Safe and effective portable generator operation for residential power supply involves careful planning and execution. This includes assessing power needs, proper generator placement, safe connection methods, and adherence to manufacturer guidelines. For example, calculating wattage requirements for essential appliances and electronics ensures the generator can handle the load. Connecting appliances directly to the generator with appropriately rated cables or through a transfer switch prevents backfeeding, a dangerous phenomenon that can harm utility workers and damage equipment.
Backup power provided by portable generators offers critical support during power outages, enabling homeowners to maintain essential functions such as refrigeration, heating, lighting, and communication. This capability offers significant peace of mind, particularly in areas prone to severe weather events or unreliable grid infrastructure. Historically, portable generators have played a vital role in disaster recovery, providing a temporary power source for communities and individual households.
The following sections will detail crucial steps for safe and efficient portable generator operation, covering topics such as generator sizing, fuel and maintenance considerations, connection procedures, safety precautions, and potential legal restrictions.
Tips for Safe and Effective Portable Generator Operation
Proper generator use ensures safety and efficiency. These tips provide guidance for optimal performance and risk mitigation.
Tip 1: Calculate Power Requirements: Determine the wattage required to run essential appliances. Consult appliance labels and sum the wattages to avoid overloading the generator.
Tip 2: Select the Right Generator: Choose a generator with sufficient running watts and starting watts to handle the calculated load. Starting watts, often higher than running watts, are crucial for appliances with electric motors.
Tip 3: Ensure Proper Ventilation: Operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from windows, doors, and air intakes. Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious risk.
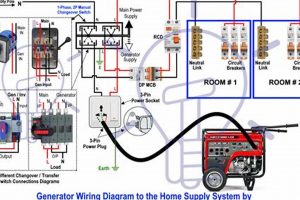
Tip 4: Utilize a Transfer Switch: A transfer switch safely connects the generator to the home’s electrical system, preventing backfeeding and ensuring proper load distribution. Consult a qualified electrician for installation.
Tip 5: Ground the Generator: Properly ground the generator according to manufacturer instructions. This crucial safety step protects against electrical shock.
Tip 6: Allow the Generator to Cool: Before refueling, allow the generator to cool completely. Hot surfaces and fuel vapors pose a fire hazard.
Tip 7: Store Fuel Safely: Store fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Rotate fuel supplies to ensure freshness.
Tip 8: Consult Local Regulations: Verify local ordinances regarding generator usage, including noise restrictions and permitting requirements.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures safe and efficient generator operation, providing reliable backup power during outages.
Careful planning and operation are essential for maximizing the benefits of portable generator ownership. The following section concludes with additional resources and important considerations.
1. Safety First
Safe operation is paramount when utilizing a portable generator for residential power. Negligence in safety protocols can lead to severe consequences, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire hazards, and electrical shocks. Understanding and implementing appropriate safety measures is crucial for protecting individuals and property.
- Ventilation
Generators produce carbon monoxide, an odorless, colorless, and lethal gas. Operating a generator in a confined or poorly ventilated space can lead to rapid carbon monoxide buildup, posing a serious health risk. Generators must be placed outdoors, far from windows, doors, and air intakes, to ensure adequate ventilation and prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Grounding
Proper grounding is essential to prevent electrical shocks. A grounded generator provides a safe path for electrical current to flow in the event of a fault, protecting users from electrocution. Consult the generator’s owner’s manual for grounding instructions and ensure the grounding system is correctly implemented.
- Fuel Handling
Gasoline and other fuels used in portable generators are flammable. Spilled fuel or improper refueling procedures can create fire hazards. Allow the generator to cool completely before refueling and store fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources.
- Connection Procedures
Incorrect connection to a home’s electrical system can lead to backfeeding, a dangerous phenomenon that sends power back into the utility grid. This poses a serious risk to utility workers and can damage appliances. A properly installed transfer switch is crucial for safe connection and prevents backfeeding. Consult a qualified electrician for transfer switch installation.
These safety precautions are integral to proper portable generator operation. Careful adherence to these guidelines mitigates risks and ensures the safe and effective provision of backup power during outages. Ignoring these precautions can have severe consequences, underscoring the importance of prioritizing safety when operating a portable generator.
2. Proper Connection
Proper connection is a critical aspect of safe and effective portable generator usage for residential power supply. Incorrect connection methods can lead to hazardous situations, including backfeeding, which poses significant risks to utility line workers and can damage household appliances and the generator itself. A direct connection to household wiring without a transfer switch creates a backfeeding risk. For example, if a homeowner directly connects a generator to a wall outlet during a power outage, the electricity can flow back into the utility grid, energizing downed power lines and potentially electrocuting utility workers attempting repairs.
A transfer switch, installed by a qualified electrician, provides a safe and reliable connection point for a portable generator. It isolates the home’s electrical system from the utility grid during generator operation, eliminating the risk of backfeeding. This isolation ensures that the generator powers only the selected circuits within the house and prevents electricity from flowing back onto the grid. Transfer switches also offer a more convenient and organized method for connecting the generator to household circuits compared to individually plugging in appliances.
Understanding and implementing the correct connection procedures are fundamental to safe and efficient portable generator usage. Failure to establish a proper connection through a transfer switch compromises safety and risks damage to equipment and potential harm to utility personnel. Therefore, professional installation of a transfer switch is a crucial investment for anyone relying on a portable generator for backup power, reflecting a commitment to safety and responsible generator operation.
3. Load Calculation
Accurate load calculation is fundamental to safe and effective portable generator use for residential applications. Understanding the power demands of essential appliances and devices is crucial for selecting a generator with sufficient capacity and preventing overload, which can damage both the generator and connected equipment. A precise load calculation ensures the generator can handle the required wattage during a power outage.
- Identifying Essential Appliances
Determining which appliances are crucial during a power outage forms the basis of load calculation. Essential appliances may include refrigerators, freezers, sump pumps, furnaces, and essential lighting. Prioritizing needs and creating a list of must-run appliances is the first step in accurate load calculation. For example, a household might prioritize powering a refrigerator, a few lights, and a furnace, while foregoing less critical devices like televisions or entertainment systems during an outage.
- Determining Wattage Requirements
Each appliance has a specific wattage requirement, representing its power consumption. This information is typically found on an appliance’s label or in its owner’s manual. Summing the wattages of the identified essential appliances provides the total running wattage required. For instance, a refrigerator might require 150 running watts, a furnace fan 300 running watts, and several LED lights a combined 50 watts, resulting in a total running wattage requirement of 500 watts.
- Considering Starting Wattage
Appliances with electric motors, such as refrigerators and sump pumps, require a surge of power upon startup, known as starting wattage. Starting wattage is often significantly higher than running wattage. Generator capacity must account for these higher starting wattage demands to prevent overload during appliance startup. Failing to consider starting wattage can lead to the generator stalling or failing to start the appliance. For example, a refrigerator requiring 150 running watts might have a starting wattage requirement of 600 watts.
- Applying Safety Margin
Adding a safety margin to the calculated load is recommended to prevent overloading the generator and to accommodate potential future needs. A safety margin of 10-20% above the calculated total wattage ensures ample capacity and prevents the generator from operating at its maximum limit continuously. This margin provides flexibility and safeguards against unexpected load increases. For a calculated load of 500 running watts and 600 starting watts, adding a 20% safety margin results in a recommended generator capacity of 600 running watts and 720 starting watts.
Accurate load calculation is therefore not merely a technical step but an essential component of responsible generator ownership and safe operation. By correctly assessing power requirements, individuals can choose an appropriately sized generator, ensuring reliable power supply during outages and preventing equipment damage caused by overload. This careful planning translates to efficient and effective use of a portable generator for residential backup power, optimizing performance and enhancing safety.
4. Fuel Management
Fuel management is integral to the safe and effective operation of a portable generator for residential power supply. Proper fuel handling, storage, and usage practices directly impact the generator’s performance, longevity, and overall safety. Neglecting fuel management can lead to equipment malfunction, fire hazards, and environmental contamination. For example, using stale or contaminated fuel can clog the carburetor and prevent the generator from starting or running smoothly. Similarly, improper storage of gasoline, such as in unapproved containers or near ignition sources, significantly increases the risk of fire.
Effective fuel management involves several key practices. Storing gasoline in approved, sealed containers in a well-ventilated area away from living spaces and ignition sources minimizes fire hazards and evaporation. Rotating fuel supplies, using older fuel first, prevents fuel degradation and ensures optimal generator performance. Regularly checking the fuel level and avoiding running the generator out of fuel minimizes strain on the engine and prolongs its lifespan. Understanding the generator’s fuel consumption rate allows for accurate estimation of fuel needs during extended outages. For instance, knowing a generator consumes one gallon of gasoline per hour allows homeowners to calculate the required fuel reserve for a projected outage duration. Furthermore, adhering to local regulations regarding fuel storage limits and disposal methods demonstrates responsible environmental stewardship.
Proper fuel management, therefore, represents a critical component of responsible generator ownership and operation. It directly influences the generator’s reliability, safety, and environmental impact. Careful attention to fuel handling, storage, and usage procedures ensures optimal generator performance, minimizes risks, and promotes safe and sustainable backup power solutions for residential applications. Overlooking these practices can compromise not only the generator’s functionality but also the safety and well-being of the individuals relying on it.
5. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for the safe, reliable, and efficient operation of a portable generator used for residential power supply. Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to decreased performance, increased fuel consumption, unexpected breakdowns, and potentially hazardous situations. A well-maintained generator provides dependable power during outages, maximizing its lifespan and minimizing the risk of malfunctions.
- Oil Changes
Regular oil changes are crucial for lubricating engine components, reducing friction, and preventing overheating. Engine oil degrades over time and loses its lubricating properties. Following the manufacturer’s recommended oil change intervals, typically based on operating hours, ensures optimal engine performance and longevity. For example, a generator might require an oil change every 50 operating hours. Neglecting oil changes can lead to increased engine wear, reduced efficiency, and potential engine failure.
- Air Filter Maintenance
Clean air filters are essential for proper engine combustion. A clogged air filter restricts airflow to the engine, reducing power output and increasing fuel consumption. Regularly inspecting and cleaning or replacing the air filter, as specified in the owner’s manual, ensures sufficient airflow and maintains efficient engine operation. Operating a generator in dusty environments may necessitate more frequent air filter maintenance. A clean air filter contributes to optimal fuel efficiency and prevents engine damage from dust and debris.
- Spark Plug Inspection and Replacement
Spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine cylinder. Worn or fouled spark plugs can cause misfires, reducing engine performance and increasing fuel consumption. Periodically inspecting and replacing spark plugs, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, ensures reliable ignition and efficient combustion. Spark plug condition can indicate underlying engine issues, providing valuable diagnostic information. Maintaining proper spark plug function contributes to smooth engine operation and optimal fuel efficiency.
- Fuel System Maintenance
Maintaining a clean fuel system is vital for preventing clogs and ensuring consistent fuel delivery to the engine. Stale fuel can leave deposits and varnish in the fuel tank, fuel lines, and carburetor, leading to performance issues and starting difficulties. Using fuel stabilizer and periodically draining or cleaning the fuel system, as outlined in the owner’s manual, helps prevent fuel-related problems. Regular fuel system maintenance ensures reliable generator operation and prevents costly repairs. For example, draining the fuel system before storing the generator for an extended period prevents fuel degradation and potential clogging.
Adhering to a regular maintenance schedule, as outlined in the generator’s owner’s manual, is essential for ensuring reliable performance, maximizing lifespan, and minimizing the risk of malfunctions and hazardous situations. Proper maintenance reflects responsible generator ownership and contributes significantly to the safe and efficient provision of backup power during outages, ultimately enhancing the value and utility of the generator for residential power supply.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the safe and effective use of portable generators for residential power supply. Clear and concise answers aim to provide practical guidance for homeowners.
Question 1: How is the correct generator size determined for a specific home?
Generator size selection depends on the wattage requirements of the appliances intended for use during a power outage. Calculating the combined running watts of essential appliances and adding a safety margin is crucial for ensuring adequate power supply.
Question 2: What is the safest method for connecting a portable generator to a home’s electrical system?
A properly installed transfer switch is the safest connection method. Transfer switches prevent backfeeding, a dangerous occurrence that can harm utility workers and damage equipment. Direct connection to outlets or circuits should be avoided.
Question 3: Where should a portable generator be placed during operation?
Generators must operate outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from windows, doors, and air intakes. This placement minimizes carbon monoxide poisoning risks and ensures adequate airflow for cooling.
Question 4: What type of fuel is typically used in portable generators, and how should it be stored?
Gasoline is the most common fuel. It should be stored in approved, sealed containers in a well-ventilated area, away from ignition sources and living spaces. Fuel stabilizer helps prevent degradation during storage.
Question 5: How frequently should a portable generator undergo maintenance?
Maintenance frequency depends on usage and the manufacturer’s recommendations. Regular maintenance typically includes oil changes, air filter cleaning or replacement, spark plug inspection, and fuel system cleaning. Adhering to the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Question 6: Are there any legal restrictions or permits required for operating a portable generator?
Local ordinances may regulate generator usage, including noise levels and operating hours. Consulting local authorities or homeowner associations is advisable to determine any applicable regulations or permit requirements.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of portable generator usage contributes significantly to safe and effective operation, ensuring reliable backup power during outages and protecting both individuals and property. Thorough planning and preparation are essential for maximizing the benefits of portable generator ownership.
Additional resources and contact information for professional assistance can be found in the following section.
Safe and Effective Portable Generator Operation for Residential Use
Safe and effective portable generator operation for residential power supply necessitates careful planning and execution. This encompasses accurate load calculation, proper generator placement and connection through a transfer switch, adherence to safety guidelines regarding ventilation and fuel handling, and a commitment to regular maintenance. Understanding and implementing these critical aspects ensures reliable backup power during outages while mitigating potential risks.
Portable generators offer significant value during power disruptions, enabling essential household functions to continue. However, responsible operation requires diligent adherence to safety protocols and established best practices. Preparedness and informed operation are crucial for maximizing the benefits of portable generator ownership and ensuring the safety of individuals and communities.