A compact, readily movable power source, typically fueled by gasoline or propane, provides temporary electrical service during outages. Imagine a homeowner using such a device to power essential appliances like a refrigerator, sump pump, or a few lights during a storm-related blackout.
These devices offer crucial peace of mind and practical functionality for homeowners. Power disruptions can lead to food spoilage, flooded basements, security system failures, and disrupted communication. A readily available alternate power supply mitigates these risks, ensuring essential services remain operational during emergencies. Historically, relying solely on utility companies left consumers vulnerable during outages. These independent power sources empower homeowners, granting greater control over their well-being and property protection during unforeseen events.
This article will further explore various aspects of these devices, including fuel types, power outputs, maintenance requirements, and safety considerations to help consumers make informed decisions when selecting a unit appropriate for their specific needs.
Essential Tips for Selecting and Operating a Backup Power Source
Careful consideration and planning are essential for maximizing the effectiveness and safety of a backup power source. The following tips provide valuable guidance for homeowners.
Tip 1: Calculate Power Requirements: Determine the wattage needed to run essential appliances. Sum the wattage of devices intended for simultaneous use during an outage. This calculation ensures the selected unit possesses sufficient capacity.
Tip 2: Choose an Appropriate Fuel Source: Gasoline-powered units offer greater portability, while propane units provide longer run times and extended fuel storage capabilities. Consider fuel availability and storage limitations when making a selection.
Tip 3: Prioritize Safety: Never operate a unit indoors or in enclosed spaces. Carbon monoxide poisoning poses a serious risk. Ensure adequate ventilation. Additionally, maintain a safe distance from flammable materials.
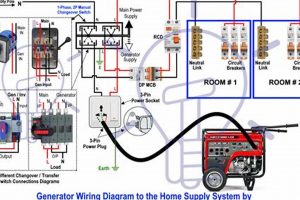
Tip 4: Invest in Proper Installation: Professional installation of a transfer switch is recommended. A transfer switch safely connects the unit to the home’s electrical system, preventing backfeeding and protecting utility workers.
Tip 5: Perform Regular Maintenance: Adhering to manufacturer recommendations for oil changes, air filter replacements, and general upkeep ensures reliable operation during emergencies.
Tip 6: Consider Noise Levels: Some units operate at higher noise levels than others. Research noise output specifications and consider the unit’s proximity to neighbors when selecting a model.
Tip 7: Store Fuel Safely: Store fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Rotate fuel supplies periodically to maintain freshness.
By following these guidelines, consumers can effectively safeguard their homes and ensure uninterrupted power during unforeseen outages. Proper planning and maintenance are critical for maximizing the benefits of owning a backup power source.
This information provides practical guidance for selecting and operating a backup power solution, ensuring preparedness for future power disruptions.
1. Power Output
Power output represents a critical factor when selecting a portable backup generator for home use. This specification, measured in watts, directly determines the number and type of appliances a unit can power simultaneously. Understanding power output requirements ensures appropriate device selection to meet specific needs during power outages.
- Starting vs. Running Watts
Appliances require a surge of power upon startup, known as starting wattage, which significantly exceeds the power needed for continuous operation (running watts). For example, a refrigerator might require 2,000 starting watts but only 700 running watts. Generators must accommodate both values; choosing a unit based solely on running watts may lead to insufficient power during appliance startup.
- Total Wattage Calculation
Accurately calculating total power requirements necessitates summing the running watts of all intended simultaneously powered appliances, plus the highest starting wattage of any single appliance within that group. This calculation provides a realistic estimate of the minimum generator power output required.
- Power Output and Appliance Selection
Available power output influences appliance choices during an outage. A smaller unit might only power essential lighting and a refrigerator, while a larger output unit could support additional appliances like a sump pump, furnace fan, or well pump. Understanding these limitations allows for prioritized appliance usage during power disruptions.
- Overloading and Generator Damage
Exceeding a generator’s power output capacity by connecting too many appliances can lead to overloading. Overloading results in voltage fluctuations, potential equipment damage, and possible generator shutdown. Selecting a unit with adequate power output is crucial for safe and reliable operation.
Careful consideration of power output, coupled with accurate wattage calculations, ensures appropriate generator selection for individual needs. Matching generator capacity to anticipated load prevents overloading, protects appliances, and guarantees effective backup power during outages.
2. Fuel Type
Fuel type represents a crucial consideration when selecting a portable backup generator for home use. The choice of fuel directly impacts several key operational factors, including runtime, storage requirements, availability, and cost. Understanding the nuances of different fuel types empowers informed decision-making, aligning generator capabilities with specific needs and circumstances.
- Gasoline
Gasoline offers widespread availability and ease of acquisition. Generators utilizing gasoline typically offer higher power output relative to their size. However, gasoline has a limited shelf life and requires periodic replacement to prevent degradation and engine issues. Storage requires approved containers and careful attention to safety precautions due to flammability. Gasoline-powered units are generally more portable due to the higher energy density of the fuel.
- Propane
Propane exhibits a longer shelf life than gasoline, simplifying long-term storage. Propane burns cleaner, reducing emissions and minimizing maintenance requirements. Storage typically involves larger tanks, which can limit portability compared to gasoline units. Propane-powered generators often offer longer run times due to the larger fuel capacity. Fuel availability can be a concern during widespread emergencies.
- Dual Fuel
Dual fuel generators offer operational flexibility by accommodating both gasoline and propane. This adaptability proves advantageous during fuel shortages or fluctuating prices. Dual fuel units allow users to switch between fuel sources seamlessly, extending runtime and maximizing fuel utilization. These units often incorporate automatic fuel switching capabilities for uninterrupted operation.
- Diesel
Diesel offers excellent fuel efficiency and extended run times. Diesel-powered generators are known for their durability and reliability, often preferred for heavy-duty or commercial applications. However, these units tend to be larger, heavier, and less portable than gasoline or propane counterparts. Diesel fuel also has storage considerations related to temperature and potential gelling in cold climates.
The choice of fuel type directly influences generator performance, maintenance requirements, and overall cost of ownership. Careful consideration of these factors, in conjunction with individual power needs and storage capabilities, ensures selection of the most appropriate fuel type for a portable backup generator for home use. Balancing fuel availability, runtime requirements, and storage limitations optimizes generator effectiveness during power outages.
3. Portability
Portability represents a defining characteristic of these power sources, directly influencing their practical application and overall utility. The ease with which a unit can be moved and positioned significantly impacts its effectiveness during power outages. Analyzing the components and implications of portability provides valuable insights for selecting the appropriate unit for specific needs.
- Weight and Size
Physical dimensions and weight directly influence maneuverability. A lighter, more compact unit allows for easier transport and placement, particularly crucial for individuals with physical limitations or when navigating challenging terrain. Conversely, larger, heavier units may require assistance or specialized equipment for relocation, potentially limiting their practicality in certain situations.
- Wheel Design and Handles
Integrated wheels and ergonomically designed handles contribute significantly to ease of movement. Larger, never-flat wheels facilitate transport across uneven surfaces, while sturdy handles provide secure grip and control. Well-designed portability features minimize strain and effort during relocation, crucial during emergency situations.
- Compactness and Storage
Compact design simplifies storage when not in use. Smaller units occupy less space in garages or storage sheds, optimizing space utilization. Consideration of storage dimensions ensures seamless integration within existing storage solutions, maximizing convenience and accessibility.
- Placement Flexibility
Portability enables flexible placement for optimal power delivery. Units can be positioned close to the required appliances while maintaining safe distances from windows and doors, ensuring efficient power distribution while adhering to safety guidelines.
Portability significantly enhances the practicality and usability of a backup power source. Careful consideration of weight, size, wheel design, and overall compactness ensures effortless maneuverability and convenient storage. Prioritizing portability features empowers users to deploy these units effectively during outages, maximizing their functionality and providing reliable power where needed most.
4. Runtime
Runtime represents a critical performance metric for portable backup generators, directly impacting their ability to provide continuous power during outages. Runtime, defined as the duration a generator can operate continuously on a single fuel tank, dictates the extent of coverage provided during power disruptions. Understanding the factors influencing runtime and its practical implications is crucial for informed generator selection.
Several factors influence generator runtime. Fuel tank capacity directly correlates with potential runtime; larger tanks generally yield longer operation. Load, represented by the power demand of connected appliances, inversely affects runtime. Higher power consumption reduces the operational duration on a single fuel tank. Engine efficiency also plays a significant role; more efficient engines maximize fuel utilization, extending runtime. For example, a generator with a large fuel tank powering a few essential appliances will have a significantly longer runtime than the same generator powering numerous high-wattage devices. Selecting a generator with sufficient runtime requires careful consideration of anticipated power needs and outage durations. Extended outages necessitate larger fuel tanks or supplemental fuel supplies.
Practical implications of runtime are significant. A generator with insufficient runtime may fail to provide adequate coverage during extended outages, jeopardizing essential services. For instance, a homeowner relying on a generator with limited runtime during a multi-day outage might experience interruptions in refrigeration, sump pump operation, or heating, leading to food spoilage, flooding, or discomfort. Conversely, a generator with ample runtime ensures continuous operation of critical systems, safeguarding against these potential issues. Accurately assessing power needs and anticipated outage durations enables selection of a generator with appropriate runtime capabilities, maximizing preparedness and minimizing disruption during power failures.
5. Noise Level
Noise level represents a significant consideration when selecting a portable backup generator for home use. Operating noise can impact both the homeowner and the surrounding neighborhood. Understanding the factors influencing noise levels and their practical implications facilitates informed decision-making and promotes harmonious coexistence during power outages.
- Decibel Ratings and Human Perception
Noise output is typically measured in decibels (dB). Higher dB values indicate louder operation. Human perception of sound is logarithmic; a 10 dB increase represents a perceived doubling of loudness. A generator operating at 70 dB, comparable to a vacuum cleaner, will sound twice as loud as one operating at 60 dB, similar to normal conversation. Considering decibel ratings helps users anticipate the perceived noise level and its potential impact.
- Muffler Design and Noise Suppression
Muffler design plays a crucial role in mitigating noise output. Advanced muffler technology incorporates sound-dampening materials and optimized airflow paths to minimize exhaust noise. Investing in a generator with an effective muffler contributes significantly to reducing noise pollution and maintaining a quieter environment.
- Distance and Noise Propagation
Sound intensity decreases with distance. Positioning the generator farther from living spaces and neighboring properties reduces noise impact. Strategic placement, utilizing barriers or sound-absorbing materials, further minimizes noise propagation and helps maintain acceptable sound levels.
- Operating Mode and Noise Variation
Noise levels can vary based on generator operating mode. Units under heavy load typically produce more noise than those operating at lower capacities. Understanding this variability allows users to anticipate noise fluctuations and implement appropriate mitigation strategies during periods of high power demand.
Careful consideration of noise level contributes to a more peaceful and considerate environment during power outages. Selecting a quieter generator, employing strategic placement techniques, and understanding the relationship between distance and noise propagation minimizes disturbance to both homeowners and their neighbors. Prioritizing noise reduction features enhances overall quality of life during emergency power situations.
6. Safety Features
Safety features are paramount when operating a portable backup generator for home use. These devices, while providing essential power during outages, present potential hazards if not operated cautiously. Understanding and utilizing integrated safety features mitigates risks, protects users, and ensures safe operation during emergency power situations.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO) Detection and Shutdown
Carbon monoxide, a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas, poses a significant threat during generator operation. Units equipped with CO sensors continuously monitor exhaust emissions. Upon detecting elevated CO levels, these sensors trigger an automatic shutdown, preventing dangerous accumulation. This critical safety feature protects users from CO poisoning, a potentially fatal consequence of improper generator usage.
- Overload Protection
Overloading occurs when the electrical load exceeds the generator’s rated output capacity. This can lead to overheating, equipment damage, and potential fire hazards. Overload protection circuits continuously monitor power output. When overload conditions are detected, the circuit interrupts power delivery, preventing damage to the generator and connected appliances. This safeguard ensures safe operation within the generator’s specified limits, preventing potential electrical hazards.
- Low-Oil Shutdown
Maintaining adequate oil levels is essential for proper engine lubrication and performance. Low oil levels can lead to engine damage and potential seizure. Generators equipped with low-oil shutdown sensors automatically cease operation when oil levels fall below a critical threshold. This preventative measure protects the engine from damage, ensuring longevity and reliable performance.
- Covered Outlets and GFCI Protection
Covered outlets protect against moisture and debris intrusion, reducing the risk of electrical shock. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) protection further enhances electrical safety. GFCI outlets detect imbalances in electrical current flow, quickly tripping the circuit to prevent electrical shock hazards. These features provide enhanced protection against electrical hazards, especially in outdoor or damp environments.
Prioritizing safety features when selecting a portable backup generator for home use significantly reduces potential hazards. CO detection, overload protection, low-oil shutdown, and covered outlets with GFCI protection safeguard users and equipment. Understanding and utilizing these features ensures safe and reliable operation during power outages, mitigating risks and maximizing the benefits of backup power.
7. Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for reliable and safe operation of a portable backup generator for home use. Neglecting routine maintenance can lead to decreased performance, shortened lifespan, and increased risk of malfunctions during critical power outages. A well-maintained generator ensures consistent power delivery when needed most, while a neglected unit can become a liability. For instance, failing to change the oil regularly can lead to engine seizure, rendering the generator useless during an outage. Similarly, neglecting air filter replacement can restrict airflow, reducing power output and potentially causing overheating.
Practical maintenance tasks include regular oil changes, air filter replacements, spark plug inspections, and fuel system cleaning. The frequency of these tasks depends on the generator model and usage. Consulting the manufacturer’s recommendations provides specific guidance for maintenance intervals and procedures. Adhering to these guidelines ensures optimal performance and extends the generator’s operational life. Furthermore, periodic testing under load simulates real-world usage and verifies proper functionality. This proactive approach identifies potential issues before they escalate, ensuring the generator remains ready for immediate use during an outage. For example, running the generator under load for a short period each month can reveal fuel delivery problems or voltage fluctuations that might otherwise go unnoticed until an actual outage occurs.
Proper maintenance safeguards against unexpected failures and ensures reliable power delivery during outages. A proactive maintenance schedule minimizes downtime, extends the generator’s operational life, and provides peace of mind during emergencies. Neglecting these essential tasks can lead to costly repairs, premature failure, and potentially dangerous situations during power disruptions. Understanding the direct link between regular maintenance and reliable operation is crucial for maximizing the benefits and ensuring the long-term functionality of a portable backup generator for home use.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding portable backup generators for home use, providing concise and informative responses to facilitate informed decision-making and safe operation.
Question 1: How is the appropriate generator size determined?
Generator size selection depends on the intended load. Calculate the total running watts of appliances planned for simultaneous use during an outage, then add the highest starting wattage of any single appliance within that group. This sum represents the minimum required generator output.
Question 2: What are the primary fuel options?
Common fuel types include gasoline, propane, and diesel. Gasoline offers widespread availability, propane provides extended runtimes and cleaner burning, while diesel offers superior efficiency and longevity. Dual-fuel generators provide flexibility by utilizing both gasoline and propane.
Question 3: Where should a generator be operated?
Generators must always operate outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from windows, doors, and flammable materials. Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Question 4: What is a transfer switch, and is it necessary?
A transfer switch safely connects the generator to the home’s electrical system, preventing dangerous backfeeding to the utility grid. Professional installation of a transfer switch is strongly recommended for safety and code compliance.
Question 5: How frequently should maintenance be performed?
Maintenance schedules vary by model and usage. Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific intervals. Typical maintenance includes regular oil changes, air filter replacements, spark plug checks, and fuel system cleaning.
Question 6: What safety precautions should be observed during operation?
Always allow the generator to cool completely before refueling. Never refuel a hot generator. Store fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Inspect the generator and its surroundings for potential hazards before each use.
Careful consideration of these frequently asked questions promotes safe and effective generator operation. Prioritizing safety and adhering to manufacturer recommendations ensures reliable performance and mitigates potential risks.
For further information and specialized guidance, consult qualified electricians and generator specialists.
Portable Backup Generators for Home
This exploration of portable backup generators for home use has highlighted their crucial role in mitigating the impact of power disruptions. Key considerations, including power output, fuel type, portability, runtime, noise level, safety features, and maintenance requirements, have been examined to provide a comprehensive understanding of these devices. Appropriate unit selection requires careful evaluation of individual needs, anticipated load demands, and desired runtime. Prioritizing safety features and adhering to manufacturer recommendations ensures safe and reliable operation, protecting both users and connected appliances.
Reliable access to electricity is paramount in modern society. Power outages, whether caused by natural disasters or grid failures, disrupt daily life and can jeopardize safety and well-being. Portable backup generators empower homeowners to maintain essential services during such disruptions, ensuring continuity and mitigating potential risks. Investing in a properly sized and maintained unit represents a proactive measure toward preparedness and resilience in the face of unforeseen power interruptions. Informed decision-making, coupled with diligent maintenance, ensures these devices provide reliable backup power when needed most, safeguarding homes and enhancing peace of mind.