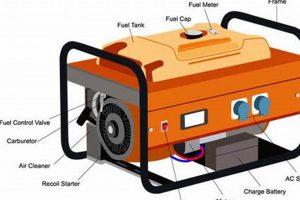
Portable generators provide backup power during outages by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. A typical gasoline-powered unit contains an internal combustion engine coupled to an alternator. The engine burns fuel to drive the alternator’s rotor, creating a rotating magnetic field. This field induces voltage in the stator windings, producing alternating current (AC) electricity. This electricity then powers connected appliances and devices through outlets on the generator’s control panel.
Access to reliable electricity is essential for modern life. Power outages, caused by severe weather, grid failures, or other disruptions, can severely impact homes and businesses. Having a backup power solution ensures critical systems like refrigerators, heating, and medical equipment remain operational. The development of portable generators has offered a relatively accessible and convenient way to mitigate the risks associated with power disruptions, enabling increased resilience and peace of mind.
Understanding the functionality of portable generators involves examining the roles of key components such as the engine, alternator, fuel system, and control panel. Additionally, topics like generator sizing, safety procedures, and maintenance requirements are essential considerations for effective and safe operation.
Operating Portable Generators Safely and Effectively
Proper operation ensures both safety and the longevity of a portable generator. Adhering to recommended guidelines is essential.
Tip 1: Calculate Power Requirements: Determine the wattage needed to run essential appliances. Generator capacity should exceed the combined wattage of intended devices.
Tip 2: Proper Ventilation: Operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from windows and doors. Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious risk.
Tip 3: Grounding: Ground the generator according to manufacturer instructions to prevent electrical shock.
Tip 4: Dry Operation: Protect the generator from rain and moisture. Use a canopy or other suitable cover if necessary.
Tip 5: Fuel Safety: Refuel only when the generator is cool and turned off. Store fuel in approved containers away from heat sources.
Tip 6: Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Tip 7: Load Management: Avoid overloading the generator. Prioritize essential appliances and add loads incrementally.
Tip 8: Professional Installation (for Standby Generators): While portable generators offer plug-and-play convenience, permanently installed standby units require professional installation for safe connection to the home’s electrical system.
Adhering to these guidelines promotes safe and efficient generator operation, maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential risks.
By understanding these crucial aspects of portable generator usage, consumers can make informed decisions and utilize this technology responsibly.
1. Engine
The engine forms the heart of a portable generator, serving as the primary source of mechanical energy. Internal combustion engines, typically gasoline-powered, are commonly used. The engine’s operation follows a cyclical process: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust. Fuel and air are drawn into the cylinder (intake), compressed by the piston (compression), ignited by the spark plug (combustion), and the resulting exhaust gases are expelled (exhaust). This controlled combustion generates rotational force applied to the alternator.
The engine’s power output directly influences the generator’s capacity. A higher horsepower engine can drive a larger alternator, producing more electrical power. Engine speed, typically regulated to maintain a consistent 60 Hz frequency for AC power, is crucial for stable electrical output. For instance, a generator designed to provide 5,000 watts will necessitate a sufficiently powerful engine to sustain that electrical load. Different engine designs, such as single-cylinder or twin-cylinder, influence factors like fuel efficiency, noise levels, and overall lifespan.
Proper engine maintenance is essential for reliable generator performance. Regular oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacements are vital. Neglecting these maintenance tasks can lead to reduced efficiency, increased fuel consumption, and potential engine damage. Understanding the engine’s function within the broader context of portable generator operation allows for effective troubleshooting and ensures reliable power delivery during outages.
2. Alternator
The alternator is the component responsible for converting the engine’s mechanical energy into electrical energy. This process relies on the principles of electromagnetic induction. The alternator consists of a stationary stator and a rotating rotor. The rotor, driven by the engine, contains a magnetic field. As the rotor spins, the magnetic field interacts with the stator’s windings, inducing an alternating current (AC) voltage. This voltage is the source of electrical power provided by the generator.
The alternator’s output is characterized by voltage and frequency. Voltage, measured in volts, represents the electrical potential difference. Frequency, measured in Hertz (Hz), denotes the number of cycles per second of the alternating current. Most household appliances in North America require a 60 Hz frequency. The alternator’s design and the engine speed are carefully regulated to maintain this frequency, ensuring compatibility with connected devices. For instance, the alternator in a 5,000-watt generator will be designed to produce a voltage of 120/240 volts and a frequency of 60 Hz to power common household appliances. Different alternator designs may incorporate features like voltage regulation to maintain consistent output under varying loads.
The alternator’s efficiency directly impacts the generator’s overall performance. Factors influencing alternator efficiency include the design of the windings, the strength of the magnetic field, and the quality of the materials used. A high-efficiency alternator minimizes energy losses during the conversion process, leading to better fuel efficiency and reduced operating costs. Understanding the alternator’s function as the core of electrical generation in a portable generator is crucial for troubleshooting, maintenance, and selecting an appropriate generator for specific power needs.
3. Fuel System
The fuel system plays a critical role in the operation of a portable generator, directly impacting its ability to produce power. This system ensures a consistent supply of fuel to the engine, enabling sustained operation. Several key components comprise the fuel system, including the fuel tank, fuel lines, fuel filter, fuel pump (for some models), carburetor or fuel injector, and the air filter. These components work together to deliver the correct air-fuel mixture to the engine’s combustion chamber. The fuel system’s design and capacity influence the generator’s runtime, a crucial factor determining how long the generator can operate on a single tank of fuel. For example, a larger fuel tank allows for extended operation without refueling, while a smaller tank requires more frequent refills. Fuel type is another significant consideration, with common options including gasoline, propane, and diesel. Each fuel type has distinct characteristics impacting the generator’s performance, maintenance requirements, and environmental impact.
The type of fuel system employed depends on the engine design and fuel type. Gasoline-powered generators commonly utilize a carburetor to mix air and fuel in the appropriate ratio for combustion. Propane-powered generators, on the other hand, utilize a regulator to control the flow of propane to the engine. Diesel-powered generators often employ fuel injection systems for precise fuel delivery. The fuel filter is a crucial component that removes impurities from the fuel, preventing clogs and ensuring smooth engine operation. Regular maintenance, such as replacing the fuel filter and checking for fuel leaks, is essential for reliable and safe operation. Neglecting fuel system maintenance can lead to performance issues, including starting difficulties, reduced power output, and potential engine damage.
Understanding the fuel system’s function is essential for effectively operating and maintaining a portable generator. Proper fuel management, including selecting the correct fuel type and adhering to recommended storage and handling procedures, is crucial for safety and optimal generator performance. For instance, using stale or contaminated fuel can lead to engine problems and reduced generator lifespan. Careful consideration of the fuel system’s design and requirements ensures reliable power generation during outages and contributes to the generator’s overall longevity. Addressing potential fuel system issues proactively, such as clogged fuel lines or a faulty fuel pump, minimizes downtime and ensures the generator remains a reliable power source when needed.
4. Power Outlets
Power outlets represent the crucial interface between a portable generator and the devices it powers, forming the final link in the energy conversion chain. These outlets provide the connection points for appliances and electronics, delivering the generated electricity to where it’s needed. The number and type of outlets available on a generator directly influence its versatility and ability to power multiple devices simultaneously. Different outlet types accommodate various plug configurations, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of equipment. For instance, a generator might offer standard 120-volt outlets for common household appliances, along with a dedicated 240-volt outlet for heavier-duty equipment like well pumps or air conditioners. The placement and configuration of these outlets are designed for safe and convenient access, minimizing the risk of accidental contact or damage. Understanding the power outlet configuration is crucial for selecting the appropriate generator to meet specific power requirements during an outage. For example, a homeowner needing to power a refrigerator, a sump pump, and several lights would require a generator with enough outlets and the correct voltage and amperage ratings to handle the combined load.
The relationship between power outlets and overall generator functionality is symbiotic. The generator’s internal components work in concert to produce the electricity, but the power outlets are the essential conduits for delivering that power to external devices. The quality and construction of these outlets are critical for safety and reliable performance. Durable, weather-resistant outlets are essential for protecting against electrical hazards, especially in outdoor environments. Generators intended for use in construction or industrial settings may feature specialized outlets designed for higher voltage or amperage demands. Understanding the power outlet specifications, including voltage, amperage, and wattage ratings, helps users avoid overloading the generator or connecting incompatible devices, which can damage both the generator and the connected equipment. Consider the scenario of a homeowner using a generator to power sensitive electronics during a power outage. Utilizing a generator with surge-protected outlets adds a layer of protection against voltage fluctuations, safeguarding valuable equipment from damage.
Safe and effective utilization of a portable generator’s power outlets is paramount. Overloading outlets can lead to overheating, posing a fire hazard. Properly distributing loads across available outlets and prioritizing essential appliances helps prevent overload situations. Using extension cords safely and appropriately is also crucial. Overlong or improperly rated extension cords can cause voltage drops, reducing appliance efficiency and potentially causing damage. Understanding the limitations and capabilities of the power outlets on a portable generator ensures safe and reliable operation, maximizing its utility during power disruptions. This knowledge empowers users to make informed decisions regarding appliance usage, load management, and overall power distribution, ensuring efficient and safe power delivery during critical situations.
5. Control Panel
The control panel serves as the central command center for a portable generator, bridging the gap between the generator’s internal workings and the user’s control over its operation. This interface houses essential controls and indicators that govern various aspects of the generator’s functionality, playing a crucial role in safe and efficient power delivery. Components typically found on the control panel include the start/stop switch, circuit breakers, voltage meter, and various indicator lights. These elements provide crucial feedback on the generator’s status, alerting users to potential issues or overload conditions. The control panel’s layout and functionality can vary depending on the generator’s size and features. For instance, a basic portable generator might offer a simple on/off switch and a few circuit breakers, while a more sophisticated model could include features like an automatic voltage regulator (AVR), a digital display showing output voltage and frequency, and GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) protected outlets. The interaction between the control panel and the generator’s internal systems illustrates the cause-and-effect relationship between user input and generator output. Starting the generator, engaging the choke, and monitoring output voltage are all managed through the control panel, directly influencing the generator’s operational state.
The control panel’s importance is underscored by its role in safeguarding both the generator and connected devices. Circuit breakers integrated into the control panel provide crucial overcurrent protection. If a connected appliance draws excessive current, the corresponding circuit breaker trips, interrupting the circuit and preventing damage to the generator and the appliance. This protective mechanism highlights the control panel’s practical significance in real-life scenarios. Imagine a homeowner connecting a power-hungry appliance like a space heater to a portable generator. If the space heater draws more current than the generator’s circuit is rated for, the circuit breaker on the control panel will trip, preventing potential overheating or damage to the generator’s windings. Voltage regulation, often managed through the control panel, ensures a stable output voltage, protecting sensitive electronic devices from fluctuations that could cause damage. Furthermore, indicator lights on the control panel, such as low oil or overload warnings, provide valuable diagnostic information, allowing users to address potential issues proactively and prevent more serious problems. Understanding these indicators enables effective troubleshooting and preventative maintenance.
Effective operation hinges on understanding the control panel’s functionality. Correctly interpreting indicator lights, utilizing the start/stop controls appropriately, and managing circuit breakers are essential for safe and efficient power delivery. Misinterpreting a low-fuel warning, for instance, could lead to the generator running out of fuel mid-operation, potentially damaging connected appliances or causing data loss if a computer is being powered. Conversely, understanding how to reset a tripped circuit breaker allows users to restore power quickly and safely after addressing the underlying overload issue. The control panel represents the critical junction between user interaction and generator performance, and proficiency in its operation empowers users to utilize their portable generators safely and effectively during power outages. Mastering the control panel’s functions transforms the generator from a complex piece of machinery into a reliable and user-friendly power source, providing peace of mind and essential power during critical situations.
Frequently Asked Questions about Portable Generators
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the operation and functionality of portable home generators.
Question 1: How is the size of a portable generator determined?
Generator size is determined by wattage, representing the amount of power it can produce. Calculating the wattage requirements of intended appliances is crucial for selecting an appropriately sized generator.
Question 2: What safety precautions are essential when operating a portable generator?
Operating generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas away from structures is crucial to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. Proper grounding and protection from moisture are also essential safety measures.
Question 3: What type of fuel do portable generators use?
Common fuel types include gasoline, propane, and diesel. Each fuel has advantages and disadvantages regarding cost, availability, and storage requirements.
Question 4: How long can a portable generator run continuously?
Runtime depends on the generator’s fuel capacity and the load. Larger fuel tanks and lower power consumption contribute to longer runtimes.
Question 5: What maintenance is required for a portable generator?
Regular maintenance, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement, is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific maintenance intervals.
Question 6: Can a portable generator be connected directly to a home’s electrical system?
Direct connection requires a transfer switch installed by a qualified electrician. Improper connection can be dangerous and may damage appliances and the generator. Never connect a generator directly to a wall outlet.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of portable generator operation promotes safe and effective usage, ensuring reliable power during outages.
Further exploration of specific generator models and features can provide additional insights for informed decision-making.
Understanding How Portable Home Generators Work
This exploration has provided a comprehensive overview of the operational principles behind portable home generators. From the mechanical energy generated by the engine to the electrical output delivered through power outlets, the intricacies of each componentthe engine, alternator, fuel system, and control panelhave been detailed. Emphasis has been placed on the importance of proper sizing, safe operation, and regular maintenance for optimal performance and longevity. Understanding these interconnected systems empowers consumers to make informed decisions, ensuring reliable backup power during unforeseen outages.
Reliable access to electricity is paramount in modern society. Portable generators offer a practical solution for mitigating the disruptions caused by power outages, enabling households and businesses to maintain essential operations. Careful consideration of power needs, generator specifications, and adherence to safety guidelines ensures responsible and effective utilization of this valuable technology. Further research into specific models and features will enhance preparedness and facilitate informed decision-making when selecting a portable generator.