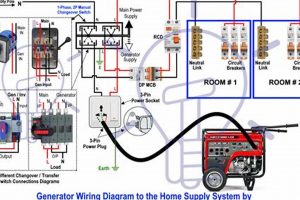
A top-tier, easily transportable power source designed for residential emergency use offers critical support during outages. Such units supply electricity to essential appliances and devices, maintaining comfort and safety until grid power is restored. For instance, during a severe storm, a compact, mobile generator can power refrigerators, lighting, and critical medical equipment.
Reliable backup power provides crucial peace of mind and can prevent significant disruptions to daily life caused by unexpected power loss. Historically, homes relied on less convenient and often less environmentally friendly options. Modern advancements in generator technology now offer compact, fuel-efficient solutions capable of powering a wide range of household appliances, mitigating the impact of power outages on safety, comfort, and productivity.
Key considerations for selecting a suitable unit include power output, fuel type, runtime, noise level, and portability features. The following sections will explore these factors in detail, providing guidance on choosing the optimal solution for individual needs and circumstances. Further topics will address safe operation, maintenance, and long-term storage.
Tips for Selecting a Portable Generator for Home Backup
Careful consideration of several factors ensures optimal generator performance and safety. Selecting the right unit involves assessing power requirements, fuel options, and operational characteristics.
Tip 1: Calculate Power Needs: Determine the wattage required to operate essential appliances. Sum the running watts of devices planned for simultaneous use during an outage. Add a safety margin for starting wattage, which can be significantly higher for appliances with electric motors.
Tip 2: Choose the Right Fuel Type: Gasoline, propane, and dual-fuel options offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. Gasoline offers widespread availability but requires careful storage. Propane burns cleaner and stores longer but may require larger tanks. Dual-fuel models provide flexibility.
Tip 3: Consider Runtime: Assess the desired duration of operation on a single tank of fuel. Longer runtimes minimize refueling frequency, especially important during extended outages.
Tip 4: Evaluate Noise Levels: Generators produce varying degrees of noise. Consider noise levels, especially if operating near neighbors or during nighttime hours. Inverter generators generally operate more quietly.
Tip 5: Assess Portability: Consider the generator’s weight and integrated features like wheels and handles. Ease of movement is crucial for convenient storage and deployment.
Tip 6: Prioritize Safety Features: Look for features such as automatic shut-off for low oil levels and overload protection. These safeguards protect the generator and connected appliances.
Tip 7: Consult Reviews and Ratings: Research reputable brands and models. Independent reviews and ratings offer valuable insights into performance, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
Selecting a generator based on these guidelines ensures reliable power during outages, contributing to household safety and minimizing disruption.
By carefully evaluating individual needs and generator specifications, consumers can make informed decisions, investing in a power solution offering long-term value and peace of mind.
1. Power Output
Power output, measured in watts, represents a critical factor in selecting a suitable portable generator for home backup. This specification directly dictates which appliances can be operated simultaneously during a power outage. Understanding power requirements involves calculating the combined running wattage of essential devices and factoring in the higher starting wattage demands of appliances with electric motors, such as refrigerators and air conditioners. For example, a refrigerator might require 700 running watts but need a surge of 2,000 watts to start. Insufficient generator output leads to overloaded circuits, potential equipment damage, and ultimately, failure to provide necessary backup power.
Accurately assessing power needs is crucial. Underestimating requirements can render the generator ineffective during an outage, while overestimating can lead to unnecessary expense. Practical applications include creating a prioritized list of essential appliances and calculating their combined wattage. Online resources and appliance manuals provide wattage information. Adding a safety margin to the total calculated wattage ensures sufficient power for reliable operation. For instance, a homeowner needing to power a refrigerator (700W), a sump pump (1,000W), and several lights (100W) would require a generator with an output exceeding 2,000W, including a safety margin.
Selecting a generator with appropriate power output ensures effective backup power during outages. A thorough understanding of wattage requirements, starting vs. running watts, and the potential impact of underestimation or overestimation allows informed decisions. This careful consideration contributes significantly to choosing the optimal generator, aligning power supply with specific needs and mitigating the disruption caused by power loss.
2. Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency represents a critical aspect of portable generator selection for home backup, directly impacting operational costs and environmental impact. Efficient fuel consumption translates to longer runtimes on a given fuel volume, reducing the frequency of refueling during extended outages and minimizing long-term expenses. Understanding the factors influencing fuel efficiency aids in choosing a generator that balances performance with economic and environmental considerations.
- Fuel Type and Consumption Rate:
Different fuel types exhibit varying energy densities and consumption rates. Propane generally burns cleaner than gasoline but may offer slightly lower energy density. Generator specifications often provide fuel consumption rates at different load levels, allowing comparisons and estimations of runtime based on fuel tank capacity. A generator consuming less fuel per kilowatt-hour (kWh) produced offers greater efficiency and longer operation between refueling.
- Load Management and Efficiency:
Operating a generator at its optimal load level typically yields the highest fuel efficiency. Running the generator significantly below its rated capacity can reduce efficiency, while exceeding the rated load risks damage. Prioritizing essential appliances and managing power consumption during an outage optimizes fuel use and extends runtime. For instance, powering only essential lights, refrigerator, and critical medical equipment instead of simultaneously running less critical appliances maximizes fuel efficiency.
- Engine Technology and Design:
Advanced engine technologies, such as inverter generators, contribute significantly to fuel efficiency. Inverter generators adjust engine speed based on power demand, resulting in lower fuel consumption compared to traditional generators running at a constant speed. This dynamic adjustment optimizes fuel use, particularly during periods of lower power demand.
- Maintenance and Long-Term Efficiency:
Regular maintenance, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement, plays a vital role in maintaining optimal fuel efficiency throughout the generator’s lifespan. Neglecting maintenance can lead to decreased efficiency, increased fuel consumption, and potential engine damage. Adhering to manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules ensures consistent performance and long-term fuel economy.
By considering fuel type, load management, engine technology, and maintenance practices, consumers can select a portable generator that provides reliable backup power while minimizing fuel consumption and operating costs. Prioritizing fuel efficiency not only reduces expenses but also contributes to a lower environmental impact, aligning with responsible energy use during power outages.
3. Runtime
Runtime, representing the duration a portable generator can operate continuously on a single fuel tank, constitutes a critical factor influencing its suitability for home backup. Runtime directly impacts the generator’s ability to provide uninterrupted power during extended outages, influencing decisions regarding fuel storage, refueling logistics, and overall preparedness. A generator’s runtime capability significantly influences its effectiveness in mitigating the disruption caused by prolonged power loss.
Several factors influence a generator’s runtime. Fuel tank capacity directly correlates with potential runtime, assuming a consistent load. However, load significantly influences actual runtime; higher power demands deplete fuel more rapidly, shortening the operational period. Fuel type also plays a role; propane and gasoline exhibit different energy densities, affecting the duration of operation on comparable fuel volumes. Furthermore, engine efficiency impacts fuel consumption rate; more efficient engines generally extend runtime under equivalent load conditions. For instance, a generator with a large fuel tank but low engine efficiency may offer a shorter runtime than a smaller, more efficient unit under the same load. Conversely, a highly efficient generator with a small fuel tank may necessitate frequent refueling during extended outages. Understanding these interconnected factors facilitates informed decisions based on anticipated outage durations and power requirements. A homeowner anticipating frequent short outages might prioritize a smaller, fuel-efficient generator, while someone residing in an area prone to prolonged outages might require a larger tank and extended runtime capability.
Optimizing generator runtime for home backup involves careful consideration of fuel capacity, anticipated load, fuel type, and engine efficiency. Balancing these factors ensures the selected generator aligns with specific needs and outage scenarios. Adequate runtime contributes significantly to maintaining essential services, safeguarding comfort, and minimizing disruption during power loss. Selecting a generator with appropriate runtime characteristics enhances preparedness and resilience in the face of power outages.
4. Noise Level
Noise level represents a critical factor in selecting a portable generator for home backup, impacting both the user experience and neighborhood relations. Excessive noise can cause significant disturbance, especially during extended operation or in densely populated areas. Understanding the factors influencing generator noise and mitigation strategies allows informed decisions, balancing power needs with noise considerations.
- Decibel Levels and Human Perception:
Generator noise is measured in decibels (dB). A lower dB rating indicates quieter operation. Prolonged exposure to high dB levels can cause hearing damage and stress. Understanding the logarithmic nature of the decibel scale is crucial; a small numerical difference can represent a significant change in perceived loudness. For example, a 10 dB increase is perceived as roughly twice as loud. Comparing dB ratings across different generator models facilitates informed choices regarding noise impact.
- Generator Technology and Noise Output:
Different generator technologies exhibit varying noise profiles. Conventional generators tend to produce higher noise levels due to their constant engine speed. Inverter generators, however, adjust engine speed based on power demand, resulting in significantly quieter operation, especially at lower loads. Construction materials and design also influence noise output; some models incorporate noise-dampening features like mufflers and sound enclosures.
- Operational Factors and Noise Variation:
Operating conditions influence noise levels. Higher loads typically result in increased noise as the engine works harder. Proper maintenance, including air filter cleaning and muffler inspection, helps minimize noise output. Placement also plays a role; positioning the generator on a stable, non-resonant surface can reduce noise transmission. Furthermore, directing the exhaust away from living areas minimizes noise intrusion.
- Mitigation Strategies and Noise Reduction:
Various strategies mitigate generator noise. Purpose-built sound enclosures or baffles can significantly reduce noise pollution. Positioning the generator at a distance from living spaces and utilizing sound-absorbing materials, like blankets or sound walls, further minimizes noise impact. Operating the generator only during necessary periods and adhering to local noise ordinances promotes harmonious neighborhood relations. Selecting a quieter generator model upfront represents the most effective long-term noise reduction strategy.
Careful consideration of noise levels when selecting a portable generator contributes significantly to a positive user experience and minimizes disturbance. Understanding the relationship between decibel levels, generator technology, operational practices, and mitigation strategies allows informed decisions. Prioritizing quieter operation enhances comfort and fosters positive community relations during power outages, demonstrating responsible generator use.
5. Portability
Portability represents a defining characteristic of generators designed for home backup, directly influencing ease of use and deployment during power outages. The portability of a generator dictates its maneuverability and storage practicality, impacting overall user experience. Lightweight construction, compact dimensions, and integrated features like wheels and handles contribute significantly to convenient transport and positioning. This ease of movement proves crucial, especially during emergencies when rapid deployment is essential. For instance, a homeowner needing to quickly connect a generator during a storm benefits significantly from its portability. Conversely, a cumbersome, difficult-to-maneuver generator hinders timely power restoration and presents logistical challenges.
The degree of portability influences practical applications. A highly portable generator easily moves between storage and connection points, adapting to various power needs. This flexibility proves valuable for powering different appliances or relocating the generator to a safe, dry location during inclement weather. Portability also extends to recreational use; a compact, lightweight generator easily transports to campsites or tailgates, providing power away from home. However, portability considerations often involve trade-offs with power output. Smaller, more portable generators typically offer lower wattage compared to larger, less maneuverable units. Balancing portability with power requirements involves assessing individual needs and anticipated usage scenarios. A homeowner requiring higher wattage for multiple appliances might prioritize power output over portability, while someone seeking backup power for essential items might opt for a smaller, more easily transportable unit.
In summary, portability plays a pivotal role in the selection of a home backup generator. Ease of movement, storage practicality, and adaptability to diverse power needs contribute significantly to the generator’s overall value and usability. Balancing portability with power output and considering specific usage scenarios ensures the selected generator aligns with individual requirements and provides reliable power during outages. Effective integration of portability features enhances user experience and contributes to the generator’s effectiveness in mitigating power loss disruptions.
6. Safety Features
Safety features represent a non-negotiable aspect of any portable generator designated for home backup, inextricably linked to user well-being and the prevention of property damage. A “best” portable generator prioritizes safety through incorporating design elements and functionalities that mitigate potential hazards associated with generator operation. These features serve as critical safeguards, protecting users, connected appliances, and the generator itself from various risks.
Several key safety features distinguish superior portable generators. Low-oil shutdown mechanisms prevent engine damage caused by insufficient lubrication. Overload protection safeguards against excessive current draw, preventing electrical fires and generator damage. Properly grounded outlets minimize the risk of electric shock, while carbon monoxide (CO) sensors and automatic shutoff systems protect against the buildup of this deadly gas, especially in enclosed or poorly ventilated areas. For instance, a CO sensor automatically shuts down the generator if dangerous levels are detected, potentially saving lives. Similarly, an overload protection feature prevents damage to sensitive electronics by cutting power when excessive current is drawn. These features illustrate the practical significance of prioritizing safety in generator design.
Neglecting safety features can have severe consequences. Operating a generator without CO protection risks fatal carbon monoxide poisoning. Ignoring overload protection can lead to electrical fires, damaging property and jeopardizing safety. Failing to ground the generator properly increases the risk of electrocution. The absence of these critical safety mechanisms transforms a potentially life-saving tool into a significant hazard. Therefore, prioritizing safety features is not merely a recommendation but a fundamental requirement when selecting a portable generator for home backup. Consumers must recognize the direct correlation between these features and their well-being. A comprehensive understanding of these safety features empowers informed decisions, aligning generator selection with a commitment to safe and responsible operation.
7. Budget
Budgetary considerations play a crucial role in selecting a portable generator for home backup. Balancing desired features and performance with financial constraints requires careful evaluation of available options. Understanding the relationship between budget and generator capabilities allows informed decisions, maximizing value and ensuring the chosen generator aligns with both power needs and financial limitations.
- Initial Purchase Price:
Generator prices vary significantly based on power output, fuel type, features, and brand reputation. Higher wattage, advanced features like inverter technology, and reputable brands typically command higher prices. Establishing a realistic budget upfront helps narrow the selection, focusing on models within a defined price range. Recognizing the correlation between price and features facilitates informed compromises, balancing performance with affordability.
- Operating Costs:
Fuel consumption represents a significant ongoing expense. Fuel efficiency varies between models and fuel types. Calculating estimated operating costs based on anticipated usage and fuel prices helps assess long-term affordability. A less expensive generator with lower fuel efficiency might prove more costly in the long run compared to a slightly more expensive, fuel-efficient model.
- Maintenance Expenses:
Routine maintenance, including oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug replacements, contributes to the overall cost of ownership. Factoring in these expenses helps avoid unexpected costs and ensures the generator remains operational throughout its lifespan. Some manufacturers offer extended warranties or maintenance plans, potentially influencing long-term budget considerations.
- Return on Investment:
A generator represents an investment in resilience against power outages. Assessing the potential cost of power disruptions, including spoiled food, lost productivity, and potential safety risks, helps contextualize the generator’s value. A higher initial investment in a reliable, feature-rich generator might offer a greater return on investment compared to a less expensive, less capable model that fails to provide adequate power during critical outages. Balancing upfront costs with long-term value ensures the chosen generator effectively mitigates the financial impact of power loss.
By carefully considering initial purchase price, operating costs, maintenance expenses, and potential return on investment, consumers can select a portable generator that aligns with both their power requirements and budgetary constraints. A comprehensive budget analysis empowers informed decisions, maximizing the value of the investment and ensuring the chosen generator provides reliable, affordable backup power when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding portable generators for home backup, providing concise and informative responses to facilitate informed decision-making.
Question 1: How is the necessary generator size determined?
Generator size is determined by calculating the total running wattage of appliances planned for simultaneous use during an outage, including a margin for starting wattage, which is typically higher for motor-driven appliances.
Question 2: What differentiates inverter generators from conventional generators?
Inverter generators produce cleaner, more stable power suitable for sensitive electronics. They also offer quieter operation and better fuel efficiency due to their variable engine speed.
Question 3: What safety precautions are essential when operating a portable generator?
Essential safety precautions include operating the generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from flammable materials. Proper grounding and connection procedures must be followed to prevent electrocution. Carbon monoxide detectors are crucial.
Question 4: What maintenance is required for a portable generator?
Regular maintenance includes oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement according to manufacturer recommendations. Proper storage practices, including fuel stabilization, are essential for long-term reliability.
Question 5: What are the primary fuel options for portable generators?
Common fuel options include gasoline, propane, and dual-fuel models. Gasoline offers widespread availability, propane offers cleaner burning and longer storage life, while dual-fuel models provide flexibility.
Question 6: How does altitude impact generator performance?
Higher altitudes can reduce engine power output and impact fuel efficiency. Consult manufacturer guidelines for altitude adjustments and derating factors to ensure optimal performance.
Understanding these key aspects of portable generator selection, operation, and maintenance contributes significantly to safe and effective power backup during outages. Careful consideration of these factors empowers informed decisions, aligning generator choice with individual needs and promoting responsible generator use.
The next section will delve into specific generator models and provide detailed comparisons to further assist in the selection process.
Conclusion
Optimal portable generator selection for home backup necessitates careful consideration of various interconnected factors. Power output, fuel efficiency, runtime, noise level, portability, safety features, and budget constraints collectively influence the suitability of a given generator for specific needs. A comprehensive understanding of these factors empowers informed decisions, ensuring the chosen generator aligns with both power requirements and desired operational characteristics. Prioritizing safety features is paramount, mitigating potential hazards associated with generator use. Thorough research, including comparing models and consulting expert reviews, facilitates optimal selection.
Investing in a reliable portable generator provides essential resilience against power disruptions, safeguarding households from the inconvenience and potential risks associated with outages. Careful planning and informed generator selection contribute significantly to maintaining essential services, ensuring safety, and minimizing disruption during unforeseen power loss. A well-chosen generator represents a valuable investment in preparedness, enhancing peace of mind and fostering self-reliance in the face of power grid instability.