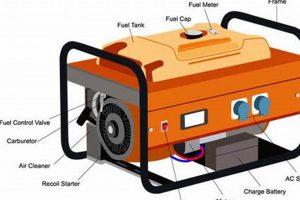
The financial outlay for a mobile electricity-producing unit designed for residential use encompasses not only the initial purchase price but also potential long-term expenses such as fuel, maintenance, and occasional repairs. For example, a smaller unit capable of powering essential appliances might have a lower upfront price than a larger, whole-house solution. However, the operational costs will vary depending on fuel type, usage frequency, and required maintenance.
Understanding the full financial commitment associated with acquiring and operating such a unit is crucial for homeowners. This knowledge allows for informed decisions, accurate budgeting, and effective comparisons between different models and fuel types. Historically, these units have transitioned from niche emergency backups to increasingly popular solutions for power outages, recreational activities, and even off-grid living, driving a wider range of options and price points in the market.
This discussion will further explore factors influencing pricing, including power output, fuel type, features, and brand reputation. It will also address strategies for minimizing expenses, such as proper maintenance and efficient usage habits. Finally, available financing options and potential return on investment will be examined.
Tips for Managing Expenditures on Mobile Residential Power Generation
Careful consideration of various factors can significantly impact the overall financial commitment associated with acquiring and operating a mobile residential power source.
Tip 1: Evaluate Power Needs: Accurately assessing power requirements prevents overspending on unnecessarily large units. Calculate the wattage of essential appliances and devices to determine the appropriate generator size.
Tip 2: Compare Fuel Types: Gasoline, propane, and diesel each offer distinct advantages and disadvantages regarding cost, availability, and storage. Consider long-term fuel expenses and convenience factors.
Tip 3: Research Brands and Models: Reputable manufacturers often offer higher quality and longer lifespans, potentially reducing long-term repair costs. Thorough research and comparison shopping are essential.
Tip 4: Factor in Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance, including oil changes and filter replacements, is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Budget for these recurring expenses to avoid unexpected costs.
Tip 5: Consider Installation and Setup: Professional installation may be necessary for safe and proper connection to home circuits. Factor these potential costs into the overall budget.
Tip 6: Explore Financing Options: Various financing options, such as loans or payment plans, can make the initial purchase more manageable. Compare interest rates and terms to find the most suitable option.
Tip 7: Prioritize Efficiency Features: Investing in models with fuel-saving features, such as inverter technology or automatic idle control, can reduce long-term operational expenses.
By carefully considering these factors, consumers can make informed decisions that minimize expenses while ensuring reliable backup power. These strategies contribute to a more cost-effective and sustainable approach to residential power generation.
This information provides a solid foundation for making informed decisions about acquiring and operating a mobile residential power source. The concluding section will summarize key takeaways and reinforce the importance of careful planning and informed decision-making.
1. Initial Price
The initial price represents a significant portion of the overall cost associated with portable home generators. Understanding the factors influencing this upfront expense is crucial for informed decision-making and effective budgeting. This section explores key components contributing to the initial price and their implications for long-term ownership.
- Generator Size and Power Output:
Larger generators capable of powering more appliances and devices command higher prices. A small generator suitable for essential circuits might cost significantly less than a whole-house unit. For example, a 2,000-watt generator may cost several hundred dollars, while a 10,000-watt generator could cost several thousand. This correlation between power output and price reflects the increased material and manufacturing complexity associated with higher wattage units.
- Fuel Type:
The choice of fuel (gasoline, propane, diesel, or inverter) impacts the initial price. Dual-fuel or tri-fuel generators, offering flexibility in fuel sources, often come with a higher price tag compared to single-fuel models. This price difference stems from the more complex engineering required to accommodate multiple fuel types.
- Features and Technology:
Advanced features such as electric starters, automatic transfer switches, and fuel gauges contribute to the initial cost. Generators equipped with inverter technology, offering cleaner and more stable power, typically come at a premium compared to conventional generators. These price variations reflect the added value and technological advancements incorporated into these features.
- Brand Reputation and Warranty:
Established brands known for reliability and durability often command higher prices. A comprehensive warranty can also influence the initial cost, providing a sense of security and long-term value. This price difference reflects the manufacturer’s reputation and the added assurance provided by warranty coverage.
By carefully considering these factors influencing the initial price, consumers can effectively evaluate the cost-benefit trade-offs of various models and make informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific needs and budget. Understanding the interplay of these elements within the broader context of portable generator costs empowers consumers to make sound investments that ensure reliable backup power without unnecessary financial strain.
2. Fuel Expenses
Fuel expenses represent a significant recurring cost associated with operating a portable home generator. Understanding the factors influencing these expenses is crucial for accurate budgeting and efficient resource management. This section explores key facets of fuel consumption and their impact on the overall cost of portable generator ownership.
- Fuel Type and Cost:
The choice of fuel significantly impacts operational expenses. Gasoline, propane, and diesel each have distinct price points that fluctuate over time. Propane, while often more expensive per unit, offers longer shelf life and cleaner burning. Diesel, known for its efficiency, can be more costly than gasoline. Tracking fuel price trends and considering long-term cost projections are essential for informed decision-making.
- Generator Size and Load:
Larger generators consume more fuel, particularly under heavy loads. Operating a generator at full capacity will result in higher fuel consumption than running it at a lower output. Matching generator size to actual power needs optimizes fuel efficiency and minimizes expenses. For example, a 10,000-watt generator powering a few small appliances will consume significantly less fuel than when powering an entire house during an outage.
- Runtime and Usage Frequency:
Extended runtimes and frequent usage directly correlate with higher fuel expenses. Infrequent usage for short durations minimizes fuel consumption. Calculating estimated runtimes based on anticipated power outage durations or planned usage helps in accurate budgeting. A generator used weekly for recreational purposes will incur higher fuel costs compared to one used only during emergencies.
- Fuel Efficiency and Technology:
Inverter generators generally offer better fuel efficiency than conventional generators due to their variable engine speed. This technology adjusts engine output to match the load, conserving fuel during periods of lower power demand. Investing in fuel-efficient models can lead to long-term cost savings, particularly for frequent users. While potentially having a higher initial cost, the reduced fuel consumption over time may offer a significant return on investment.
Careful consideration of these fuel-related factors provides a more complete understanding of the long-term operating costs associated with portable home generators. Integrating these insights into the overall cost assessment enables consumers to make informed decisions, optimize fuel efficiency, and effectively manage the financial aspects of generator ownership. Ultimately, understanding fuel expenses contributes to a more comprehensive and realistic evaluation of the true cost of portable power generation.
3. Maintenance Costs
Maintenance costs represent a crucial aspect of portable home generator ownership, directly impacting the long-term financial commitment. Overlooking these recurring expenses can lead to unexpected financial burdens and potentially compromise the generator’s performance and lifespan. This section explores key maintenance requirements and their implications for the overall cost of owning a portable generator.
- Regular Oil Changes:
Oil changes are essential for maintaining engine health and ensuring optimal performance. Frequency depends on the generator model and usage intensity. Neglecting oil changes can lead to premature engine wear and costly repairs. The cost of oil and filters contributes to recurring maintenance expenses. For example, frequent users might require oil changes every 50 hours of operation, while occasional users might require them annually.
- Air Filter Replacement:
Clean air filters are vital for proper engine combustion and efficiency. Clogged filters reduce airflow, leading to increased fuel consumption and potential engine damage. Replacement frequency depends on operating conditions and air quality. Replacing air filters regularly minimizes performance issues and extends the generator’s lifespan.
- Spark Plug Maintenance:
Spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine. Worn or fouled spark plugs can cause starting problems, rough running, and reduced efficiency. Periodic inspection and replacement are necessary for reliable operation. Spark plug replacement is a relatively inexpensive maintenance task but essential for preventing more significant engine problems.
- Fuel System Maintenance:
Fuel system maintenance includes cleaning or replacing fuel filters and checking for leaks or blockages. Stale fuel can cause gum and varnish buildup, leading to performance issues. Proper fuel storage and periodic fuel system checks help prevent costly repairs and maintain reliable operation. For instance, using fuel stabilizers can extend the shelf life of gasoline and prevent fuel-related problems.
By acknowledging and addressing these maintenance requirements, generator owners can mitigate the risk of unexpected breakdowns and costly repairs. Budgeting for these recurring expenses provides a more realistic assessment of the total cost of portable generator ownership. Ultimately, a proactive approach to maintenance contributes to the generator’s longevity, reliability, and overall cost-effectiveness.
4. Installation Fees
Installation fees contribute significantly to the overall cost of portable home generator ownership. While often overlooked in initial budget estimations, these expenses can represent a substantial investment depending on the complexity of the installation. A basic installation involving a simple transfer switch and connection to existing circuits might cost a few hundred dollars. However, more complex installations requiring new wiring, dedicated circuits, or integration with existing home automation systems can escalate costs into the thousands. For example, connecting a generator to a detached garage or shed would typically incur higher installation fees due to the additional wiring and labor required.
Several factors influence installation costs. Local electrician rates vary based on region and demand. The distance between the generator’s location and the main electrical panel impacts wiring costs. The complexity of the electrical system and the need for additional components, such as subpanels or transfer switches, further contribute to the overall expense. For instance, installing a whole-house automatic transfer switch typically costs more than a manual transfer switch for a few essential circuits. Understanding these contributing factors allows for more accurate budgeting and informed decision-making.
Careful consideration of installation requirements and associated costs is crucial for accurate cost projections. Obtaining multiple quotes from qualified electricians ensures competitive pricing and transparency. Incorporating installation fees into the overall budget avoids unexpected financial burdens and provides a more realistic assessment of the total investment. A comprehensive understanding of installation costs empowers consumers to make informed choices and manage the financial aspects of portable generator ownership effectively. Neglecting this critical cost component can lead to inaccurate budgeting and potentially compromise the long-term feasibility of generator ownership.
5. Running Costs
Running costs represent a critical ongoing financial commitment intrinsically linked to portable home generator ownership. These expenses, often overlooked during initial purchase considerations, significantly impact the long-term affordability and overall value proposition of a portable generator. A comprehensive understanding of these recurring costs is essential for informed decision-making and effective budget management.
Several factors contribute to running costs. Fuel consumption, heavily influenced by generator size, load, and runtime, forms a major component. Regular maintenance, including oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug servicing, adds to recurring expenses. Occasional repairs, while unpredictable, should be factored into long-term cost projections. For example, a homeowner relying heavily on a portable generator during frequent power outages will experience significantly higher running costs compared to someone using a generator for occasional recreational purposes. Similarly, operating a large generator at full capacity to power multiple appliances will consume more fuel and potentially accelerate component wear, leading to increased maintenance and repair expenses.
Accurate estimation of running costs requires careful consideration of anticipated usage patterns, fuel prices, and maintenance schedules. Neglecting these factors can lead to unexpected financial strain and potentially compromise the generator’s long-term viability. A comprehensive understanding of running costs empowers consumers to make informed decisions about generator sizing, fuel type selection, and maintenance practices. This proactive approach ensures cost-effective operation and maximizes the return on investment. Ultimately, recognizing the significance of running costs as an integral component of portable home generator cost ensures responsible ownership and facilitates informed financial planning.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the financial aspects of portable generator ownership, providing clarity and promoting informed decision-making.
Question 1: What is the typical price range for portable generators?
Pricing varies significantly based on power output, features, and brand. Small generators (around 2,000 watts) can start around a few hundred dollars, while larger units (7,000 watts and above) can cost several thousand dollars. Investing in higher wattage, advanced features, or reputable brands typically increases the upfront cost.
Question 2: How do fuel costs factor into the overall expense?
Fuel expenses depend on fuel type, generator size, and usage frequency. Gasoline generators are typically less expensive upfront but may incur higher running costs due to fuel price fluctuations. Propane offers longer storage life but can be more costly. Diesel generators are often more fuel-efficient but come with a higher initial price tag.
Question 3: What are the typical maintenance expenses associated with owning a portable generator?
Regular maintenance includes oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug servicing. These costs depend on the generator model and usage frequency. Neglecting maintenance can lead to more expensive repairs down the line, emphasizing the importance of preventative care.
Question 4: Are there any hidden costs associated with generator ownership?
Potential hidden costs include installation fees, extension cords, and storage solutions. Professional installation, while sometimes optional, is often recommended for safety and optimal performance. Adequate storage and weather protection are essential for preserving the generator’s lifespan.
Question 5: How can one minimize the overall cost of owning a portable generator?
Cost minimization strategies include accurate power needs assessment, fuel-efficient operation, regular maintenance, and proper storage. Investing in a slightly larger generator than immediately necessary can accommodate future power needs and avoid premature replacement. Fuel stabilizers can extend fuel shelf life, reducing waste.
Question 6: What are the long-term cost implications of owning a portable generator?
Long-term costs include fuel expenses, maintenance, potential repairs, and eventual replacement. A comprehensive understanding of these costs, alongside initial purchase price, provides a more realistic assessment of the total financial commitment. Proper maintenance and efficient usage can significantly extend the generator’s lifespan and minimize long-term expenses.
Careful consideration of these frequently asked questions equips potential buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions and effectively manage the financial aspects of portable generator ownership.
The following section will delve into specific examples of various portable generator models and their associated costs, offering practical illustrations of the concepts discussed.
Portable Home Generator Cost
Careful evaluation of portable home generator cost reveals a multifaceted financial commitment extending beyond the initial purchase price. Factors such as fuel type, power output, anticipated usage, and required maintenance significantly influence long-term expenses. A comprehensive cost analysis, encompassing upfront investment, recurring operational costs, and potential repairs, provides a realistic basis for informed decision-making. Strategies for mitigating expenses include optimizing generator size, adopting fuel-efficient practices, and adhering to recommended maintenance schedules.
Prudent financial planning and thorough research empower consumers to navigate the complexities of portable home generator cost. Investing in a reliable power source requires a holistic understanding of both immediate and long-term financial implications. Informed decision-making ensures not only reliable backup power but also responsible resource management and sustainable cost control. Preparedness requires a balanced approach, weighing the benefits of power security against the financial realities of generator ownership.