generator usage, influencing all subsequent operations.
A typical starting procedure involves several key steps. Initially, the generator should be placed outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from structures and flammable materials. The fuel level must be checked and replenished if necessary, using the correct fuel type as specified by the manufacturer. The engine oil level should also be verified and maintained within the recommended range. The choke lever, if present, is typically engaged for cold starts and gradually disengaged as the engine warms up. The start switch or recoil starter is then used to initiate the engine. Once the engine starts, it should be allowed to stabilize and warm up before connecting any electrical loads. Failure to follow this sequence can result in engine damage, difficulty starting, and potential safety risks.
For instance, attempting to start a generator with low oil can cause significant engine wear and potential seizure. Similarly, neglecting to disengage the choke after the engine warms up can lead to excessive fuel consumption and engine fouling. Furthermore, connecting electrical loads before the engine has stabilized can overload the generator, potentially causing damage to both the generator and the connected appliances. Practical understanding of the starting procedure’s impact on overall generator performance emphasizes its crucial role in safe and efficient usage. Mastering this foundational element ensures reliable power generation and prolongs the generator’s service life.
5. Load Management
Load management represents a critical aspect of portable generator operation. Generators possess a finite power output capacity. Exceeding this capacity through connection of excessive electrical loads leads to generator overload, potentially causing damage to the generator itself and connected appliances. Effective load management ensures the generator operates within its designed parameters, maximizing efficiency and prolonging its operational lifespan. Furthermore, proper load management optimizes power distribution during outages, ensuring critical appliances receive necessary power.
Understanding the wattage requirements of connected appliances is fundamental to effective load management. Each appliance consumes a specific amount of power, measured in watts. The sum of these wattages represents the total load on the generator. This total load must remain within the generator’s rated capacity. For example, a generator rated at 5000 watts cannot continuously power a combined load exceeding this limit. Attempting to do so risks overloading the generator, leading to potential damage or shutdown. Prioritizing essential appliances during outages, such as refrigerators, freezers, and medical equipment, becomes crucial. Non-essential appliances should be disconnected to manage the load effectively. Rotating appliance usage can also contribute to load management, ensuring the generator remains within its operating capacity. This approach might involve running the refrigerator for a few hours, then switching to a sump pump, while ensuring the total load at any given time remains within the generator’s limits.
Effective load management directly impacts the generator’s performance and longevity. Consistent overloading significantly reduces the generator’s lifespan and increases the likelihood of malfunctions. Conversely, careful load management, based on accurate wattage calculations and prioritization of essential appliances, ensures safe and efficient operation, maximizing the generator’s utility during power outages. Understanding and implementing proper load management strategies represent crucial components of responsible generator ownership and utilization.
6. Shutdown Process
The shutdown process represents a crucial final stage in portable generator operation, impacting both equipment longevity and user safety. A properly executed shutdown procedure ensures the generator and connected appliances are protected from potential damage, while mitigating risks associated with fuel and electrical systems. Correctly shutting down the generator contributes to its overall lifespan and prevents complications that can arise from improper procedures.
- Disconnecting Loads
Before stopping the generator, disconnect all connected electrical loads. This prevents power surges that can occur during shutdown, potentially damaging sensitive electronics and appliances. Disconnecting loads also ensures a smoother shutdown process for the generator itself. For instance, if a large load, such as a refrigerator, remains connected during shutdown, the sudden interruption of power can strain the generator’s components. Methodically disconnecting each appliance prior to shutdown mitigates this risk.
- Cooling Down Period
After disconnecting the loads, allow the generator to run for a few minutes without any load. This cooling-down period allows the engine to dissipate heat gradually, reducing wear and tear on internal components. Immediately shutting down a hot engine can lead to accelerated wear and potential damage. This cool-down period, although brief, significantly contributes to the generator’s overall lifespan.
- Turning Off the Engine
Once the cooling-down period is complete, use the designated engine shutdown switch or key to stop the generator. Avoid simply turning off the fuel valve, as this can lead to fuel remaining in the carburetor, potentially causing starting issues in the future. Using the proper shutdown procedure ensures the engine stops correctly and prepares the generator for subsequent use.
- Fuel Valve (For Storage)
If the generator is being stored for an extended period, turn off the fuel valve to prevent fuel from leaking into the carburetor or other engine components. This step prevents fuel degradation and potential starting problems when the generator is needed again. For shorter periods of inactivity, turning off the fuel valve is not strictly necessary but remains a recommended practice.
Adhering to a proper shutdown process safeguards both the generator and connected appliances, contributing to the generator’s longevity and promoting safe operation. Each step in the process plays a vital role in protecting the generator from damage, ensuring its reliability for future use, and preventing potential safety hazards. Integrating these procedures into routine generator operation establishes a foundation for safe and effective power generation during emergency situations.
7. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance forms an integral part of responsible portable generator ownership and directly influences the generator’s performance, lifespan, and reliability. Neglecting routine maintenance procedures can lead to decreased efficiency, mechanical failures, and potentially hazardous operating conditions. A well-maintained generator provides dependable power during outages, while a neglected unit may malfunction precisely when needed most. This underscores the crucial link between regular maintenance and the effective use of a portable generator. Maintenance schedules, detailed in the owner’s manual, provide model-specific guidance on required procedures and recommended intervals.
Regular maintenance encompasses several key areas. Oil changes, at intervals specified by the manufacturer, ensure proper engine lubrication, reducing wear and tear on internal components. Air filter cleaning or replacement prevents dust and debris from entering the engine, maintaining optimal combustion and fuel efficiency. Spark plug inspection and replacement, as needed, ensure consistent ignition and reliable engine starting. Fuel system maintenance, including periodic draining or adding fuel stabilizer, prevents fuel degradation and carburetor clogging, particularly during extended storage periods. Neglecting these procedures can have significant consequences. For example, failing to change the oil can lead to engine seizure, while a clogged air filter can reduce power output and increase fuel consumption. Real-life examples abound, highlighting the importance of adhering to prescribed maintenance schedules. Reports of generator failures during critical power outages often trace back to inadequate maintenance practices, demonstrating the practical significance of proactive maintenance.
Understanding the direct relationship between regular maintenance and reliable generator operation is paramount. Implementing a consistent maintenance schedule, following manufacturer guidelines, ensures optimal performance and prolongs the generator’s operational life. This proactive approach not only safeguards the investment but also guarantees dependable power generation when needed, mitigating the risks associated with unexpected power outages. Regular maintenance, therefore, constitutes not just a recommendation but a crucial aspect of responsible generator ownership and effective utilization.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding portable generator operation, providing concise and informative responses to enhance user understanding and promote safe and effective usage.
Question 1: What type of fuel should be used?
The appropriate fuel type is specified by the manufacturer. Common fuel types include gasoline, propane, and diesel. Using an incorrect fuel type can damage the engine and void the warranty.
Question 2: How far from the house should a portable generator be placed?
A minimum distance of 20 feet from the house is generally recommended to minimize carbon monoxide exposure risks. Further distances may be necessary depending on prevailing wind conditions and the presence of open windows or doors.
Question 3: Can a portable generator be used indoors?
Never operate a portable generator indoors. Generator exhaust contains carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and deadly gas. Outdoor operation in a well-ventilated area is essential to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
Question 4: What is a transfer switch, and is it necessary?
A transfer switch safely connects a portable generator to a home’s electrical system. It prevents backfeeding, which can endanger utility workers. While not strictly required for all setups, a transfer switch significantly enhances safety and convenience, especially for connecting multiple circuits.
Question 5: How often should generator maintenance be performed?
Consult the owner’s manual for model-specific maintenance schedules. General guidelines include regular oil changes, air filter cleaning or replacement, and spark plug inspection. Adhering to the recommended maintenance schedule ensures optimal performance and extends the generator’s lifespan.
Question 6: What precautions should be taken during refueling?
Always allow the generator to cool down completely before refueling. Hot engine components and fuel can create a fire hazard. Refuel outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from ignition sources. Avoid spilling fuel, and never refuel a running generator.
Understanding these frequently asked questions equips individuals with essential knowledge for safe and effective portable generator operation. Thorough review of the owner’s manual and adherence to safety guidelines remain paramount for responsible generator usage.
Further information regarding specific generator models and local safety regulations should be obtained from the manufacturer and relevant authorities.
Safe and Effective Portable Generator Operation
Mastery of portable generator operation necessitates diligent adherence to established safety protocols and operational guidelines. Prioritizing safety through proper placement, connection procedures, load management, and routine maintenance ensures reliable performance while mitigating potential hazards. Understanding the intricacies of starting, operating, and shutting down the generator, coupled with consistent maintenance practices, safeguards both the equipment and the individuals relying on its power. This comprehensive approach to portable generator usage empowers individuals to effectively utilize this valuable resource during emergency situations.
Reliable access to backup power provides critical support during unforeseen outages, safeguarding essential household functions and enhancing overall safety. Portable generators represent a significant investment in preparedness and resilience, demanding responsible operation and proactive maintenance. Adherence to established safety protocols and informed operational practices ensures the long-term viability of this crucial resource, empowering individuals to navigate power disruptions with confidence and security.