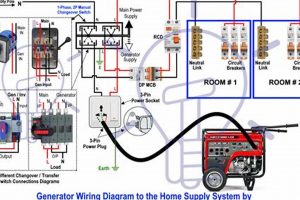
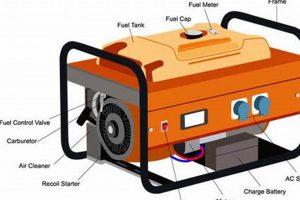
Compact, fuel-powered devices capable of generating electricity independently of the main power grid, these units utilize propane as a fuel source and are designed for residential applications. They offer a practical solution for powering essential appliances during outages or providing electricity in locations lacking grid access. For instance, during a power outage, such a unit could power refrigerators, lighting, and small heating appliances.
Backup power supplies offer significant advantages, particularly in areas prone to power disruptions due to weather events or grid instability. These independent power sources provide crucial electricity for essential appliances and devices, ensuring safety and comfort. Historically, reliance on noisy, gasoline-fueled generators was common. Advancements in technology have led to the development of quieter, cleaner-burning propane-powered options that provide a more convenient and environmentally conscious alternative for homeowners.
This article will further explore key aspects of these devices, including selecting the appropriate size, understanding proper maintenance procedures, and addressing safety considerations.
Tips for Operating Propane-Powered Generators
Safe and efficient operation of propane-fueled generators requires careful consideration of several factors. The following tips provide guidance for optimal performance and safety.
Tip 1: Proper Sizing: Accurate load calculations are crucial for selecting a generator with sufficient capacity. Undersized units risk overload and damage, while oversized units waste fuel. Consulting a qualified electrician is recommended for accurate load assessments.
Tip 2: Safe Placement: Units must be placed outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from windows and doors, to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. A stable, level surface is essential to prevent tipping and spills.
Tip 3: Regular Maintenance: Routine maintenance, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement, ensures optimal performance and extends the generator’s lifespan. Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific maintenance schedules.
Tip 4: Fuel Storage and Handling: Propane cylinders should be stored upright in a secure, well-ventilated area away from heat sources. Connections should be checked regularly for leaks.
Tip 5: Connection to Appliances: Directly connecting appliances to the generator through approved extension cords is recommended. Overloading the generator can cause damage. Prioritizing essential appliances is important during extended outages.
Tip 6: Operational Checks: Periodically testing the generator under load helps ensure it functions correctly during an outage. Familiarization with the starting and operating procedures is essential.
Tip 7: Professional Installation: While some units are designed for DIY installation, professional installation by a qualified electrician is often recommended for safe and proper connection to home circuits.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures safe, reliable power during outages, maximizing the generator’s lifespan and minimizing potential hazards.
By understanding and implementing these operational best practices, homeowners can effectively utilize their generators and maintain a safe and reliable backup power source.
1. Portability
Portability is a defining characteristic of these generators, directly influencing their practicality and suitability for various applications. The ease with which a unit can be moved and positioned significantly impacts its usability in both emergency and recreational contexts.
- Weight and Size
The physical dimensions and weight of a generator directly affect its portability. Compact, lightweight units are easily maneuvered and transported, while larger, heavier models may require assistance or specialized transport. For example, a smaller unit might be easily carried from a storage shed to a patio, while a larger unit might require a wheel kit or a truck for transport.
- Integrated Handles and Wheels
Ergonomic features such as integrated handles and wheels significantly enhance portability. Well-designed handles provide a secure grip for lifting, while durable wheels facilitate movement across various terrains. A unit equipped with sturdy wheels and a telescoping handle can be easily rolled across a lawn or gravel driveway.
- Compact Design
A compact design minimizes the generator’s footprint, allowing for convenient storage and placement in confined spaces. This is particularly advantageous for users with limited storage space or those who require a portable power source for recreational activities. A compact unit can be easily stored in a garage or the back of a vehicle.
- Power Source Considerations
The type and size of the propane tank also influence portability. Smaller, disposable propane cylinders offer greater portability, while larger, refillable tanks provide longer runtimes but may be less convenient to transport. For camping trips, smaller propane canisters might be preferable, while for extended home use during outages, a larger refillable tank might be more practical.
The portability of a unit significantly affects its suitability for different applications. Careful consideration of weight, size, and design features is crucial for selecting a generator that meets specific portability requirements, whether for emergency home backup power or recreational use.
2. Propane Fuel
Propane’s characteristics make it a well-suited fuel source for portable generators intended for residential applications. Its availability, storage properties, and clean-burning nature contribute significantly to the practicality and efficiency of these devices. The fuel’s widespread availability through various retail channels ensures convenient access for homeowners. Unlike gasoline, propane does not degrade over time, allowing for extended storage without compromising performance. This characteristic is crucial for emergency preparedness, ensuring fuel readiness when needed most. Furthermore, propane’s combustion produces fewer emissions than gasoline, minimizing environmental impact. For instance, during extended power outages, a readily available propane supply can power essential appliances, highlighting the practical significance of this fuel choice.
Propane’s energy density, measured in BTU per gallon, plays a critical role in determining a generator’s runtime. A higher energy density translates to longer operation on a given volume of fuel. This attribute is particularly important during extended outages when refueling may be challenging or impossible. Propane’s relatively high energy density contributes to the extended runtimes of these generators, enhancing their value as reliable backup power sources. Consider a scenario where a homeowner relies on a propane-fueled generator during a multi-day power outage. Propane’s energy density allows the generator to operate for extended periods, ensuring critical appliances remain functional.
The utilization of propane as a fuel source directly influences the overall design and operation of portable generators. Propane’s distinct properties necessitate specific engine components and fuel delivery systems. These specialized components are engineered to optimize propane combustion efficiency and ensure safe operation. Understanding this connection between fuel type and generator design provides homeowners with valuable insights for selecting and maintaining their units. It reinforces the importance of using only propane fuel in designated generators and adhering to manufacturer guidelines for optimal performance and safety. Challenges associated with propane fuel, such as availability during widespread emergencies, should also be considered in preparedness planning. This understanding helps homeowners make informed decisions regarding fuel storage and contingency plans.
3. Power Output
Power output, measured in watts or kilowatts, represents a critical specification for portable propane generators, directly determining the number and types of appliances they can power. Understanding power output is fundamental for selecting a generator that effectively meets specific needs, whether for backup power during outages or powering devices off-grid. A mismatch between generator output and appliance requirements can lead to overloads, potentially damaging both the generator and connected devices. Careful consideration of power output is therefore paramount for safe and efficient operation.
- Starting Watts vs. Running Watts
Starting watts refer to the surge of power required to initially start motor-driven appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners. Running watts represent the power needed to sustain appliance operation after starting. Starting watts typically exceed running watts. A generator must accommodate both to prevent overloads. For example, a refrigerator might require 1,500 starting watts and 700 running watts. Selecting a generator with sufficient starting wattage is crucial for operating such appliances.
- Calculating Total Power Requirements
Accurately calculating the combined power requirements of all intended appliances is essential for determining the appropriate generator size. This involves summing the running watts of each appliance and factoring in the highest starting wattage. Online calculators and consultation with electricians can assist with accurate load assessments. For instance, a homeowner intending to power a refrigerator, a sump pump, and several lights would need to calculate the combined running watts of these appliances and add the highest starting wattage among them to determine the required generator output.
- Overload Protection
Generators typically incorporate overload protection mechanisms, such as circuit breakers, to prevent damage from excessive power demands. These safety features automatically interrupt the power supply when the load exceeds the generator’s capacity. Understanding the generator’s overload protection capabilities is vital for safe operation. Regularly checking and resetting circuit breakers, as needed, ensures proper function.
- Power Output and Fuel Consumption
Power output directly influences fuel consumption. Higher power output generally correlates with higher fuel consumption rates. This relationship underscores the importance of selecting a generator with adequate power output while avoiding unnecessarily large units that consume excessive fuel. Understanding this interplay allows users to optimize runtime and minimize fuel costs. For example, a homeowner might choose a slightly larger generator than minimally required to accommodate potential future power needs, but avoid excessively large units to manage fuel consumption.
Matching power output to specific needs is fundamental for the effective use of portable propane generators. Careful consideration of starting and running watts, accurate load calculations, and understanding the generator’s overload protection ensure reliable and safe power delivery while optimizing fuel efficiency. This knowledge empowers consumers to select the most suitable generator for their specific backup power requirements.
4. Runtime
Runtime, representing the duration a generator can operate continuously on a single fuel source, constitutes a critical factor influencing the practicality of portable propane generators for home use. This duration directly impacts the generator’s ability to provide uninterrupted power during outages, making it a central consideration in generator selection and fuel management. Understanding the factors affecting runtime and strategies for maximizing it is essential for ensuring reliable backup power.
- Fuel Tank Capacity
The capacity of the propane tank directly influences runtime. Larger tanks hold more fuel, enabling longer operation before refueling. A 20-pound propane tank will typically provide a longer runtime than a smaller 5-pound tank. Choosing an appropriately sized tank is crucial for balancing portability and desired runtime. For example, during an extended outage, a larger tank capacity ensures continuous operation of essential appliances, reducing the frequency of refueling trips.
- Load Size and Power Output
The power demand placed on the generator directly affects runtime. Higher power consumption by connected appliances reduces the duration of operation on a given fuel supply. Operating a refrigerator and a few lights will consume less fuel and provide a longer runtime compared to powering an entire house. Understanding and managing the load is crucial for extending runtime. Prioritizing essential appliances during outages maximizes the available power.
- Generator Efficiency
The generator’s efficiency rating indicates how effectively it converts fuel into usable power. More efficient generators extract more power from the same amount of fuel, extending runtime. Inverter generators are generally more fuel-efficient than conventional generators. This efficiency translates into longer operating durations and reduced fuel costs. Investing in a more efficient generator, while potentially incurring a higher initial cost, often leads to long-term savings through reduced fuel consumption.
- External Factors
External factors such as ambient temperature can influence runtime. Extreme temperatures can affect engine performance and fuel consumption. Operating a generator in extremely cold or hot conditions can impact its efficiency and runtime. Taking these factors into account is important for accurate runtime estimations. Providing adequate ventilation and protecting the generator from extreme weather conditions helps maintain optimal performance.
Runtime is intrinsically linked to the practical value of portable propane generators for home use. Careful consideration of fuel tank capacity, load management, generator efficiency, and external factors empowers users to optimize runtime and ensure a reliable backup power supply during outages. Understanding these interconnected elements is vital for informed decision-making regarding generator selection and operation.
5. Safety Features
Safety features are paramount in portable propane generators designed for residential use. These features mitigate inherent risks associated with fuel combustion and electricity generation, safeguarding users and property. Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning, a significant hazard associated with incomplete combustion, is addressed through CO sensors and automatic shutoff mechanisms. These sensors detect elevated CO levels and trigger generator shutdown, preventing potential exposure. Similarly, low-oil shutdown features protect the engine from damage caused by insufficient lubrication, a common cause of generator failure. Overload protection, often implemented through circuit breakers, prevents damage from excessive electrical loads, safeguarding connected appliances and the generator itself. For instance, a CO sensor activating during operation within an enclosed space prevents potential harm to occupants, illustrating the practical significance of this safety feature.
The integration of these safety features directly impacts the generator’s design, operation, and overall cost. Incorporating advanced safety mechanisms typically increases manufacturing complexity and cost, but significantly enhances user safety and equipment longevity. For example, automatic voltage regulation, a feature that stabilizes voltage fluctuations, protects sensitive electronics from damage. This feature, while potentially increasing the generator’s initial cost, prevents costly repairs or replacements of connected devices. Understanding the connection between safety features, generator design, and cost empowers consumers to make informed purchasing decisions, balancing cost with essential safety considerations. Furthermore, the presence and proper functioning of these safety mechanisms influence maintenance procedures. Regular inspection and testing of safety features are crucial for ensuring ongoing protection. Neglecting these maintenance tasks can compromise safety and increase the risk of accidents.
Safe operation of propane generators necessitates user vigilance and adherence to safety guidelines. While integrated safety features provide crucial protection, user responsibility remains paramount. Operating the generator in a well-ventilated area, away from flammable materials, is essential. Regularly inspecting fuel lines for leaks and ensuring proper grounding further mitigate risks. Ignoring these precautions, even with advanced safety features, can lead to accidents and equipment damage. Understanding the limitations of safety features and adhering to recommended safety practices is essential for responsible generator operation. A comprehensive approach encompassing both inherent safety mechanisms and user diligence ensures the safe and effective utilization of these power sources in residential settings.
6. Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the reliable and safe operation of portable propane generators intended for home use. Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to decreased performance, increased fuel consumption, and potentially hazardous malfunctions. A well-maintained generator provides consistent power during outages, maximizing its lifespan and minimizing the risk of unexpected failures.
- Regular Oil Changes
Engine oil degrades over time, losing its lubricating properties. Regular oil changes, as specified in the manufacturer’s guidelines, are crucial for maintaining engine health and preventing premature wear. Using the recommended oil type and viscosity ensures optimal engine performance and longevity. For example, failing to change the oil regularly can lead to increased engine friction, reducing efficiency and potentially causing overheating or damage. Regular oil changes, therefore, directly impact the generator’s reliability and lifespan.
- Air Filter Maintenance
Clean air filters are essential for proper engine combustion. A clogged air filter restricts airflow, reducing engine efficiency and increasing fuel consumption. Regularly cleaning or replacing the air filter, according to manufacturer recommendations, ensures optimal airflow and maintains combustion efficiency. For example, a clogged air filter can lead to incomplete fuel combustion, resulting in increased emissions and reduced power output. Maintaining a clean air filter contributes to both efficient operation and environmental responsibility.
- Spark Plug Replacement
Spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mixture within the engine. Worn spark plugs can lead to misfires, reduced power output, and increased fuel consumption. Replacing spark plugs at the recommended intervals ensures reliable ignition and optimal engine performance. Using the correct spark plug type is essential for proper function. For instance, worn spark plugs can make it difficult to start the generator, especially in cold weather. Timely spark plug replacement contributes to reliable starting and consistent power delivery.
- Fuel System Inspection
Regular inspection of the fuel system, including the propane tank, fuel lines, and connections, is crucial for preventing leaks and ensuring safe operation. Checking for leaks and ensuring tight connections minimizes the risk of fire hazards. For example, a leaking propane connection can create a dangerous accumulation of flammable gas. Regular inspection and prompt repair of any leaks are paramount for safe generator operation. Storing propane tanks properly, in a well-ventilated area away from heat sources, further mitigates risks.
Consistent adherence to a comprehensive maintenance schedule is integral to maximizing the lifespan and ensuring the safe operation of portable propane generators used in residential settings. Regular maintenance not only enhances reliability and performance but also minimizes the risk of costly repairs and potential hazards. Understanding and implementing these maintenance procedures is essential for responsible generator ownership and ensures a reliable backup power source when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, operation, and maintenance of portable propane generators for residential applications.
Question 1: How is the appropriate generator size determined for specific household needs?
Determining the correct generator size requires calculating the total wattage required to run essential appliances. Sum the running watts of each appliance and factor in the highest starting wattage. Consulting an electrician can assist with accurate load assessments.
Question 2: What are the key safety considerations for operating a propane generator?
Operating a propane generator safely necessitates placement in a well-ventilated outdoor area, away from doors and windows. Regularly checking for leaks and ensuring proper grounding are also crucial safety practices.
Question 3: How frequently should maintenance tasks be performed on a propane generator?
Maintenance schedules vary depending on the generator model and usage frequency. Consulting the manufacturer’s guidelines provides specific maintenance intervals for tasks such as oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement.
Question 4: What are the advantages of using propane as a fuel source for home generators?
Propane offers several advantages as a generator fuel, including a longer shelf life compared to gasoline, cleaner combustion, and widespread availability. These characteristics make propane a practical and convenient fuel choice for residential generator applications.
Question 5: What are the typical runtimes of portable propane generators?
Generator runtime varies depending on factors such as fuel tank capacity, load size, and generator efficiency. Larger fuel tanks and lower power demands typically extend runtime. Manufacturer specifications provide estimated runtimes under various load conditions.
Question 6: Where should propane generators be placed during operation?
Placement outdoors, away from enclosed spaces, is crucial due to carbon monoxide emissions. A stable, level surface is essential to prevent tipping and spills. Maintaining adequate clearance around the generator for ventilation is also vital for safe operation.
Understanding these key aspects contributes to informed decisions and responsible generator operation. Consulting reputable resources and manufacturer guidelines provides further clarification and promotes safe and effective power generation.
The subsequent sections will delve into specific generator models and provide comparative analyses to aid selection.
Portable Propane Generators for Home Use
This exploration of portable propane generators for home use has highlighted their significance as reliable backup power sources during outages and for off-grid applications. Key aspects, including portability, fuel considerations, power output, runtime, safety features, and maintenance requirements, have been examined. Proper sizing, safe operation, and diligent maintenance are crucial for maximizing the benefits and ensuring longevity. Understanding these elements empowers homeowners to make informed decisions regarding generator selection and utilization.
Reliable access to electricity is fundamental in modern life. Portable propane generators offer a practical solution for maintaining essential services during power disruptions. Careful consideration of the factors presented herein ensures effective utilization of these devices, contributing to preparedness and resilience in the face of power outages. Investing in a properly sized and maintained portable propane generator provides peace of mind and safeguards against the disruptions of unforeseen power loss.