Compact power sources designed for residential use provide electricity during outages or in locations lacking traditional grid access. These units, typically fueled by gasoline or propane, offer a range of power outputs suitable for powering essential appliances, lighting, and electronic devices. For instance, a homeowner might utilize such a device to operate a refrigerator, sump pump, and several lights during a power outage.
The ability to maintain critical household functions during emergencies makes these devices valuable assets. They offer peace of mind and can prevent costly disruptions caused by power loss. Historically, backup power solutions for homes were limited and expensive. Advancements in engine and generator technology have led to smaller, more affordable, and more fuel-efficient options, making power reliability increasingly accessible.
Further exploration will delve into specific aspects of these power solutions, including various sizes, fuel types, maintenance requirements, and safety considerations. This comprehensive overview will provide consumers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions based on their individual power needs and circumstances.
Operational and Safety Guidance for Portable Generators
Safe and efficient operation of portable generators requires careful consideration of several key factors. Following these guidelines will ensure optimal performance and mitigate potential hazards.
Tip 1: Proper Placement is Crucial: Operate the generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from windows, doors, and vents. Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious risk.
Tip 2: Grounding is Essential: Proper grounding protects against electrical shock. Consult the owner’s manual for grounding instructions specific to the unit.
Tip 3: Never Refuel a Hot Generator: Allow the generator to cool completely before refueling to prevent fires. Spilled fuel on a hot engine can ignite.
Tip 4: Regular Maintenance Extends Lifespan: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement.
Tip 5: Appropriate Extension Cord Usage: Utilize heavy-duty, outdoor-rated extension cords designed for the generator’s wattage output. Overloading cords can cause overheating and fires.
Tip 6: Safe Storage of Fuel: Store fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources.
Tip 7: Dry Operation Prevention: Ensure the generator has sufficient oil before starting and during operation. Running a generator without oil can cause severe damage.
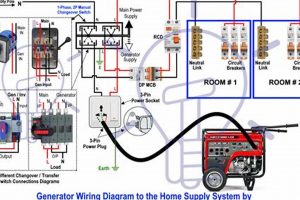
Tip 8: Professional Installation of Transfer Switches: For safe connection to home circuits, consult a qualified electrician for proper installation of a transfer switch. Direct connection to household wiring is unsafe and can damage appliances and endanger utility workers.
Adherence to these guidelines promotes safe operation and prolongs the functional life of the equipment, ensuring reliable power when needed.
This operational guidance provides a foundation for safe and effective usage. Consulting the manufacturer’s documentation for specific model information is essential before operation.
1. Power Output
Power output, measured in watts, is a critical specification for portable generators. It directly determines the number and type of appliances a generator can operate simultaneously. A generator’s power output must exceed the combined wattage requirements of the intended loads. For instance, a generator with a 3000-watt running capacity could power a 1500-watt refrigerator, a 1000-watt microwave, and several smaller devices totaling 500 watts or less. Exceeding the rated output leads to overloading, potentially damaging the generator and connected appliances.
Choosing the correct power output involves careful consideration of anticipated power needs. Homeowners should create an inventory of essential appliances and their respective wattage requirements. This inventory informs the selection of a generator with sufficient capacity to handle critical loads during an outage. Generators typically list both running watts and starting watts. Starting watts, often significantly higher than running watts, are required for appliances with electric motors, such as refrigerators and air conditioners. This surge in power demand during startup must be factored into the generator selection process. Opting for a generator with inadequate starting watts may prevent certain appliances from functioning correctly.
Careful assessment of power requirements is crucial for successful generator operation. Understanding the distinction between running and starting watts ensures appliances operate reliably without overloading the generator. This careful planning ensures effective power delivery during outages and protects both the generator and connected devices.
2. Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency plays a significant role in the operational cost and practicality of portable generators. Generators consume fuel to produce electricity, and the rate of consumption directly impacts the duration of operation on a given fuel supply. A more fuel-efficient generator requires less fuel to produce the same amount of power, translating to lower operating costs and longer runtimes. This efficiency becomes particularly critical during extended power outages when refueling might be difficult or impossible. For example, a highly fuel-efficient generator might run for 10 hours on a single tank of gasoline, while a less efficient model providing the same power output might only run for 6 hours on the same amount of fuel. This difference can be substantial in a prolonged outage scenario. Manufacturers achieve fuel efficiency through various engine technologies, including advanced combustion systems, electronic fuel injection, and variable speed control. These technologies optimize fuel consumption based on the power demand, reducing waste and maximizing runtime.
The practical implications of fuel efficiency extend beyond cost savings. Reduced fuel consumption also translates to less frequent refueling, minimizing disruptions and inconvenience during outages. Furthermore, from an environmental perspective, more fuel-efficient generators produce fewer emissions, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint. For users in remote locations or areas prone to extended power outages, fuel efficiency is a paramount consideration. Choosing a fuel-efficient model ensures a reliable power supply for a longer duration without the need for frequent refueling trips. In disaster preparedness scenarios, a fuel-efficient generator can be a critical lifeline, providing essential power for extended periods.
In summary, fuel efficiency is a crucial factor influencing the long-term value and usability of a portable generator. It directly affects operating costs, runtime, and environmental impact. Consumers should carefully consider fuel efficiency alongside power output and other features when selecting a generator to ensure it meets their specific needs and circumstances. Understanding the practical implications of fuel efficiency allows for informed decision-making and contributes to a more sustainable and cost-effective approach to backup power solutions.
3. Runtime
Runtime represents a critical factor influencing the practicality of portable generators, particularly in extended outage scenarios. It signifies the duration a generator can operate continuously on a single fuel tank. This duration directly correlates with fuel tank capacity and the generator’s fuel consumption rate. A larger fuel tank and higher fuel efficiency contribute to a longer runtime. For instance, a generator with a large fuel tank and efficient engine might operate for 10 hours at 50% load, while a smaller, less efficient unit might only manage 5 hours under the same load. This difference becomes paramount when sustained power is required, such as during prolonged power outages caused by natural disasters. Understanding runtime characteristics is crucial for selecting a generator that aligns with anticipated outage durations.
The practical implications of runtime extend beyond simply powering appliances. Extended runtimes minimize the frequency of refueling, a significant advantage in situations where fuel availability is limited or access is restricted. Consider a scenario where a homeowner relies on a portable generator during a multi-day power outage. A generator with a longer runtime reduces the number of refueling trips necessary, conserving fuel and minimizing disruptions. This extended operation becomes particularly vital for essential appliances like refrigerators, sump pumps, and medical equipment. Furthermore, longer runtimes contribute to convenience, reducing the need for frequent monitoring and intervention. This factor becomes important for users who require uninterrupted power for essential tasks or comfort.
In summary, runtime represents a pivotal consideration when evaluating portable generators. It directly influences the generator’s ability to provide continuous power during outages, affecting both practicality and convenience. Understanding the interplay between fuel tank capacity, fuel consumption rate, and load requirements empowers informed decision-making. Careful consideration of runtime characteristics ensures the selected generator meets the demands of specific scenarios, providing reliable power when needed most.
4. Noise Levels
Noise levels represent a significant consideration when evaluating portable generators, particularly for residential use. These generators produce noise during operation due to engine combustion and cooling fan activity. The level of noise, measured in decibels (dB), varies depending on the generator’s size, engine design, and operating load. Lower noise levels contribute to a more pleasant user experience, especially during extended operation or in noise-sensitive environments. For instance, a generator operating at 60 dB, comparable to normal conversation, is considerably less intrusive than one operating at 75 dB, akin to a vacuum cleaner. Manufacturers employ various noise-reduction technologies, including mufflers, sound-dampening enclosures, and advanced engine design, to minimize operational noise. Selecting a quieter generator enhances usability in residential settings and promotes neighborly harmony.
The practical implications of generator noise extend beyond simple annoyance. In residential areas, excessive noise can disrupt daily activities, impact sleep quality, and potentially violate local noise ordinances. For users seeking to power sensitive electronic equipment, noise can also introduce interference. Consider a scenario where a homeowner utilizes a generator during a power outage. A quieter generator minimizes disruption to family activities and avoids disturbing neighbors. In camping or recreational settings, lower noise levels contribute to a more peaceful outdoor experience. Furthermore, for professional applications, such as on film sets or at outdoor events, quieter generators are essential for maintaining a professional atmosphere. Understanding the noise levels of various generator models empowers users to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and environment.
In conclusion, noise levels are a critical factor influencing the suitability of portable generators for various applications. The noise output significantly impacts user experience, neighborly relations, and adherence to local regulations. Careful consideration of noise levels, alongside power output, runtime, and other key features, ensures the selected generator aligns with specific operational requirements and environmental considerations. This understanding promotes responsible generator usage and minimizes noise-related disruptions.
5. Portability
Portability is a defining characteristic of these generators, directly influencing their usability and suitability for various applications. The ease with which a generator can be transported and positioned significantly impacts its practicality in emergency situations, recreational activities, and professional settings. Understanding the factors contributing to portability allows for informed selection and optimal utilization.
- Weight and Dimensions
The physical size and weight of a generator directly impact its portability. Compact and lightweight models are easier to maneuver and transport, while larger, heavier units may require assistance or specialized equipment for relocation. A lightweight generator might be easily carried by a single individual, whereas a heavier model might necessitate a wheeled cart or multiple people for safe movement. This factor becomes particularly crucial in emergency situations or when accessing remote locations.
- Integrated Handles and Wheels
Ergonomic features such as built-in handles and wheels enhance portability. Well-designed handles provide a secure grip for lifting and carrying, while durable wheels facilitate easy rolling across various terrains. A generator equipped with never-flat wheels, for instance, can be easily maneuvered across uneven ground, while a foldable handle simplifies storage. These features contribute to user convenience and reduce strain during transport.
- Compact Design
A compact design minimizes storage space requirements and enhances transportability. Generators with a smaller footprint occupy less space in vehicles or storage areas, allowing for efficient transport and convenient storage. A compact, stackable generator, for example, maximizes space utilization in a truck bed or storage shed. This consideration becomes particularly relevant for users with limited storage capacity or who frequently transport their generator.
- Frame Material and Construction
The frame material and overall construction of a generator influence its durability and resistance to damage during transport and handling. Robust frames constructed from durable materials, such as steel or heavy-duty plastic, protect internal components and ensure longevity. A generator with a reinforced steel frame, for example, offers greater protection against impacts during transport compared to a lightweight plastic frame. This durability is essential for maintaining the generator’s integrity and functionality over time.
These elements of portability collectively influence the ease of use and practicality of portable generators across diverse applications. Whether powering a campsite, providing backup power during an outage, or serving as a reliable power source on a job site, portability directly impacts the generators effectiveness. Careful consideration of these factors ensures selection of a generator that aligns with specific needs and usage scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding portable generators for residential applications. Understanding these key aspects facilitates informed decision-making and ensures safe and effective generator usage.
Question 1: What size generator is needed to power essential household appliances?
Generator sizing depends on the combined wattage of the appliances one intends to operate simultaneously. Calculating the total wattage requirement of essential appliances, including refrigerators, sump pumps, and lighting, is crucial for selecting a generator with adequate capacity. Consulting an electrician for guidance is recommended.
Question 2: What type of fuel is most suitable for portable generators?
Gasoline and propane are common fuel sources. Gasoline offers wider availability, while propane provides longer storage life and cleaner burning. The choice depends on individual needs and fuel availability during emergencies.
Question 3: How often should a portable generator undergo maintenance?
Regular maintenance, as outlined in the manufacturer’s instructions, is essential for optimal performance and longevity. Typical maintenance includes oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement at recommended intervals. Adherence to the maintenance schedule ensures reliable operation and extends the generator’s lifespan.
Question 4: Where should a portable generator be placed during operation?
Generators should always be operated outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from doors, windows, and vents. This placement minimizes the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning, a serious hazard associated with generator exhaust.
Question 5: Is it safe to connect a portable generator directly to household wiring?
Direct connection to household wiring is unsafe and potentially dangerous. A qualified electrician should install a transfer switch for safe connection to home circuits. This prevents backfeeding, which can endanger utility workers and damage appliances.
Question 6: What safety precautions are essential when operating a portable generator?
Essential safety precautions include allowing the generator to cool before refueling, grounding the unit properly, and using appropriate extension cords. Consulting the owner’s manual for model-specific safety guidelines is crucial before operation.
Understanding these frequently asked questions promotes safe and effective generator operation. Further research and consultation with qualified professionals are recommended for comprehensive knowledge and safe usage practices.
The following section provides additional resources and information regarding portable generator selection, operation, and maintenance.
Investing in Power
Careful consideration of factors such as power output, fuel efficiency, runtime, noise levels, and portability is crucial when selecting a portable generator. Understanding these elements ensures the chosen unit aligns with specific power requirements and operational circumstances. Prioritizing safety through proper grounding, ventilation, and connection procedures is paramount for mitigating potential hazards. Regular maintenance, in accordance with manufacturer guidelines, ensures optimal performance and prolongs the generator’s operational lifespan. Informed decision-making, combined with responsible usage practices, maximizes the benefits of these valuable power solutions.
Reliable access to backup power provides peace of mind and safeguards against disruptions caused by unforeseen outages. Investing in a portable generator represents a commitment to preparedness, ensuring essential services remain operational during critical periods. Continued exploration of advancements in generator technology promises even more efficient, sustainable, and user-friendly power solutions for the future. A well-informed consumer, equipped with the knowledge presented here, is empowered to make a sound investment in power resilience and household preparedness.