A compact, mobile power source, typically fueled by gasoline or propane, can provide temporary electrical power to a residence during outages or in locations lacking utility grid access. These units offer varying power outputs, catering to essential appliances or entire household circuits, depending on their capacity. For instance, a smaller unit might power lights and refrigerators, while a larger one could run HVAC systems and other high-demand electronics.
Backup power supplies offer crucial support during natural disasters, grid failures, or planned outages, ensuring continuity of essential services and enhancing safety. Historically, reliance on such solutions has grown alongside increasing electrification of homes and the recognition of vulnerabilities within centralized power grids. Their value extends beyond emergencies, providing power for remote locations, construction sites, or outdoor events.
Understanding the selection, safe operation, and maintenance of these devices is essential for maximizing their effectiveness and longevity. This involves consideration of power requirements, fuel type, runtime, noise levels, and safety features. Subsequent sections will explore these topics in detail, offering guidance for potential users.
Tips for Utilizing Backup Power
Effective and safe operation of a backup power supply requires careful planning and adherence to safety guidelines. The following tips offer crucial insights into essential considerations.
Tip 1: Accurate Power Assessment: Calculate the wattage requirements of appliances intended for connection. This ensures the unit’s capacity adequately meets demand, preventing overload and potential damage.
Tip 2: Proper Placement: Operate units outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from windows and doors, to minimize carbon monoxide exposure risks.
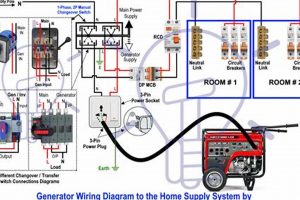
Tip 3: Safe Connection: Utilize a transfer switch for safe connection to household circuits, avoiding direct connection to wall outlets, which can create backfeeding hazards for utility workers.
Tip 4: Fuel Management: Store fuel safely in approved containers and in well-ventilated areas. Exercise caution during refueling, ensuring the unit is cool to prevent fire hazards.
Tip 5: Regular Maintenance: Adhere to manufacturer recommendations for oil changes, air filter cleaning, and other routine maintenance to optimize performance and longevity.
Tip 6: Grounding: Ensure proper grounding to prevent electrical shocks. Consult a qualified electrician if grounding procedures are unclear.
Tip 7: Weather Protection: Shield the unit from the elements during operation, using a canopy or other appropriate cover, while maintaining adequate ventilation.
Adherence to these guidelines contributes significantly to the safe and efficient use of backup power, ensuring reliable performance during outages and minimizing potential risks.
Careful consideration of these points will facilitate informed decisions regarding the selection and operation of a unit best suited to individual needs and circumstances.
1. Power Output
Power output, measured in watts, represents a critical factor in selecting a portable generator for residential use. This specification directly dictates the number and type of appliances the generator can power simultaneously. Understanding power requirements is essential to avoid overloading the unit, which can lead to damage or failure. A higher wattage translates to a greater capacity to operate multiple or high-demand appliances concurrently. For example, a refrigerator might require 700 watts, while a sump pump could demand 1500 watts. Attempting to run both simultaneously on a 1000-watt generator would likely result in an overload.
Calculating the cumulative wattage of essential appliances provides a baseline for determining the necessary generator capacity. Adding a safety margin to this calculation is advisable to accommodate potential surges or unforeseen power demands. This proactive approach ensures the generator can handle fluctuations and prevents disruptions during operation. Different generator models offer varying power outputs, catering to diverse needs. Smaller units typically provide power for essential appliances, while larger units can support entire household circuits during extended outages. Selecting the appropriate power output ensures reliable operation and prevents costly equipment damage.
Choosing a generator with inadequate power output can lead to operational limitations and potential safety hazards. Conversely, selecting a generator with excessive power output can result in unnecessary fuel consumption and higher purchase costs. Therefore, careful assessment of power needs is paramount in optimizing generator selection for efficiency and effectiveness. Matching the generator’s power output to specific requirements ensures reliable performance and avoids unnecessary expenditure.
2. Fuel Type
Fuel type significantly influences the practicality and cost-effectiveness of a portable generator for residential use. Common fuel options include gasoline, propane, and diesel. Each presents distinct advantages and disadvantages, impacting generator selection based on individual needs and circumstances. Gasoline offers widespread availability and generally lower upfront generator costs. However, gasoline has a limited shelf life, requiring periodic replacement to prevent fuel degradation and engine issues. Propane offers extended storage stability and cleaner combustion, reducing maintenance requirements. Propane generators often operate more quietly than gasoline counterparts. Diesel fuel provides high energy density and exceptional runtime, making it suitable for extended outages or continuous operation. However, diesel generators tend to be more expensive initially.
The choice of fuel type depends on factors such as anticipated usage frequency, storage capacity, and budget constraints. For infrequent, short-duration outages, gasoline may suffice. For longer outages or in areas with frequent power disruptions, propane or diesel offers greater reliability. Fuel availability also plays a crucial role. During emergencies, gasoline supplies can become strained, whereas propane might be more readily accessible depending on local infrastructure. Considering these factors helps ensure the chosen fuel aligns with specific requirements and anticipated operating conditions.
Understanding the characteristics of each fuel type allows for informed decisions, optimizing generator performance and mitigating potential drawbacks. Careful consideration of fuel-related factors ensures reliable power generation when needed, minimizes operational disruptions, and aligns with individual budgetary and logistical constraints. Ultimately, the optimal fuel choice depends on a balanced assessment of these practical considerations.
3. Runtime
Runtime, representing the duration a portable generator can operate continuously on a single fuel tank, constitutes a crucial factor influencing its suitability for various applications. This duration directly impacts the generator’s ability to provide uninterrupted power during outages or in off-grid scenarios. Understanding runtime characteristics is essential for matching a generator to specific power needs and anticipated usage patterns. Runtime considerations become particularly critical during extended power outages or in locations lacking readily available fuel resupply.
- Fuel Tank Capacity:
Larger fuel tanks generally translate to longer runtimes. A higher fuel capacity reduces the frequency of refueling, especially crucial during extended outages. For instance, a generator with a 10-gallon tank will typically run longer than one with a 5-gallon tank, assuming comparable fuel consumption rates. This extended operation reduces interruptions and ensures continuous power supply for essential appliances or equipment.
- Load:
The power demand placed on the generator directly affects its runtime. Higher loads consume fuel more rapidly, shortening the operational duration. Running a few essential appliances will allow for a longer runtime than powering an entire household. Understanding load requirements and managing power consumption can significantly extend the generator’s operational period on a single tank.
- Generator Efficiency:
More fuel-efficient generators generally offer longer runtimes for a given fuel tank size. Technological advancements in engine design and power management contribute to improved fuel efficiency. A more efficient generator minimizes fuel consumption, maximizing runtime and reducing operating costs. This efficiency becomes especially valuable during extended operation.
- Fuel Type:
The type of fuel used also influences runtime. Diesel generators often offer longer runtimes compared to gasoline or propane equivalents due to diesel’s higher energy density. This characteristic makes diesel generators suitable for prolonged operation with fewer refueling interruptions. However, the choice of fuel also depends on factors such as availability, storage practicality, and cost considerations.
Matching runtime characteristics to specific power requirements is essential for ensuring uninterrupted power during outages or off-grid usage. Careful consideration of fuel tank capacity, load management, generator efficiency, and fuel type allows users to select a generator that aligns with their anticipated needs and usage patterns. Optimizing runtime ensures reliable power availability, reduces the frequency of refueling, and enhances the overall practicality of the generator for residential applications.
4. Noise Level
Noise level represents a significant consideration when selecting a portable generator for residential use. Measured in decibels (dB), this factor impacts neighborhood tranquility and user comfort. Generators produce varying noise levels depending on their size, engine type, and construction. Operating a loud generator can create disturbances for both the user and surrounding neighbors, potentially leading to noise complaints or strained relationships. Conversely, quieter generators minimize noise pollution, contributing to a more peaceful environment. For instance, a generator operating at 70 dB, comparable to a vacuum cleaner, will be significantly less intrusive than one operating at 90 dB, similar to a motorcycle. This difference can be substantial, especially during extended operation or overnight use.
Manufacturers often specify noise levels in their product literature. However, real-world operating conditions can influence the perceived noise level. Factors such as terrain, proximity to reflective surfaces, and load can affect the perceived sound intensity. Understanding these influences helps manage noise impact effectively. Some manufacturers employ noise-reduction technologies, such as mufflers and sound-dampening enclosures, to minimize operational noise. Selecting a generator with lower decibel ratings and considering its placement contributes significantly to reducing noise pollution. Locating the generator farther from living areas and using sound-absorbing barriers can further mitigate noise impact.
Considering noise level during generator selection promotes peaceful coexistence with neighbors and enhances user comfort. Evaluating manufacturer specifications, understanding environmental influences, and employing noise-reduction strategies contributes to a more positive generator ownership experience. Prioritizing quieter operation minimizes disruptions, fosters positive community relations, and ensures a less intrusive presence during power outages or off-grid activities. This attention to noise level demonstrates consideration for others and enhances the overall quality of life for both the user and the surrounding community.
5. Safety Features
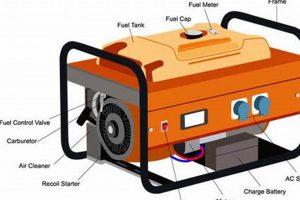
Safety features in portable generators designed for residential use are paramount for mitigating potential hazards associated with electricity and combustion byproducts. These features play a crucial role in protecting users, property, and connected appliances from harm. Overlooking or neglecting these safety mechanisms can lead to serious consequences, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire, electrocution, or equipment damage. For instance, a generator lacking a properly functioning low-oil shutoff could experience engine seizure and potential fire hazards due to overheating. Similarly, operating a generator without adequate grounding can create a risk of electrocution. A carbon monoxide detector integrated within the generator serves as a critical safeguard against the buildup of this odorless, colorless, and potentially lethal gas. Automatic voltage regulation protects sensitive electronics from damage caused by voltage fluctuations, ensuring the safe operation of connected devices.
Several crucial safety features contribute significantly to the safe operation of portable generators. A properly functioning low-oil shutoff automatically shuts down the engine when oil levels drop below a critical threshold, preventing engine damage and potential fire hazards. Overload protection circuits prevent damage to the generator and connected appliances by automatically shutting down the unit in case of excessive power demand. A well-maintained spark arrestor prevents the escape of sparks from the exhaust, reducing the risk of fire, particularly in dry or flammable environments. These safety mechanisms work in concert to create a safer operating environment, mitigating potential risks associated with generator operation.
Understanding and utilizing these safety features is crucial for responsible generator operation. Regular inspection and maintenance of these features ensure their continued effectiveness in preventing accidents and protecting users. Consulting the manufacturer’s operating manual and adhering to recommended safety guidelines are essential for maximizing safety and minimizing potential risks. Neglecting these precautions can compromise safety and lead to preventable accidents. Prioritizing safety features during generator selection and operation safeguards users, protects property, and ensures the reliable and secure provision of backup power. This proactive approach to safety contributes to a more secure and reliable power solution for residential applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the selection, operation, and maintenance of portable generators for residential applications.
Question 1: How is the appropriate generator size determined for a specific residence?
Generator sizing depends on the cumulative wattage of appliances intended for simultaneous operation. Calculating the total wattage requirement and adding a safety margin ensures adequate capacity. Consulting an electrician can provide further guidance.
Question 2: What are the primary fuel options for portable generators, and how do they differ?
Common fuel types include gasoline, propane, and diesel. Gasoline offers widespread availability but has storage limitations. Propane offers extended storage stability but requires larger tanks. Diesel provides high efficiency and long runtimes but comes at a higher initial cost. The optimal fuel type depends on individual needs and circumstances.
Question 3: Where should a portable generator be placed during operation for safety?
Generators should always be operated outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from windows, doors, and other openings. This placement minimizes carbon monoxide exposure risks and ensures adequate airflow for proper combustion.
Question 4: What are the essential safety precautions to observe when using a portable generator?
Essential safety precautions include never refueling a hot generator, ensuring proper grounding, using a transfer switch for safe connection to household circuits, and operating the generator in a dry location away from flammable materials. Regularly inspecting and maintaining safety features, such as the low-oil shutoff and carbon monoxide detector, is crucial.
Question 5: How frequently should a portable generator undergo maintenance?
Maintenance frequency depends on usage and manufacturer recommendations. Regular maintenance typically includes oil changes, air filter cleaning, spark plug replacement, and checking fuel lines. Adhering to the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Question 6: What is the significance of a transfer switch when using a portable generator?
A transfer switch provides a safe and reliable method for connecting a generator to a home’s electrical system. It prevents backfeeding, a dangerous condition that can energize downed power lines, posing risks to utility workers. Professional installation of a transfer switch is recommended.
Understanding these frequently asked questions contributes to safer and more effective generator utilization. Consulting the manufacturer’s documentation and seeking professional advice when needed further enhance safe and reliable operation.
For further information on specific models and technical specifications, please consult individual product documentation or contact qualified professionals.
Portable Generator for House
Careful consideration of factors such as power output, fuel type, runtime, noise level, and safety features is essential when selecting a portable generator for residential use. Understanding these elements ensures the chosen unit aligns with specific power requirements and operating conditions. Proper operation and regular maintenance are crucial for maximizing the generator’s lifespan and ensuring safe and reliable performance during power outages or off-grid activities. Prioritizing safety features and adhering to manufacturer guidelines mitigates potential risks associated with generator operation.
Reliable access to backup power provides peace of mind and safeguards against disruptions caused by unforeseen events. Investing in a portable generator represents a proactive measure to ensure continuity of essential services and enhance safety during emergencies. Informed decision-making and responsible operation contribute significantly to the effective utilization of this valuable resource. Advancements in generator technology continue to improve efficiency, reduce noise levels, and enhance safety, further solidifying the role of portable generators in providing reliable backup power for residential applications.