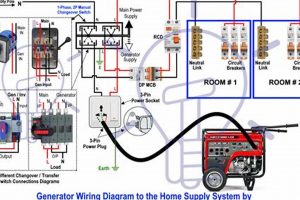
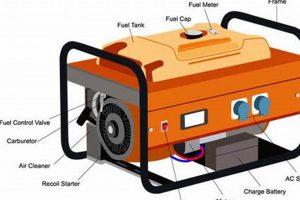
High-quality, easily transportable power sources designed for home inverters must offer a balance of power output, portability, and clean energy generation. These units typically employ inverter technology to produce stable alternating current (AC) electricity, making them suitable for sensitive electronics and appliances often powered by home inverters during outages or off-grid situations. A prime example would be a compact, gasoline-powered generator with a built-in inverter, capable of quietly powering a refrigerator, television, and several lights through a home’s inverter system.
Reliable backup power is increasingly critical for maintaining essential household functions during power disruptions. Compact, fuel-efficient generators coupled with home inverters offer a practical solution for homeowners. Historically, portable generators were often noisy and produced fluctuating power unsuitable for sensitive electronics. The advent of inverter technology addressed these limitations, enabling safe, stable power delivery for a wider range of devices. This evolution has made portable inverter generators an indispensable tool for ensuring uninterrupted operation of critical systems within a home environment.
Factors influencing generator selection include power requirements, runtime, fuel type, noise levels, and portability. Understanding these elements is essential for choosing the right generator to integrate seamlessly with a home inverter setup. Subsequent sections will delve into each of these considerations in detail, providing guidance on selecting the most appropriate generator for specific needs and circumstances. Additional topics will cover safety guidelines, maintenance procedures, and emerging trends in portable power generation.
Tips for Selecting a Portable Inverter Generator for Home Use
Choosing a suitable portable inverter generator requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with home inverter systems. The following tips provide guidance for navigating the selection process.
Tip 1: Calculate Power Requirements: Determine the wattage needs of the appliances intended for backup power. Sum the wattage ratings of essential devices, including refrigerators, lights, and electronics, to estimate the minimum generator capacity required. Consider starting wattage demands, which can be significantly higher than running wattage for certain appliances like refrigerators.
Tip 2: Evaluate Runtime Needs: Assess the desired duration of backup power during an outage. Generators offer varying runtimes depending on fuel capacity and load. Longer runtimes necessitate larger fuel tanks and potentially more efficient engines.
Tip 3: Consider Fuel Type and Availability: Common fuel options include gasoline, propane, and dual-fuel models. Factor in fuel availability and storage convenience when selecting a generator. Propane offers longer shelf life, while gasoline is more readily accessible.
Tip 4: Prioritize Low Noise Levels: Inverter generators are generally quieter than conventional generators, but noise levels still vary. Opt for models with lower decibel ratings, especially for residential use where noise pollution can be a concern.
Tip 5: Assess Portability Features: Consider the generator’s weight, size, and built-in handles or wheels for ease of transport and storage. Compact and lightweight models are more convenient for maneuvering and storing.
Tip 6: Ensure Inverter Compatibility: Verify that the generator’s inverter technology aligns with the home’s inverter system. Compatibility ensures stable power delivery and prevents damage to sensitive electronics.
Tip 7: Research Safety Features: Look for essential safety features such as overload protection, low-oil shutoff, and carbon monoxide detectors. These features protect both the generator and users from potential hazards.
By considering these factors, homeowners can select a portable inverter generator that effectively meets their backup power needs, integrates seamlessly with their home’s electrical system, and ensures reliable operation during outages.
This information provides a foundational understanding of key considerations for generator selection. The concluding section will summarize best practices and emphasize the importance of professional installation and maintenance.
1. Power Output
Power output, measured in watts, represents a critical factor when selecting a portable inverter generator for home use. This specification directly dictates the number and type of appliances the generator can power simultaneously. Understanding power output requirements is essential for matching the generator’s capabilities to the intended load.
- Running Watts vs. Starting Watts
Running watts refer to the continuous power required to operate an appliance, while starting watts represent the surge of power needed for initial startup. Motor-driven appliances, such as refrigerators and air conditioners, typically have higher starting wattage requirements. Generators must accommodate both running and starting wattage demands to prevent overload and ensure reliable operation. For example, a refrigerator might require 700 starting watts and 200 running watts. The chosen generator must handle the 700-watt surge while consistently supplying the 200 running watts.
- Total Wattage Calculation
Accurately calculating total wattage requirements involves summing the running watts of all intended appliances and factoring in the highest starting wattage of any single appliance. This calculation ensures that the generator can handle the combined load without being overwhelmed. Overloading a generator can lead to damage and potential safety hazards. For a home requiring 500 running watts for essential appliances and having a refrigerator with a 700-watt starting requirement, the minimum generator capacity needed would be 700 watts.
- Power Output and Generator Size
Power output directly correlates with generator size and weight. Higher power output generators are generally larger and heavier. Balancing power needs with portability considerations is essential, especially for users requiring easy transport and maneuverability. A smaller generator might suffice for powering essential lights and electronics, while a larger unit may be necessary for running power-hungry appliances during extended outages.
- Impact on Runtime
Power output influences generator runtime. Higher power output under heavy load reduces the generator’s running time on a single tank of fuel. Understanding the relationship between power output, load, and runtime helps users determine the appropriate fuel capacity and optimize generator usage during extended power outages. Running a high-wattage appliance continuously will deplete the fuel tank faster than powering a few low-wattage devices.
Matching the generator’s power output to the specific load requirements of a home inverter system is crucial for efficient and safe operation. Careful consideration of running watts, starting watts, total wattage calculations, and the impact on runtime ensures the selection of a generator that reliably meets power demands during outages while maintaining optimal fuel efficiency and portability.
2. Inverter Technology
Inverter technology plays a crucial role in distinguishing the best portable generators for home inverters. Unlike conventional generators that produce raw alternating current (AC) power, inverter generators utilize sophisticated electronics to create stable, clean electricity. This refined power output is essential for protecting sensitive electronic devices commonly powered by home inverters.
- Pure Sine Wave Output
Inverter generators generate a pure sine wave output, closely mimicking the stable power delivered by utility companies. This clean power is critical for sensitive electronics like laptops, televisions, and medical equipment, preventing damage and ensuring optimal performance. Conventional generators, conversely, often produce fluctuating power that can harm these devices. For example, a laptop powered by a conventional generator might experience glitches or even permanent damage, while an inverter generator ensures safe, reliable operation.
- Voltage Regulation
Precise voltage regulation is a hallmark of inverter generator technology. This feature ensures consistent voltage output regardless of the load, preventing fluctuations that could affect appliance performance or lifespan. Stable voltage is particularly important for devices with sensitive electronic components, protecting them from power surges or dips. A refrigerator, for example, benefits from stable voltage, ensuring consistent cooling and preventing compressor damage from voltage fluctuations.
- Fuel Efficiency
Inverter generators utilize variable engine speed technology, adjusting engine RPM based on the power demand. This dynamic adjustment significantly improves fuel efficiency compared to conventional generators, which typically run at a constant speed regardless of the load. This feature translates to longer runtimes on a single tank of fuel and reduced operating costs. When powering a small load, the inverter generator’s engine slows down, conserving fuel, while a conventional generator continues to operate at full speed, consuming more fuel.
- Reduced Noise Levels
The variable engine speed of inverter generators contributes to significantly lower noise levels. At lower loads, the engine runs quieter, minimizing noise pollution. This feature is especially valuable in residential settings where noise can be a concern. During nighttime operation with a minimal load, an inverter generator can operate much quieter than a conventional generator, minimizing disturbance to users and neighbors.
These facets of inverter technology collectively contribute to the superior performance and suitability of these generators for home inverter systems. The clean power output, precise voltage regulation, fuel efficiency, and reduced noise levels offer significant advantages over conventional generators, making them the preferred choice for powering sensitive electronics and appliances during outages or off-grid scenarios. Choosing a generator with robust inverter technology safeguards valuable equipment and ensures reliable power delivery when needed most.
3. Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency represents a critical consideration when selecting a portable inverter generator, particularly for home inverter systems. Efficient fuel consumption translates directly to longer runtimes, reduced operating costs, and minimized environmental impact. Understanding the factors influencing fuel efficiency empowers consumers to make informed decisions aligned with their power needs and budgetary constraints.
- Runtime and Fuel Capacity
Runtime, the duration a generator can operate on a single tank of fuel, is directly linked to fuel efficiency and tank capacity. Highly fuel-efficient generators maximize runtime, especially crucial during extended power outages. A larger fuel tank coupled with efficient fuel consumption ensures prolonged operation without frequent refueling. For instance, a generator with a larger tank and superior fuel efficiency can power essential appliances for significantly longer periods compared to a less efficient model with a smaller tank.
- Engine Technology and Load
Inverter generators typically employ advanced engine technologies that adjust engine speed based on the load. Under lighter loads, the engine operates at lower RPM, significantly reducing fuel consumption. This dynamic adjustment optimizes efficiency and extends runtime compared to conventional generators that run at a fixed speed regardless of power demand. A generator powering a few small electronics will consume less fuel due to the engine running at a lower speed, maximizing efficiency.
- Fuel Type and Cost
The choice of fuel type gasoline, propane, or dual-fuel impacts both operating costs and environmental considerations. Propane offers a longer shelf life and cleaner burning properties, while gasoline is generally more readily available. Dual-fuel models provide flexibility but may require careful consideration of fuel type availability and cost fluctuations in specific regions. Opting for propane might be advantageous for users prioritizing cleaner emissions and longer fuel storage, while readily available gasoline might be preferred for convenience.
- Eco-Mode and Power Management
Many inverter generators feature an “eco-mode” or similar power management functionality. This setting further optimizes fuel efficiency by dynamically adjusting engine speed based on real-time power demand. Eco-mode can significantly extend runtime, particularly under lighter loads, while minimizing fuel consumption and emissions. Activating eco-mode when powering a small load further reduces engine speed and fuel consumption, maximizing efficiency.
Prioritizing fuel efficiency in generator selection directly impacts operational costs, runtime, and environmental impact. By understanding the interplay between fuel capacity, engine technology, fuel type, and power management features, consumers can choose the best portable inverter generator for their home inverter system, ensuring reliable power delivery while minimizing fuel consumption and maximizing long-term value.
4. Noise Levels
Noise levels represent a crucial factor in evaluating portable inverter generators, especially for home use. Excessive noise can disrupt daily life and create neighborhood disturbances. Selecting a quiet generator enhances user comfort and maintains positive community relations. Understanding noise output and its implications is essential for choosing the best portable generator for a home inverter setup.
- Decibel Ratings and Human Perception
Generator noise is measured in decibels (dB). Lower dB ratings indicate quieter operation. Perceived loudness doubles approximately every 10 dB increase. A 60 dB generator is perceived as twice as loud as a 50 dB model. Choosing a generator with a low decibel rating minimizes noise intrusion and promotes a peaceful environment. For example, a generator operating at 50 dB might be comparable to normal conversation, while a 70 dB unit could be as loud as a vacuum cleaner.
- Inverter Technology and Noise Reduction
Inverter generators inherently produce less noise than conventional generators due to their variable engine speed. Under lighter loads, the engine operates at lower RPM, significantly reducing noise output. This feature makes inverter generators particularly suitable for residential applications where noise is a major concern. When powering a small load, an inverter generator’s engine runs slower and quieter, minimizing disturbance compared to a consistently loud conventional generator.
- Operational Modes and Noise Variation
Many inverter generators offer different operational modes that impact noise levels. “Eco-mode” or similar settings prioritize fuel efficiency by reducing engine speed, resulting in quieter operation. However, under heavy loads, the engine speed increases, leading to higher noise levels. Understanding these variations helps users manage noise output based on power demands. Running in eco-mode with a light load minimizes noise, while powering demanding appliances at full capacity will naturally increase noise output.
- Placement and Noise Mitigation
Strategic generator placement can further mitigate noise impact. Positioning the generator away from living areas and windows minimizes noise intrusion. Using sound-dampening materials or enclosures can further reduce noise propagation. Proper placement and noise mitigation strategies contribute to a quieter environment and minimize disturbances. Placing a generator behind a barrier or within a sound-dampening enclosure significantly reduces noise reaching living spaces.
Careful consideration of noise levels is essential for selecting the best portable generator for a home inverter. Lower decibel ratings, inherent noise reduction from inverter technology, operational modes, and strategic placement contribute to quieter operation and enhanced user experience. Prioritizing noise reduction ensures minimal disruption during power outages and fosters positive community relations.
5. Portability
Portability represents a defining characteristic of generators intended for home inverter systems, directly influencing their practicality and usability. The portability of a generator impacts ease of transport, storage, and deployment during power outages or off-grid scenarios. Weight, dimensions, and integrated features like handles and wheels contribute significantly to overall portability and user experience. A lightweight, compact generator with ergonomic handles is easily maneuvered and transported, even in challenging terrain or confined spaces. Conversely, a heavy, bulky unit can prove cumbersome and impractical, especially for users needing frequent relocation or limited storage space. Consider a homeowner needing to move a generator from a storage shed to a patio outlet during a power outage. A highly portable unit simplifies this process, while a heavy, unwieldy generator presents logistical challenges. This practical consideration underscores the importance of portability in generator selection.
The connection between portability and a “best” portable generator hinges on balancing power output with manageable size and weight. While larger generators typically offer higher power output, excessive weight and bulk can compromise portability. Users must carefully assess their power needs and weigh them against portability requirements. For example, a camping enthusiast might prioritize a lightweight, compact generator for easy transport, even if it means sacrificing some power output. Conversely, a homeowner requiring backup power for multiple appliances during extended outages might opt for a slightly larger, more powerful unit, accepting a trade-off in portability for increased power capacity. Understanding this balance is crucial for informed decision-making.
Ultimately, optimal portability enhances the practical value of a portable generator for home inverter systems. Ease of movement and storage contributes to user convenience and facilitates rapid deployment during emergencies. Careful consideration of weight, dimensions, and integrated portability features empowers users to select a generator that aligns with their specific needs and circumstances, ensuring reliable backup power when and where it is needed most. Failure to prioritize portability can lead to difficulties in transport and deployment, potentially hindering access to critical power during outages, reinforcing the practical significance of this attribute.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection and utilization of portable inverter generators for home inverter systems. Clear and concise answers aim to provide practical guidance for informed decision-making.
Question 1: What size portable inverter generator is suitable for a typical home?
Generator sizing depends on the intended load. Calculate the total wattage of appliances requiring backup power, including starting wattage demands. Consider a margin of safety for unexpected power needs. Professional electricians can assist with accurate load calculations and generator sizing.
Question 2: How does inverter technology benefit sensitive electronics?
Inverter technology produces clean, stable power, mimicking utility-supplied electricity. This “pure sine wave” output protects sensitive electronics from damage and ensures optimal performance. Conventional generators, in contrast, can produce fluctuating power harmful to delicate circuitry.
Question 3: What fuel types are available for portable inverter generators?
Common fuel options include gasoline, propane, and dual-fuel models. Gasoline offers widespread availability, while propane provides longer storage life and cleaner burning. Dual-fuel models offer flexibility in fuel choice depending on availability and cost.
Question 4: How can generator noise be minimized during operation?
Inverter generators are inherently quieter than conventional models. Operating in “eco-mode” further reduces noise. Strategic placement away from living areas and the use of sound-dampening materials or enclosures can additionally minimize noise impact.
Question 5: What safety precautions should be observed when using a portable generator?
Operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. Never connect a generator directly to household wiring without a transfer switch installed by a qualified electrician. Follow manufacturer instructions for safe refueling and maintenance.
Question 6: What maintenance is required for a portable inverter generator?
Regular maintenance, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement, is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific maintenance intervals and procedures. Professional servicing is advisable for complex repairs or maintenance tasks.
Addressing these common inquiries provides a foundational understanding for selecting and operating a portable inverter generator safely and effectively. Careful consideration of power needs, inverter technology, fuel options, noise levels, safety precautions, and maintenance requirements ensures reliable backup power for home inverter systems.
The concluding section will provide a concise summary of key takeaways and actionable recommendations for prospective generator owners.
Conclusion
Optimal portable generator selection for home inverter systems necessitates careful consideration of several interconnected factors. Power output must align with anticipated load requirements, while inverter technology ensures clean, stable power delivery, safeguarding sensitive electronics. Fuel efficiency directly impacts runtime and operating costs, influencing long-term value. Noise levels are critical for residential applications, impacting both user experience and neighborhood harmony. Portability considerations influence ease of transport, storage, and deployment. A comprehensive evaluation of these elements empowers informed decision-making, aligning generator capabilities with specific needs and circumstances. Prioritizing safety and adhering to manufacturer guidelines for operation and maintenance are paramount for ensuring safe, reliable performance and maximizing generator lifespan.
Investing in a high-quality portable inverter generator represents a crucial step in ensuring uninterrupted power supply for essential household systems. Reliable backup power mitigates disruptions during outages, providing peace of mind and safeguarding critical operations. Careful generator selection, coupled with diligent maintenance, yields a robust power solution, enhancing household resilience and preparedness for unforeseen power disruptions. The evolving landscape of portable power generation promises continued advancements in efficiency, noise reduction, and environmentally conscious operation, further solidifying the role of portable inverter generators as essential components of modern home power infrastructure.