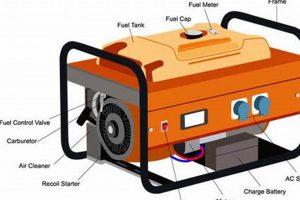
A compact, fuel-powered device provides temporary electrical power during outages. Imagine a power failure during a severe storm. This device could keep essential appliances like refrigerators, lights, and heating systems operational, ensuring safety and comfort.
Reliable access to electricity is crucial for modern life. These devices offer a critical safety net against unforeseen disruptions, protecting against food spoilage, maintaining communication lines, and powering medical equipment. Historically, extended power outages have underscored the value of backup power solutions, driving innovation and increasing accessibility for homeowners.
This discussion will delve further into selecting the appropriately sized unit, essential safety precautions during operation, and recommended maintenance practices to ensure reliable performance.
Tips for Safe and Effective Generator Use
Careful planning and operation are essential for maximizing the benefits and minimizing the risks associated with backup power generation.
Tip 1: Accurate Power Needs Assessment: Calculate the wattage required to run essential appliances. Consider both starting and running wattage, as some appliances require a surge of power upon startup. Overloading a generator can damage both the unit and connected devices.
Tip 2: Professional Installation: A qualified electrician should install a transfer switch, which safely isolates the generator’s power from utility lines, preventing backfeeding and protecting utility workers.
Tip 3: Proper Ventilation: Generators produce carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and deadly gas. Operate the unit outdoors in a well-ventilated area, far from windows, doors, and vents.
Tip 4: Regular Maintenance: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule. This typically includes oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement. Regular maintenance ensures reliable performance and extends the generator’s lifespan.
Tip 5: Fuel Storage Safety: Store fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Never refuel a hot or running generator.
Tip 6: Dry Operation Prevention: Running a generator without sufficient oil can cause severe damage. Check the oil level regularly and top off as needed.
Tip 7: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Protection: Use GFCI-protected outlets to minimize the risk of electrical shock, particularly in damp or wet conditions.
Adhering to these guidelines ensures safe and efficient operation, providing a reliable power source during outages.
By understanding these crucial aspects, one can make informed decisions about backup power and its vital role in maintaining safety and comfort during unforeseen power disruptions.
1. Power Output
A crucial factor in selecting a suitable backup power solution is its power output, measured in watts. This specification determines which appliances can be operated simultaneously and ensures the generator adequately meets household needs during a power outage.
- Starting vs. Running Watts:
Appliances require a surge of power upon startup (starting watts) which is significantly higher than the power needed to maintain operation (running watts). For example, a refrigerator might require 1,200 starting watts but only 250 running watts. Accurately calculating both values is essential to prevent overloading the generator.
- Total Wattage Calculation:
Determining the combined wattage requirements of essential appliances is critical. Add the running watts of appliances intended for simultaneous use. Include the highest starting wattage of any single appliance within that group. This sum represents the minimum power output required from the generator.
- Generator Size and Capacity:
Generators are available in a range of power outputs. Smaller units are suitable for powering essential lights and a refrigerator, while larger models can handle additional appliances like sump pumps, air conditioners, or well pumps. Selecting an appropriately sized generator ensures sufficient power without unnecessary expense or fuel consumption.
- Overload Protection:
Most generators incorporate overload protection mechanisms to prevent damage from exceeding the unit’s capacity. However, consistently operating near the generator’s maximum output can shorten its lifespan. Opting for a generator with a slightly higher power output than the calculated requirement provides a safety margin and prolongs the unit’s operational life.
Careful consideration of power output ensures the selected generator aligns with specific needs, preventing overload and maximizing the effectiveness of the backup power solution during an outage.
2. Fuel Type
Fuel type significantly influences the practicality and effectiveness of a home backup portable generator. Several options exist, each with advantages and disadvantages affecting cost, availability, storage, and environmental impact. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for selecting the most suitable fuel source.
Gasoline: Widely available and relatively inexpensive, gasoline is a common fuel choice. However, it has a limited shelf life and requires stabilizer to prevent degradation during storage. Gasoline generators tend to be more affordable but can produce higher emissions. Practical considerations include the potential for fuel shortages during emergencies and the flammability of gasoline.
Propane: Propane offers a longer shelf life than gasoline, eliminating the need for stabilizers. Propane generators typically produce cleaner emissions. Propane can be stored indefinitely in readily available tanks, offering convenience during extended outages. However, propane requires specialized tanks and connections, and availability can be impacted by regional supply disruptions.
Diesel: Diesel generators are known for their durability and efficiency, often providing a longer lifespan than gasoline or propane models. Diesel fuel has a longer shelf life than gasoline. However, diesel generators tend to be more expensive and can produce higher noise levels. Diesel fuel can also gel in cold temperatures, potentially affecting operability in winter climates.
Dual Fuel or Tri-Fuel: Some generators offer the flexibility of operating on multiple fuel types, such as gasoline and propane or gasoline, propane, and natural gas. This adaptability provides fuel source redundancy during emergencies. However, dual or tri-fuel generators often come at a premium price and may require specific conversion kits or adjustments for different fuel types.
Selecting the appropriate fuel type requires careful consideration of individual circumstances, including fuel availability, storage capacity, budget, and environmental concerns. Balancing these factors ensures the chosen generator aligns with long-term backup power requirements.
3. Runtime
Runtime, a critical factor for home backup portable generators, represents the duration a unit can operate continuously on a single fuel tank. Understanding runtime characteristics is essential for effective power management during outages.
- Fuel Tank Capacity:
Larger fuel tanks generally translate to longer runtimes. A higher capacity tank reduces the frequency of refueling, especially crucial during extended outages. However, larger tanks also increase the generator’s overall size and weight.
- Load Size:
The connected load directly impacts runtime. Operating fewer appliances or those with lower wattage requirements extends the generator’s running time. Conversely, powering multiple high-wattage devices significantly reduces the time between refueling.
- Generator Efficiency:
Fuel efficiency varies between generator models. More efficient generators extract more power from the same amount of fuel, resulting in longer runtimes. Efficiency is influenced by engine design and overall generator construction.
- Power Management Strategies:
Strategic load management can significantly extend runtime. Prioritizing essential appliances and staggering their use minimizes peak power demand, maximizing the available fuel supply. Rotating appliance usage can stretch the runtime considerably during extended outages.
Evaluating runtime characteristics in conjunction with power needs and potential outage durations allows for informed generator selection and effective power management during emergencies. A clear understanding of runtime ensures the chosen generator can provide sufficient power for the required duration, maximizing its utility during unforeseen power disruptions.
4. Portability
Portability is a defining characteristic of these generators, directly influencing their practicality and ease of use. While providing backup power, their mobility allows for versatile placement and convenient storage. Understanding the nuances of portability helps users maximize the benefits of these devices.
- Weight and Size:
Physical dimensions and weight significantly impact portability. Lighter, more compact units are easier to maneuver and transport, especially for individuals with physical limitations. However, smaller size often correlates with lower power output. Balancing power needs with manageable weight and size is crucial for practical portability.
- Wheels and Handles:
Integrated wheels and ergonomic handles simplify movement, even over uneven terrain. Larger wheels generally handle rough surfaces better, while sturdy handles provide secure grip during transport. These features are essential for convenient relocation and positioning of the generator.
- Compact Storage:
When not in use, compact storage is essential. Generators designed for efficient storage minimize their footprint in garages, sheds, or other storage areas. Foldable handles or removable components further enhance space-saving capabilities.
- Placement Flexibility:
Portability allows for optimal generator placement, maximizing safety and effectiveness. Moving the generator to well-ventilated areas, away from windows and doors, reduces carbon monoxide risks. Placement flexibility also ensures convenient access to power outlets and connection points.
Considering these portability factors ensures convenient operation and storage, maximizing the utility of a home backup portable generator. The appropriate balance of size, weight, and features enhances the generator’s overall practicality during power outages.
5. Noise Level
Noise level is a significant consideration when selecting a home backup portable generator. Operating noise can disrupt household activities, disturb neighbors, and violate local noise ordinances. Understanding the factors influencing noise levels and available mitigation strategies is essential for responsible generator operation.
- Decibel Ratings:
Manufacturers typically provide decibel (dB) ratings, indicating the loudness of the generator at a specific distance. Lower dB ratings signify quieter operation. Comparing dB ratings across models allows for informed decisions based on acceptable noise levels. Understanding the logarithmic nature of the decibel scale is crucial; a small numerical difference can represent a substantial change in perceived loudness.
- Engine Design and Construction:
Engine type and construction contribute significantly to noise output. Some engine designs inherently produce less noise than others. Features like mufflers and sound-dampening enclosures can further reduce operational noise. Researching specific models and their noise-reduction features helps identify quieter options.
- Load Level:
The generator’s noise level typically increases with the connected load. Operating the generator at lower loads, by prioritizing essential appliances, can minimize noise output. Strategic load management helps balance power needs with noise reduction goals.
- Placement and Distance:
Strategic generator placement can significantly impact perceived noise. Positioning the unit farther from living areas and neighboring properties minimizes noise disturbance. Barriers, such as fences or walls, can further attenuate sound propagation.
Careful consideration of noise levels and mitigation strategies ensures responsible generator operation, minimizing disruption and maintaining positive community relations. Selecting a quieter model and implementing appropriate operational practices contribute significantly to a more peaceful and considerate backup power solution.
6. Safety Features
Safety features are paramount for home backup portable generators, mitigating inherent risks associated with fuel-powered electrical generation. These features protect users, connected appliances, and the broader electrical grid from potential hazards. Ignoring these safeguards can lead to serious consequences, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire, electrocution, and damage to the generator or connected devices. For example, a generator operating without proper ventilation can accumulate lethal levels of carbon monoxide in enclosed spaces. Similarly, improper connection to household wiring can backfeed electricity into utility lines, endangering utility workers.
Several key safety features are commonly incorporated into modern generators. Carbon monoxide detectors automatically shut down the generator if dangerous levels are detected, preventing potential fatalities. Overload protection circuits prevent damage to the generator and connected appliances by cutting off power in case of excessive electrical demand. Low-oil shutdown safeguards the engine from damage due to insufficient lubrication. Properly grounded outlets minimize the risk of electrical shock, especially in damp conditions. Built-in circuit breakers provide further protection against overloads and short circuits.
Understanding and utilizing these safety features is crucial for responsible generator ownership. Regularly testing and maintaining these features ensures their effectiveness. Consulting the owner’s manual for specific safety procedures and recommendations is essential. Adherence to safety guidelines minimizes risks and ensures the safe and effective operation of a home backup portable generator, providing reliable power during outages without compromising well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common inquiries regarding home backup portable generators provides clarity for safe and effective utilization of these devices.
Question 1: How is the correct generator size determined?
Calculating the total wattage required to run essential appliances determines the necessary generator size. Consider both running watts and starting watts, especially for appliances with high starting demands like refrigerators and air conditioners. Oversizing slightly provides a safety margin and prevents strain on the generator.
Question 2: What is a transfer switch, and why is it necessary?
A transfer switch safely connects a generator to household circuits while isolating them from the utility power grid. This prevents backfeeding, a dangerous phenomenon that can energize downed power lines, posing a risk to utility workers. Professional installation by a qualified electrician is crucial for safe and compliant transfer switch implementation.
Question 3: Where should a portable generator be operated?
Generators produce carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and deadly gas. Operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas, far from windows, doors, and vents. Never operate a generator indoors, including garages, basements, or crawl spaces.
Question 4: What type of maintenance does a portable generator require?
Regular maintenance ensures reliable performance and longevity. Consult the owner’s manual for specific maintenance schedules, typically including oil changes, air filter cleaning or replacement, and spark plug replacement. Regularly checking fuel levels and ensuring proper storage prevents fuel-related issues.
Question 5: What safety precautions should be observed during refueling?
Always allow the generator to cool completely before refueling. Gasoline spills on a hot engine can ignite. Refuel in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Store fuel in approved containers and in a safe location.
Question 6: How long can a portable generator run continuously?
Runtime depends on several factors, including fuel tank capacity, load size, and generator efficiency. Consult the manufacturer’s specifications for estimated runtimes under various load conditions. Power management strategies, such as prioritizing essential appliances, can extend runtime during extended outages.
Understanding these frequently asked questions promotes safe and effective generator operation, ensuring reliable backup power during unforeseen outages.
Further exploration of specific generator models and features provides a comprehensive understanding for informed purchasing decisions.
Home Backup Portable Generator
Home backup portable generators offer crucial protection against power disruptions, ensuring the continuity of essential services and enhancing safety during unforeseen outages. Careful consideration of factors such as power output, fuel type, runtime, portability, noise level, and safety features is essential for selecting an appropriate unit. Proper installation, operation, and maintenance are critical for maximizing the generator’s effectiveness and minimizing potential risks. Understanding these elements empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding backup power solutions, safeguarding households against the impact of power disruptions.
Reliable access to electricity is fundamental to modern life. Investing in a home backup portable generator provides a critical layer of resilience against power outages, ensuring peace of mind and the ability to maintain essential functions during emergencies. Thorough research and responsible operation contribute significantly to the safe and effective utilization of these valuable devices, safeguarding homes and families from the disruptive consequences of power loss.