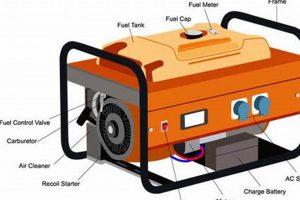
A compact, fuel-powered device capable of generating electricity for residential use is an invaluable asset for homeowners. These devices provide temporary power during outages caused by severe weather, grid failures, or planned maintenance. They can also power tools and appliances in locations without readily available electricity, such as construction sites or remote cabins.
Access to a backup power source offers significant peace of mind and can ensure the safety and comfort of a household during emergencies. Essential appliances like refrigerators, sump pumps, and heating systems can continue operating, preventing food spoilage, flooding, and discomfort. Historically, reliance on noisy and less efficient permanently-installed generators was commonplace. Advances in technology now offer more compact, quieter, and fuel-efficient portable options suitable for a wider range of needs. The evolution of these devices underscores the increasing demand for reliable, independent power solutions for residences.
This discussion will further explore various aspects of these power solutions, including their diverse types, proper operation, maintenance requirements, and key selection criteria.
Operational and Safety Guidance
Safe and efficient operation of portable generators requires careful consideration of several key factors. Adherence to these guidelines ensures optimal performance and mitigates potential risks.
Tip 1: Proper Ventilation is Crucial: Carbon monoxide poisoning presents a serious hazard. Generators must be operated exclusively in well-ventilated outdoor locations, far from windows, doors, and vents.
Tip 2: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Protection: GFCI outlets provide essential protection against electrical shock, especially in damp conditions. Ensure all connected devices are plugged into GFCI-protected outlets.
Tip 3: Fuel Handling Safety: Store fuel in approved containers and allow the generator to cool completely before refueling to prevent fires. Avoid spills and refuel in a well-ventilated area.
Tip 4: Regular Maintenance: Routine maintenance, including oil changes, spark plug replacements, and air filter cleaning, ensures optimal performance and extends the lifespan of the unit.
Tip 5: Appropriate Sizing: Select a generator with sufficient wattage to power the intended devices. Overloading a generator can damage both the unit and connected appliances.
Tip 6: Dry Operation Prevention: Running a generator without sufficient oil can cause severe engine damage. Check the oil level regularly and before each use.
Tip 7: Professional Installation for Transfer Switches: For safe and seamless integration with household wiring, engage a qualified electrician to install a transfer switch. Never directly connect a generator to a home’s electrical panel without a transfer switch.
Adhering to these guidelines promotes safe and effective operation, ensuring a reliable power supply during emergencies and other situations requiring independent power generation. Careful planning and responsible usage maximize the benefits and minimize potential risks associated with portable generator operation.
By understanding these essential operational and safety principles, users can confidently utilize portable generators as a reliable and valuable power solution.
1. Power Output
Power output, measured in watts, represents a critical specification for home portable generators. This figure directly dictates the number and type of appliances the generator can power simultaneously. A clear understanding of power requirements is essential for effective generator selection and utilization. Underestimating power needs can lead to overloaded circuits, potential damage to the generator and connected appliances, and ultimately, an insufficient power supply during critical situations. Conversely, an oversized generator adds unnecessary cost and fuel consumption. For instance, a refrigerator typically requires around 700 starting watts and 200 running watts, while a sump pump might need 1000 starting watts and 400 running watts. Attempting to operate both simultaneously on a generator with insufficient output can lead to system failure.
Careful calculation of total wattage requirements for essential appliances is therefore paramount. This involves considering both the running watts (power needed for continuous operation) and the starting watts (higher power surge required to initially start a motor-driven appliance). Online resources and generator manuals often provide wattage estimates for common household items. Prioritizing essential appliances and staggering their operation can also optimize power usage within the generator’s capacity. A generator with a higher power output offers greater flexibility in powering multiple devices concurrently but comes with increased cost, size, and fuel consumption. Balancing power needs with practicality and budget considerations is key.
Accurate power output assessment is crucial for successful portable generator implementation. Appropriate sizing prevents operational issues, maximizes efficiency, and ensures a reliable power supply when needed. Careful consideration of both running and starting wattage requirements for intended appliances allows for informed purchasing decisions and safe operation. This understanding ultimately contributes to the effectiveness of a home portable generator as a reliable backup power solution.
2. Fuel Type
Fuel type is a critical consideration when selecting a home portable generator, directly impacting its runtime, maintenance requirements, and environmental impact. Different fuel types offer varying advantages and disadvantages, necessitating careful evaluation based on individual needs and circumstances. The choice of fuel influences not only the generator’s operational characteristics but also its storage and handling requirements.
- Gasoline
Gasoline is a widely available and readily accessible fuel option, making it a popular choice for portable generators. Gasoline-powered generators typically offer a good balance between cost-effectiveness and performance. However, gasoline has a limited shelf life and can degrade over time, potentially causing carburetor issues. Proper storage and fuel stabilizer usage are essential for maintaining fuel quality and ensuring reliable generator starting. While offering convenience, gasoline generators produce emissions and contribute to air pollution.
- Propane
Propane offers a longer shelf life than gasoline, eliminating concerns about fuel degradation during storage. Propane-powered generators often run cleaner, producing fewer emissions. Propane’s availability in readily exchangeable tanks simplifies refueling. However, propane generators generally exhibit slightly lower power output compared to gasoline counterparts, and propane requires specific storage and handling procedures. The cost of propane can also fluctuate, impacting operational expenses.
- Diesel
Diesel generators are known for their durability, fuel efficiency, and long runtimes. Diesel fuel also has a longer shelf life than gasoline. These generators are often favored for heavy-duty applications and extended operation periods. However, diesel generators tend to be more expensive and produce higher noise levels. Cold weather operation can pose challenges due to fuel gelling, requiring additives or specific cold-weather blends. Diesel generators generally produce more emissions compared to propane but less than gasoline.
- Dual Fuel/Tri-Fuel
Dual-fuel and tri-fuel generators offer operational flexibility by utilizing multiple fuel sources, typically gasoline and propane, or gasoline, propane, and natural gas. This adaptability allows users to choose the most readily available or cost-effective fuel option. Switching between fuel sources often requires manual adjustment. These generators provide a valuable backup solution during fuel shortages or price fluctuations. Their complexity can lead to slightly higher maintenance requirements compared to single-fuel models.
The selection of fuel type significantly influences the practicality, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact of a home portable generator. Careful consideration of fuel availability, storage requirements, runtime expectations, and emission concerns is crucial for optimizing generator performance and ensuring its suitability for intended applications. Choosing the right fuel type ensures reliable power generation and aligns with individual operational needs and environmental priorities.
3. Portability
Portability is a defining characteristic of these generators, directly influencing their usability and suitability for various applications. While “home” suggests a fixed location, the portability aspect allows for versatile deployment in different scenarios, both within the property and beyond. Understanding the nuances of portability concerning weight, size, and maneuverability is crucial for selecting the right generator for specific needs.
- Weight and Size
The physical dimensions and weight of a generator significantly impact its portability. Smaller, lighter units are easier to transport and maneuver, making them ideal for recreational activities, camping, or powering tools at remote locations. Larger, heavier generators, while less portable, offer higher power output, suitable for backup power during extended outages. Weight distribution and integrated handles or wheels also play a role in ease of movement.
- Wheel Design and Handles
Incorporated features like never-flat wheels, ergonomic handles, and balanced weight distribution enhance portability, particularly for heavier units. Large, rugged wheels facilitate movement over uneven terrain, while strategically placed handles improve lifting and maneuvering. The presence and design of these features directly impact the ease with which the generator can be transported and positioned.
- Compactness for Storage
The generator’s physical footprint influences storage requirements. Compact designs minimize storage space, a critical consideration for homeowners with limited storage options. Foldable handles and compact frames optimize storage efficiency. A smaller footprint also simplifies transport and placement in various locations.
- Operational Location Flexibility
Portability extends beyond ease of transport to encompass operational location flexibility. The ability to easily move the generator allows for optimal placement to power specific appliances or equipment, whether indoors (with proper ventilation) during outages or outdoors for recreational activities or construction projects. This flexibility enhances the generator’s versatility and overall utility.
The portability of a home portable generator is integral to its versatility and suitability for diverse applications. Careful consideration of weight, size, maneuverability, and storage footprint is essential for selecting a generator that aligns with individual needs and intended usage scenarios. The balance between power output and portability ultimately determines the generator’s effectiveness as a versatile and reliable power solution, whether at home or on the go.
4. Safety Features
Safety features are paramount for home portable generators, mitigating inherent risks associated with fuel-powered electrical generation. These features are not mere additions but integral components ensuring user protection and preventing accidents. A generator, while providing essential power, presents potential hazards such as carbon monoxide poisoning, fire, and electric shock. Integrating robust safety mechanisms minimizes these risks, allowing for safe and reliable operation.
Consider carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning, an odorless, colorless, and potentially lethal gas. Generators produce CO as a byproduct of combustion. A critical safety feature, the CO shutoff sensor, detects elevated CO levels and automatically shuts down the generator, preventing potential exposure. Similarly, low-oil shutoff mechanisms protect the engine from damage by automatically stopping operation when oil levels fall below a critical threshold. Overload protection circuits prevent damage from excessive electrical loads by tripping a breaker, interrupting the power supply before damage occurs to the generator or connected appliances. A spark arrestor, often a legal requirement in certain areas, traps hot sparks emitted from the exhaust, preventing fires, especially in dry or wooded areas.
Understanding these safety features and their function is crucial for responsible generator operation. Regularly inspecting and testing these features ensures their proper functionality and provides early detection of potential issues. User awareness and adherence to safety guidelines, coupled with robust built-in safety mechanisms, contribute significantly to safe and reliable portable generator operation. Prioritizing safety through feature awareness and proactive maintenance ensures the benefits of portable power without compromising user well-being.
5. Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the reliable and long-lasting performance of a home portable generator. Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to decreased efficiency, unexpected failures, and a shortened lifespan. A well-maintained generator provides consistent power during critical situations, while a neglected unit can become a liability. This proactive approach not only preserves the generator’s functionality but also ensures safety by mitigating potential hazards associated with malfunctioning equipment.
Specific maintenance tasks vary depending on the generator model and fuel type, but some general principles apply universally. Regular oil changes, typically after a specified number of operating hours, are crucial for lubricating engine components and preventing premature wear. Air filter cleaning or replacement ensures optimal airflow for efficient combustion. Spark plug inspection and replacement, as needed, maintain consistent ignition and prevent performance issues. Fuel system maintenance, which might involve fuel stabilizer usage or carburetor cleaning, prevents fuel degradation and ensures reliable starting. For example, failing to change the oil can lead to increased engine wear, potentially resulting in costly repairs or even complete engine failure. Similarly, neglecting air filter maintenance can restrict airflow, reducing power output and increasing fuel consumption. Real-life scenarios underscore the importance of adherence to a consistent maintenance schedule.
Implementing a proactive maintenance schedule is a practical and necessary aspect of owning a home portable generator. This involves consulting the owner’s manual for model-specific recommendations, scheduling routine maintenance tasks, and maintaining records of completed service. This proactive approach not only safeguards the investment but also ensures the generator’s reliability when needed most. A well-maintained generator provides peace of mind, knowing that a reliable power source is available during emergencies or planned power outages. The connection between maintenance and generator performance is undeniable: consistent care translates directly into reliable operation and extended lifespan. Ultimately, the effort invested in routine maintenance yields significant returns in terms of performance, safety, and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common inquiries regarding home portable generators clarifies key aspects of their selection, operation, and maintenance. Understanding these points empowers consumers to make informed decisions and utilize these devices safely and effectively.
Question 1: What size generator is needed to power essential household appliances?
Generator sizing depends on the combined wattage requirements of the intended appliances. Calculating the running and starting wattage of essential devices like refrigerators, sump pumps, and furnaces is crucial for determining the appropriate generator size. Consulting appliance manuals or online resources provides wattage estimates. Overestimating slightly is advisable to accommodate unforeseen power needs.
Question 2: How long can a portable generator run continuously?
Runtime varies based on generator capacity, load, and fuel type. Larger fuel tanks and more efficient engines extend runtime. Operating at a lower load consumes less fuel, prolonging operation. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for runtime estimates under various load conditions.
Question 3: Where should a portable generator be operated?
Safe operation requires a well-ventilated outdoor location, far from windows, doors, and vents. Carbon monoxide poisoning presents a serious risk; never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces. Maintaining adequate clearance from combustible materials is also essential.
Question 4: What type of maintenance does a portable generator require?
Routine maintenance includes regular oil changes, air filter cleaning or replacement, spark plug inspection, and fuel system maintenance. The frequency of these tasks varies depending on the generator model and usage. Consulting the owner’s manual provides model-specific maintenance schedules.
Question 5: Is it safe to connect a portable generator directly to a home’s electrical panel?
Direct connection presents significant safety hazards and should never be attempted without a properly installed transfer switch. A transfer switch isolates the generator from the utility grid, preventing backfeeding, which can endanger utility workers and damage appliances. Professional installation of a transfer switch is recommended.
Question 6: What safety precautions are essential when using a portable generator?
Essential safety measures include operating the generator in a well-ventilated area, allowing it to cool before refueling, storing fuel safely, and using GFCI-protected outlets. Never touch the generator with wet hands or while standing in water. Familiarize oneself with the generator’s safety features and operating instructions before use.
Understanding these frequently asked questions promotes safe and effective generator operation. Prioritizing safety and adhering to manufacturer guidelines ensure reliable performance and mitigate potential risks.
Further exploration of specific generator types, features, and applications provides a more comprehensive understanding of these valuable power solutions.
Home Portable Generators
Home portable generators represent a significant advancement in residential power solutions, offering a reliable source of backup electricity during outages and enabling power access in remote locations. Careful consideration of factors such as power output, fuel type, portability, safety features, and maintenance requirements is crucial for selecting and operating these devices effectively. Understanding the operational principles, safety guidelines, and maintenance procedures ensures optimal performance and mitigates potential risks. The information presented herein provides a comprehensive overview of these crucial aspects, empowering informed decision-making and responsible generator utilization.
Reliable access to electricity is fundamental to modern life. Home portable generators offer a practical and increasingly vital solution for maintaining essential services during unforeseen disruptions. Investing in a suitable generator and adhering to proper operational and safety procedures provides peace of mind and ensures preparedness for a range of power-dependent scenarios. The evolving landscape of power generation continues to emphasize the importance of independent power solutions, and home portable generators stand as a crucial component of this evolving paradigm.