A top-tier, easily transportable power source designed for residential use during unexpected power outages offers a crucial safety net. This equipment provides electricity for essential appliances and devices, ensuring continued functionality during blackouts caused by severe weather, grid failures, or other unforeseen circumstances. For instance, a unit might power refrigerators to prevent food spoilage, sump pumps to mitigate flooding, and communication devices to maintain contact with emergency services.
Reliable backup power is paramount for maintaining safety, comfort, and connectivity during emergencies. Historical data reveals the disruptive and potentially hazardous impacts of extended power outages, highlighting the critical role of independent power generation. Access to electricity safeguards vulnerable individuals reliant on medical equipment, facilitates communication, and enables homeowners to maintain a safe and habitable environment. The ability to rapidly deploy a power source can significantly mitigate the negative impacts of unforeseen power disruptions.
Factors influencing the selection of an appropriate emergency power solution include power output, fuel type, runtime, noise level, and portability. Subsequent sections will explore these criteria in detail, providing guidance on evaluating various models and selecting the optimal solution for individual needs and circumstances.
Essential Tips for Emergency Power Preparedness
Careful planning and preparation are crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of a portable generator during emergencies. The following tips provide valuable guidance for selecting, installing, and operating a unit safely and efficiently.
Tip 1: Accurate Power Needs Assessment: Calculate the wattage required to power essential appliances and devices. Consider both starting wattage (initial surge) and running wattage (continuous operation). An undersized generator may overload and fail, while an oversized one consumes excessive fuel.
Tip 2: Appropriate Fuel Selection and Storage: Understand the fuel requirements (gasoline, propane, etc.) of the chosen generator and store fuel safely in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Rotate fuel stocks periodically to maintain freshness.
Tip 3: Safe Generator Placement: Operate generators outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from doors, windows, and air intakes. Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious hazard. Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces.
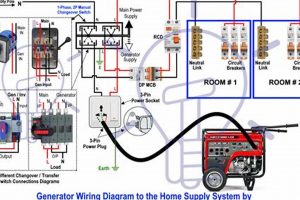
Tip 4: Proper Connection Procedures: Utilize a transfer switch for safe connection to household circuits, preventing backfeeding into the power grid, which poses a danger to utility workers. Avoid direct connection to wall outlets.
Tip 5: Routine Maintenance: Adhere to manufacturer recommendations for oil changes, air filter cleaning, and other maintenance tasks. Regular maintenance ensures reliable performance during emergencies.
Tip 6: Dry Run Testing: Periodically test the generator to verify functionality and familiarize oneself with its operation. This practice confirms operational readiness and identifies potential issues before an emergency arises.
Tip 7: Consider Local Regulations: Research and comply with local ordinances and regulations concerning generator usage. Some areas have noise restrictions or permit requirements.
Adherence to these guidelines contributes significantly to the safe and effective utilization of emergency power, ensuring household safety and minimizing disruptions during unforeseen outages.
By taking proactive steps and implementing these strategies, homeowners can effectively mitigate the impact of power outages and maintain a sense of normalcy during challenging circumstances.
1. Power Output
Power output, measured in watts, stands as a critical determinant when selecting a portable generator for emergencies. This metric directly dictates which appliances and devices the generator can power simultaneously. An inadequate power output can lead to overloaded circuits, generator failure, and potential damage to connected equipment. Conversely, an excessively high output results in unnecessary fuel consumption and increased operating costs. Calculating the required wattage involves summing the running wattage of essential appliances intended for simultaneous use during an outage. For instance, a homeowner might need to power a refrigerator (150W), a sump pump (750W), and several lights (100W total), requiring a generator with a minimum output of 1000W. Starting wattage, or the surge power required to initiate certain appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners, should also be factored in.
Understanding power output enables informed decisions tailored to specific needs. A family reliant on electrically powered medical equipment requires a significantly higher output than a household primarily concerned with lighting and basic communication. Choosing the correct power output ensures essential services remain operational during emergencies, minimizing disruption and maximizing safety. For example, a generator capable of powering a furnace during a winter storm could prevent pipes from freezing, averting potentially costly repairs. Similarly, sufficient power to operate well pumps ensures continued access to water for essential needs.
Selecting a generator with the appropriate power output is fundamental to emergency preparedness. Accurate assessment of power requirements, combined with a clear understanding of starting and running wattage, allows homeowners to invest in a generator that meets their specific needs, ensuring a reliable power source during critical situations. Failing to properly evaluate power needs can lead to inadequate performance or excessive expenditure, compromising the effectiveness of emergency power solutions.
2. Fuel Type
Fuel type significantly influences the practicality and effectiveness of a portable generator for home emergencies. Common fuel types include gasoline, propane, and diesel. Each presents distinct advantages and disadvantages impacting generator selection. Gasoline offers widespread availability but requires careful storage due to flammability and a limited shelf life. Propane, while requiring larger, heavier tanks, boasts a longer shelf life and cleaner combustion. Diesel, known for its efficiency and long engine life, often powers larger, more expensive units. Fuel choice depends heavily on individual circumstances and the anticipated duration of outages. A homeowner with limited storage space might favor propane despite its bulk, while those anticipating extended outages might opt for diesel’s efficiency. Choosing the appropriate fuel type is crucial for ensuring a readily available and reliable power source during emergencies. For instance, during a prolonged natural disaster, access to gasoline might be limited, while pre-filled propane tanks provide a readily available fuel source.
Understanding fuel-related considerations, such as storage, availability, and cost, allows for informed decisions aligned with specific needs and local conditions. Fuel costs fluctuate, impacting long-term operational expenses. Storage requirements vary significantly; gasoline requires specialized containers and periodic rotation, while propane necessitates larger, heavier tanks. Regional fuel availability plays a critical role, particularly in disaster-prone areas. Accessibility to specific fuel types during emergencies can determine a generator’s usefulness. For example, in areas prone to hurricanes, propane might be more readily available than gasoline in the immediate aftermath of a storm. Careful consideration of these factors ensures the chosen generator remains a viable power source when needed most.
Selecting the appropriate fuel type is integral to ensuring the long-term effectiveness of a portable generator for home emergencies. The chosen fuel type must align with anticipated usage patterns, storage capabilities, and regional availability. Failing to consider these factors can compromise the generator’s utility during critical situations. A comprehensive understanding of fuel-related implications allows homeowners to make informed decisions that maximize the reliability and longevity of their emergency power solutions.
3. Runtime
Runtime, representing the duration a portable generator operates on a full fuel tank, is a crucial factor influencing its suitability for home emergencies. Extended power outages necessitate generators capable of providing sustained power for essential needs. Runtime directly impacts the frequency of refueling, a critical consideration during emergencies when fuel availability might be limited or access restricted.
- Fuel Tank Capacity:
Larger fuel tanks generally translate to longer runtimes. A higher capacity tank reduces the frequency of refueling, a significant advantage during extended outages or when access to fuel is challenging. For example, a 15-gallon tank will typically provide a longer runtime than a 5-gallon tank, assuming similar fuel consumption rates. This extended operation reduces the logistical challenges associated with refueling during emergencies.
- Load:
The power demand placed on the generator significantly influences runtime. Higher loads consume fuel more rapidly, shortening the operational duration. Running fewer appliances or opting for energy-efficient models can extend the runtime. For instance, using LED lights instead of incandescent bulbs reduces power consumption and extends the generator’s runtime. Careful load management is essential for maximizing runtime during outages.
- Engine Efficiency:
Engine efficiency directly affects fuel consumption and, consequently, runtime. More efficient engines extract more energy from the fuel, leading to longer runtimes under equivalent loads. Modern inverter generators often boast higher efficiency compared to traditional models. This efficiency translates to longer operation on a single tank of fuel, a valuable advantage during emergencies.
- Fuel Type:
The type of fuel also plays a role in runtime. Diesel generators often exhibit greater fuel efficiency compared to gasoline counterparts, leading to potentially longer runtimes. However, the runtime advantage of diesel must be weighed against other factors like fuel cost and storage considerations. Choosing the right fuel type requires balancing runtime requirements with practical considerations like fuel availability and storage capacity.
Optimizing runtime involves selecting a generator with adequate fuel capacity, managing power consumption effectively, and considering engine efficiency. Matching the anticipated outage duration with the generator’s runtime capabilities is crucial for ensuring uninterrupted power for essential needs during emergencies. Balancing runtime with other factors like fuel type, portability, and cost allows homeowners to select the most appropriate generator for their specific circumstances, maximizing preparedness for extended power outages.
4. Noise Level
Noise level represents a significant consideration when selecting a portable generator for home emergencies. Excessive noise can disrupt neighbors, violate local ordinances, and create a stressful environment during already challenging circumstances. Generators produce noise primarily from engine operation and exhaust. Noise levels, measured in decibels (dB), vary considerably between models. Lower dB ratings indicate quieter operation. Choosing a quieter generator promotes neighborhood harmony and minimizes disruption during extended use. For instance, a generator operating at 70dB, comparable to normal conversation, proves considerably less intrusive than one operating at 90dB, equivalent to a lawnmower. This difference can be crucial for maintaining positive community relations and avoiding potential noise complaints, particularly during extended outages.
Several factors influence generator noise levels, including engine design, muffler effectiveness, and enclosure construction. Modern inverter generators generally operate quieter than conventional models due to their variable engine speed and advanced muffler systems. Sound-dampening enclosures further reduce noise output. Investing in a quieter generator enhances quality of life during emergencies, minimizing stress and disruption. For example, families with young children or individuals working from home benefit significantly from a low-noise generator, enabling rest and concentration during power outages. Furthermore, some municipalities enforce noise ordinances, restricting generator operation during specific hours. Selecting a quiet generator ensures compliance with these regulations, avoiding potential fines or legal issues.
Minimizing noise pollution through careful generator selection contributes to a more peaceful and less stressful emergency experience. Prioritizing low-noise models demonstrates consideration for neighbors and enhances overall well-being during challenging times. Understanding the factors influencing noise levels and considering the specific environment allows homeowners to select a generator that balances power needs with noise considerations. This informed approach ensures reliable power without compromising the peace and quiet of the surrounding community.
5. Portability
Portability represents a critical aspect of “best portable generator for home emergencies,” directly influencing usability and practicality. Weight, size, and integrated features like wheels and handles dictate ease of transport and deployment. A lightweight, compact unit with sturdy wheels allows for quick maneuvering and positioning, even in challenging terrain or during inclement weather. Conversely, a heavy, bulky generator presents logistical hurdles, potentially hindering timely deployment when power is most crucial. Consider a scenario where flooding necessitates relocating the generator to higher ground; a portable design proves essential for maintaining power in such dynamic situations. Similarly, a homeowner needing to transport the generator from storage to the desired operating location benefits significantly from a lightweight, easily maneuverable design. The practical implications of portability underscore its importance in selecting an emergency power solution.
Practical applications highlight the significance of portability. Imagine a senior citizen needing to deploy a generator independently during a power outage. A lightweight, easily maneuverable unit empowers them to restore essential power without assistance. Contrast this with a heavy generator requiring significant physical exertion, potentially rendering it unusable for certain individuals. Moreover, compact designs simplify storage, maximizing available space in garages, sheds, or other storage areas. The ability to quickly and easily transport a generator within the property facilitates optimal placement for power distribution and noise minimization. This flexibility proves invaluable in diverse situations, from powering essential appliances within the home to providing electricity for outdoor equipment during emergencies.
In conclusion, portability directly impacts the effectiveness of a generator during emergencies. Evaluating weight, size, and integrated mobility features allows for informed decisions aligned with individual needs and circumstances. A portable design enhances accessibility, simplifies deployment, and optimizes usability, ensuring a reliable and readily available power source when needed most. Failing to prioritize portability can compromise the practicality and effectiveness of a generator during critical situations, hindering access to essential power during emergencies.
6. Safety Features
Safety features represent paramount considerations when selecting a portable generator for home emergencies. These features safeguard users, protect connected equipment, and prevent hazardous situations. Overlooking safety features can lead to severe consequences, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire hazards, and electrocution. Prioritizing safety ensures the generator serves as a reliable power source without compromising well-being.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO) Detection and Shutdown:
CO, an odorless, colorless, and deadly gas, poses a significant threat during generator operation. CO sensors automatically shut down the generator if dangerous CO levels are detected, preventing potential fatalities. This feature is crucial for mitigating the risk of CO poisoning, particularly in situations where ventilation might be compromised. For example, a sudden wind shift could redirect exhaust fumes toward occupied areas, making CO detection a critical safety measure.
- Overload Protection:
Overloading a generator by exceeding its wattage capacity can damage the unit and connected appliances, potentially causing fires. Overload protection circuits automatically shut down the generator when excessive current draw is detected, preventing damage and ensuring safe operation. This feature is essential when powering multiple devices, protecting both the generator and connected electronics. For instance, attempting to run a power-hungry appliance like an air conditioner alongside other devices might overload the generator without adequate overload protection.
- Low-Oil Shutdown:
Insufficient oil levels can cause severe engine damage. Low-oil shutdown features automatically turn off the generator when oil levels drop below a safe threshold, preventing costly repairs and extending the generator’s lifespan. This proactive measure ensures the engine remains lubricated, mitigating the risk of catastrophic failure during extended operation. Without this feature, a minor oil leak could lead to extensive engine damage if the generator continues running.
- Covered Outlets and GFCI Protection:
Covered outlets protect against moisture and debris, reducing the risk of electrical shock. Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) protection further enhances safety by detecting ground faults and immediately cutting off power, preventing electrocution. These features are particularly crucial in outdoor environments where exposure to the elements is inevitable. For example, using a generator during a rainstorm necessitates covered outlets and GFCI protection to minimize the risk of electrical hazards.
Prioritizing these safety features ensures that a portable generator serves as a reliable and safe power source during emergencies. Selecting a generator equipped with these features minimizes potential hazards, protecting users and property. Investing in safety contributes significantly to peace of mind during critical situations, allowing individuals to focus on managing the emergency rather than worrying about potential generator-related dangers. A generator without adequate safety features compromises the well-being of users and increases the risk of accidents, negating the intended benefits of emergency power provision.
7. Budget
Budgetary constraints play a significant role in selecting a portable generator for home emergencies. Financial considerations influence available options, impacting power output, features, and fuel type. Balancing desired functionalities with affordability requires careful evaluation of needs versus available resources. A well-defined budget prevents overspending while ensuring the chosen generator meets essential requirements. Failing to establish a realistic budget can lead to either purchasing an inadequate generator or exceeding financial limitations.
- Initial Purchase Price:
Generator prices vary significantly based on power output, fuel type, features, and brand reputation. Higher wattage, advanced features like inverter technology, and reputable brands typically command higher prices. Establishing a clear budget helps narrow down options, focusing the search on generators within a specific price range. For example, a homeowner with a limited budget might prioritize essential power needs over advanced features, opting for a more affordable conventional generator over a feature-rich inverter model.
- Operating Costs:
Fuel consumption represents a recurring expense influencing long-term generator ownership costs. Fuel efficiency varies depending on engine type, load, and fuel type itself. Calculating estimated operating costs based on anticipated usage patterns and fuel prices helps assess the long-term affordability of different models. A more fuel-efficient generator, while potentially more expensive initially, might offer long-term cost savings, particularly for users anticipating frequent or extended operation. For instance, a diesel generator, known for its efficiency, could prove more economical in the long run compared to a gasoline equivalent despite a higher upfront cost.
- Maintenance Expenses:
Regular maintenance, including oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug replacements, contributes to overall generator ownership costs. Maintenance schedules and associated costs vary between models and manufacturers. Factoring in these expenses helps determine the true cost of ownership and prevents unexpected financial burdens. Choosing a generator with readily available and affordable replacement parts minimizes maintenance expenses over time. For example, opting for a common engine type with readily available parts can significantly reduce maintenance costs compared to a specialized model requiring proprietary components.
- Long-Term Value:
Evaluating long-term value involves considering the generator’s lifespan, durability, and resale potential. A well-maintained generator from a reputable brand typically retains value better than a less durable or lesser-known brand. Investing in a higher-quality generator, while potentially more expensive initially, might offer better long-term value, particularly for users seeking a reliable power source for years to come. For instance, a robustly constructed generator designed for heavy-duty use might represent a better long-term investment compared to a less durable model, even if the initial cost is higher.
A realistic budget guides purchasing decisions, ensuring the selected portable generator balances essential power needs with financial constraints. Considering both initial purchase price and long-term operating and maintenance expenses provides a comprehensive understanding of the true cost of generator ownership. This informed approach empowers homeowners to make sound financial decisions, selecting a reliable and affordable emergency power solution without exceeding budgetary limitations. Failing to adequately consider budgetary constraints can result in purchasing an unsuitable generator or compromising financial stability, hindering effective emergency preparedness.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding portable generators for home emergencies, providing concise and informative responses to facilitate informed decision-making.
Question 1: How is the necessary generator size determined for a specific home?
Generator sizing depends on the combined wattage requirements of appliances and devices intended for simultaneous use during an outage. Calculating the sum of running watts and factoring in starting wattage for appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners provides an accurate estimate of required generator capacity.
Question 2: What differentiates conventional and inverter generators?
Conventional generators produce power at a constant speed, while inverter generators adjust engine speed based on demand, resulting in greater fuel efficiency and quieter operation. Inverter generators also produce cleaner power, safer for sensitive electronics.
Question 3: Where should a portable generator be operated?
Generators must be operated exclusively outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from doors, windows, and air intakes. Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning.
Question 4: How is a portable generator safely connected to a home’s electrical system?
A qualified electrician should install a transfer switch, ensuring safe connection to household circuits. Transfer switches prevent backfeeding into the power grid, protecting utility workers from electrocution. Never connect a generator directly to a wall outlet.
Question 5: What maintenance is required for a portable generator?
Regular maintenance, as outlined in the manufacturer’s instructions, is essential for reliable operation. Typical maintenance includes oil changes, air filter cleaning or replacement, and spark plug replacement. Adhering to the recommended maintenance schedule ensures optimal performance and extends the generator’s lifespan.
Question 6: What safety precautions are essential when using a portable generator?
Crucial safety precautions include operating the generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area, never refueling a hot engine, storing fuel safely in approved containers, and keeping the generator dry to prevent electrical hazards. Familiarization with and adherence to all safety guidelines outlined in the owner’s manual are paramount for safe and effective operation.
Careful consideration of these frequently asked questions provides valuable insights for selecting and operating a portable generator safely and effectively during emergencies. Understanding these key aspects of generator ownership ensures informed decisions, maximizing preparedness and minimizing potential risks.
Beyond these frequently asked questions, further research and consultation with qualified professionals can provide additional guidance tailored to specific circumstances.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal portable generator for home emergencies requires careful consideration of various factors. Power output, fuel type, runtime, noise level, portability, safety features, and budget constraints all contribute significantly to the selection process. A thorough understanding of these elements ensures the chosen generator aligns with specific needs and circumstances. Adequate power output is crucial for supporting essential appliances, while the chosen fuel type must be readily available and align with storage capabilities. Runtime dictates the duration of operation on a single fuel tank, influencing refueling frequency. Noise levels impact neighborhood harmony and compliance with local ordinances. Portability affects ease of transport and deployment, while robust safety features mitigate potential hazards. Adherence to budgetary constraints ensures a cost-effective solution without compromising essential functionalities.
Investing in a reliable portable generator provides essential power during unforeseen outages, safeguarding households and minimizing disruptions. Proactive planning and informed decision-making ensure access to critical power, mitigating the impact of emergencies and enhancing overall preparedness. Careful consideration of the factors outlined herein empowers homeowners to select the most appropriate portable generator, enhancing resilience and ensuring a sense of security during challenging times. Preparation is paramount; a well-chosen generator stands as a crucial investment in household safety and well-being.