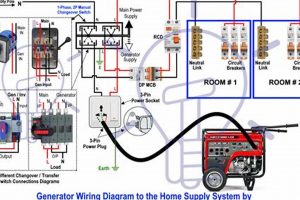
A tool designed to assist homeowners in determining the appropriate generator size for their needs helps match power output to expected load. This typically involves inputting information about appliances and devices planned for backup power, including their wattage requirements. For example, a user might enter details about refrigerators, sump pumps, and essential lighting circuits to calculate necessary generator capacity.
Accurately sizing a generator is crucial for ensuring sufficient power during outages while avoiding unnecessary expense from an oversized unit. Historically, generator selection often relied on rough estimations or generic recommendations, leading to potential underpowering or excessive fuel consumption. These tools offer a more precise and efficient approach, improving preparedness and cost-effectiveness. They empower homeowners to make informed decisions, balancing essential power needs with budget constraints.
Understanding the principles behind generator sizing, the diverse types of generators available, and practical considerations like fuel type and maintenance requirements are key aspects of emergency power planning. Exploring these topics will provide a comprehensive overview of home backup power solutions.
Tips for Accurate Generator Sizing
Proper generator sizing is crucial for ensuring adequate power during outages. These tips offer guidance for effectively utilizing online tools and understanding power requirements.
Tip 1: Inventory Appliances: Create a comprehensive list of all appliances and devices requiring backup power. This includes necessities like refrigerators, freezers, and sump pumps, as well as conveniences like lights, fans, and laptops.
Tip 2: Determine Wattage: Locate the wattage requirements for each appliance. This information is typically found on a label or in the owner’s manual. Note both running wattage (power needed for continuous operation) and starting wattage (the surge of power required to start the appliance).
Tip 3: Account for Starting Wattage: Starting wattage, often significantly higher than running wattage, must be factored into calculations. Failure to do so can lead to the generator overloading and tripping breakers.
Tip 4: Consider Future Needs: Anticipate potential future power needs. Plan for new appliances or electronic devices that may be acquired later.
Tip 5: Research Generator Types: Different generator types (portable, standby, inverter) offer varying features and benefits. Understanding these distinctions is vital for selecting the right solution.
Tip 6: Consult Electricians if Necessary: For complex electrical systems or unusual power requirements, consulting a qualified electrician is recommended. Professional guidance ensures safe and appropriate generator integration.
Accurately sizing a generator ensures sufficient power for essential needs during outages, prevents overload issues, and avoids unnecessary expenditure on an oversized unit. Following these tips contributes significantly to a robust and reliable backup power strategy.
By understanding the nuances of generator sizing and selection, homeowners can confidently prepare for power disruptions and ensure the safety and comfort of their households.
1. Power Requirements
Accurate determination of power requirements is fundamental to effective generator selection. A portable generator calculator facilitates this process by providing a structured framework for assessing energy needs and matching them to appropriate generator capacity. Understanding various facets of power requirements ensures efficient and reliable backup power during outages.
- Running Wattage
Running wattage represents the continuous power consumed by an appliance or device during operation. For instance, a refrigerator might have a running wattage of 150 watts. Accurately inputting these values into a portable generator calculator ensures the generator can sustain essential appliances during extended outages.
- Starting Wattage
Starting wattage, often significantly higher than running wattage, represents the surge of power required to initiate operation. A refrigerator’s starting wattage could be 600 watts. Calculators accommodate this surge, preventing generator overload when multiple appliances start simultaneously.
- Cumulative Wattage
Cumulative wattage represents the total power demand of all intended appliances. A calculator sums individual wattages, providing the minimum generator capacity required. This ensures sufficient power for all necessary devices, preventing underpowering and potential damage.
- Load Management
Load management strategies, such as staggering appliance usage or prioritizing essential devices, optimize power consumption. A calculator can help evaluate various load management scenarios, ensuring the chosen generator meets specific needs and budgetary constraints.
By precisely calculating running wattage, starting wattage, and cumulative wattage, a portable generator calculator enables informed generator selection. Integrating load management considerations further refines the process, optimizing performance and ensuring reliable backup power during outages.
2. Wattage Calculations
Accurate wattage calculations are essential for leveraging the full potential of a portable generator calculator. These calculations provide the foundation for selecting a generator that adequately meets power demands during outages. Understanding the nuances of wattage calculations ensures efficient generator operation and prevents costly oversights.
- Appliance Wattage Determination
Determining individual appliance wattages is the first step in accurate load assessment. This information, typically found on appliance labels or in user manuals, provides the basis for calculating total power requirements. For example, a refrigerator might require 700 watts upon startup and 150 watts for continuous operation. Precise appliance wattage data ensures accurate generator sizing.
- Starting vs. Running Wattage
Distinguishing between starting and running wattage is crucial for preventing generator overload. Starting wattage, often significantly higher than running wattage, represents the surge of power required to initiate an appliance’s operation. A generator must accommodate these starting wattage surges to prevent tripping breakers. For example, while a sump pump might require 800 starting watts, its running wattage could be 400 watts. Understanding this difference is paramount for effective generator selection.
- Cumulative Wattage Calculation
Cumulative wattage, the sum of individual appliance wattages, determines the overall power demand. This calculation, facilitated by a portable generator calculator, ensures the selected generator can handle the combined load. For instance, adding the wattages of essential appliances like a refrigerator, furnace fan, and several lights provides the total wattage required from the generator.
- Safety Margin
Incorporating a safety margin in wattage calculations is a prudent practice. A safety margin, typically 10-20% of the calculated cumulative wattage, accounts for unforeseen power demands or future appliance additions. This margin prevents overloading the generator and ensures adequate power reserves.
Accurate wattage calculations, incorporating appliance-specific data and considering both starting and running wattages, are essential for effective generator sizing. Utilizing a portable generator calculator simplifies this process, allowing homeowners to make informed decisions about backup power solutions and ensure adequate capacity during outages. A properly sized generator, based on these calculations, provides reliable power during emergencies, protecting essential appliances and enhancing household safety.
3. Fuel Consumption
Fuel consumption is a critical factor influencing the practicality and cost-effectiveness of portable generator usage. Understanding fuel consumption rates is essential for informed generator selection and efficient operation during power outages. A portable generator calculator often incorporates fuel consumption data, enabling users to estimate running costs and plan for fuel storage needs. Careful consideration of fuel consumption ensures uninterrupted power supply during emergencies while minimizing operational expenses.
- Generator Size and Load
Generator size and load directly impact fuel consumption. Larger generators generally consume more fuel, especially under heavy loads. A smaller generator operating near its maximum capacity may consume fuel at a higher rate than a larger generator operating at a lower percentage of its capacity. Accurately estimating load requirements through a portable generator calculator assists in selecting a right-sized generator, optimizing fuel efficiency. For example, a 5000-watt generator powering a 1000-watt load will consume fuel more efficiently than if powering a 4500-watt load. Careful load management reduces fuel consumption and extends runtime.
- Fuel Type
Different fuel types exhibit varying energy densities and combustion efficiencies, directly affecting fuel consumption rates. Gasoline, propane, and diesel are common generator fuels, each with unique characteristics. Gasoline offers widespread availability but tends to have a shorter shelf life. Propane burns cleaner and stores longer, while diesel provides higher energy density but can be more expensive. A portable generator calculator may incorporate fuel type into its calculations, providing more accurate runtime and cost estimations.
- Runtime Estimation
Runtime estimations, based on fuel consumption rates, are crucial for planning extended power outages. A portable generator calculator assists in determining how long a generator can operate on a given amount of fuel. This information informs fuel storage decisions and ensures uninterrupted power for critical appliances. For instance, knowing a generator can run for 8 hours on a full tank of fuel allows for informed planning during prolonged outages.
- Cost Considerations
Fuel costs represent a significant component of generator operating expenses. Understanding fuel consumption rates allows for accurate budgeting and cost comparisons between different generator models and fuel types. A portable generator calculator facilitates these comparisons, empowering users to make cost-effective decisions. Evaluating fuel efficiency alongside purchase price provides a more comprehensive view of long-term generator ownership costs.
Integrating fuel consumption data into a portable generator calculator enhances its utility as a planning tool. Accurate estimations of fuel consumption, runtime, and associated costs empower users to make informed decisions regarding generator sizing, fuel type selection, and overall emergency preparedness. This comprehensive approach ensures reliable backup power while minimizing operational expenses and environmental impact.
4. Runtime Estimates
Runtime estimates constitute a critical element within portable generator calculators designed for home use. These estimates provide a crucial link between fuel capacity, fuel consumption rate, and the duration a generator can operate without refueling. This information directly impacts preparedness strategies for power outages. A calculator facilitates informed decisions about generator sizing and fuel storage, enabling homeowners to match generator capabilities to anticipated outage durations. For example, a household anticipating frequent short-duration outages might prioritize a smaller, fuel-efficient generator, while a household located in an area prone to prolonged outages would benefit from a larger generator with extended runtime capabilities or substantial fuel reserves. The calculator bridges the gap between technical specifications and practical application, empowering users to tailor their backup power solutions to specific needs.
A clear understanding of runtime estimates allows for more effective load management during outages. By knowing how long a generator can operate under specific load conditions, homeowners can prioritize essential appliances and devices, extending available power. For instance, if a generator’s estimated runtime is 10 hours with a moderate load, a homeowner can strategically manage usage to ensure critical systems, such as refrigerators and medical equipment, remain operational throughout the outage duration. This understanding allows for proactive power allocation and minimizes disruption to essential household functions. Runtime estimates empower homeowners to develop comprehensive outage plans that address both immediate needs and long-term power requirements, enhancing overall resilience.
Accurate runtime estimations, facilitated by portable generator calculators, are fundamental to effective emergency preparedness. These calculations provide homeowners with actionable insights for optimizing generator usage, managing fuel resources, and ensuring the continuity of essential services during power disruptions. The ability to tailor power strategies based on projected runtime significantly enhances household resilience and minimizes the impact of outages on daily life. Challenges such as unforeseen load fluctuations or variations in fuel efficiency can influence actual runtime, underscoring the importance of conservative estimations and proactive fuel management.
5. Budget Considerations
Budget considerations play a significant role in selecting a portable generator for home use. A generator represents a substantial investment, and careful financial planning ensures the chosen model aligns with both power requirements and budgetary constraints. Portable generator calculators often incorporate cost factors, enabling users to evaluate various options and make informed decisions that balance performance and affordability. Understanding the financial implications of generator ownership, including purchase price, operating costs, and maintenance expenses, is crucial for responsible budgeting.
- Initial Purchase Price
The initial purchase price of a portable generator varies significantly based on factors such as power output, fuel type, and features. Smaller, less powerful generators typically have lower upfront costs, while larger, more feature-rich models command higher prices. A portable generator calculator can assist in narrowing down options within a specific budget range, ensuring affordability without compromising essential power needs. For instance, a homeowner with a limited budget might prioritize a basic gasoline-powered generator over a more expensive inverter generator, balancing initial cost with power requirements. Careful evaluation of available options ensures the chosen generator aligns with both power needs and budgetary constraints.
- Operating Costs
Operating costs, primarily driven by fuel consumption, represent a recurring expense associated with generator ownership. Fuel efficiency varies significantly between generator models and fuel types. A portable generator calculator can help estimate operating costs based on anticipated usage patterns, enabling users to factor these expenses into their budget. For example, a homeowner anticipating frequent or extended generator use might prioritize a fuel-efficient model, minimizing long-term operating costs even if the initial purchase price is slightly higher.
- Maintenance Expenses
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliable performance of a portable generator. Maintenance expenses, including oil changes, air filter replacements, and periodic tune-ups, should be factored into the overall budget. Some portable generator calculators incorporate estimated maintenance costs, providing a more comprehensive view of long-term ownership expenses. Planning for these recurring costs prevents unexpected financial burdens and ensures the generator remains operational when needed. Proper maintenance not only prolongs generator lifespan but also optimizes fuel efficiency and reduces the risk of costly repairs.
- Long-Term Value
Assessing the long-term value of a portable generator involves considering its lifespan, reliability, and resale potential. A more expensive, durable generator might offer better long-term value compared to a cheaper model with a shorter lifespan or higher maintenance requirements. A portable generator calculator can sometimes provide comparisons based on projected lifespan and maintenance costs, enabling users to make informed decisions about long-term investments. Balancing upfront costs with projected long-term value ensures the chosen generator provides reliable backup power over its intended lifespan while minimizing overall ownership expenses.
By incorporating budget considerations into the generator selection process, homeowners can make informed decisions that align with their financial resources while ensuring access to reliable backup power. A portable generator calculator facilitates this process by providing cost comparisons, runtime estimations, and other relevant financial data, empowering users to make prudent investments that meet both immediate needs and long-term budgetary goals. Effective budgeting ensures the chosen generator provides essential power during outages without imposing undue financial strain.
6. Portability Needs
Portability requirements significantly influence the selection of a portable generator for home use. A portable generator calculator aids in evaluating these needs by considering factors such as generator weight, dimensions, and intended usage scenarios. Balancing portability with power output and other features ensures the chosen generator meets practical handling and storage requirements while providing adequate power during outages. Understanding the interplay between portability, power needs, and logistical considerations is essential for informed decision-making.
- Weight and Maneuverability
Generator weight directly impacts ease of transport and maneuverability. Lighter generators are easier to move and position, while heavier units may require assistance or specialized transport mechanisms. Consideration of physical limitations and storage accessibility is essential when evaluating generator weight. For example, a homeowner with limited physical strength might prioritize a lightweight inverter generator over a heavier conventional generator, even if the latter offers higher power output. Balancing weight with power needs ensures practicality and safe handling.
- Dimensions and Storage
Generator dimensions influence storage requirements and transportation logistics. Compact generators occupy less space, simplifying storage in garages, sheds, or vehicles. Larger generators require more dedicated storage space and may present transportation challenges. Evaluating available storage space and transportation capabilities before selecting a generator ensures practical ownership. For instance, a homeowner with limited storage space might prioritize a compact generator even if it means slightly lower power output or runtime. Matching generator dimensions to available space simplifies storage and enhances portability.
- Wheel Kits and Handles
Integrated wheel kits and ergonomic handles significantly enhance generator portability. These features facilitate easier movement and positioning, reducing strain and simplifying transport. Evaluating the quality and design of these features ensures convenient handling and minimizes physical effort. For example, a generator with large, sturdy wheels and a comfortable handle is easier to maneuver across uneven terrain or up steps compared to a generator with small, flimsy wheels or an awkward handle design. Prioritizing these features enhances practicality and reduces the risk of injury during transport.
- Intended Use Cases
Intended use cases significantly influence portability needs. Generators used for recreational activities, such as camping or tailgating, prioritize compact size and lightweight design. Generators intended for home backup power during emergencies may prioritize higher power output over extreme portability, accepting a larger, heavier unit for increased capacity. A portable generator calculator helps users align portability needs with specific use cases. For instance, a homeowner might choose a heavier, higher-output generator for home backup power while selecting a smaller, lighter generator for camping trips. Matching portability to intended use ensures practicality and optimal performance in various scenarios.
By carefully evaluating portability needs in conjunction with power requirements and budget constraints, homeowners can select portable generators that effectively balance power delivery with practical handling and storage considerations. A portable generator calculator facilitates this process by providing relevant data on generator dimensions, weight, and features, empowering users to make informed decisions that optimize both performance and practicality. Ultimately, selecting a generator with appropriate portability ensures ease of use, convenient storage, and safe operation, enhancing the overall value and utility of the backup power solution.
7. Safety Features
Safety features are paramount when considering a portable generator for home use. A portable generator calculator, while focusing on sizing and power requirements, should be used in conjunction with careful consideration of these crucial safety aspects. Overlooking safety features can lead to significant hazards, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire, and electrical shock. Integrating safety considerations into the generator selection process is essential for protecting households and mitigating potential risks.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO) Detection and Shutdown
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless, and highly toxic gas produced during fuel combustion. Portable generators, often operated in close proximity to homes during outages, pose a significant CO poisoning risk. Safety features such as CO sensors with automatic shutdown mechanisms are crucial for mitigating this risk. These sensors detect elevated CO levels and automatically shut down the generator, preventing potential exposure. This feature is essential for protecting occupants from the potentially fatal consequences of CO poisoning. For example, a generator equipped with a CO safety shutdown system will automatically cease operation if CO levels reach a dangerous threshold, even if the homeowner is unaware of the accumulating gas.
- Overload Protection
Overloading a generator by exceeding its rated wattage capacity can cause overheating, damage to appliances, and potential fire hazards. Overload protection features, such as circuit breakers or overload alarms, prevent excessive current flow and protect the generator and connected appliances from damage. These features automatically interrupt power supply when the load exceeds the generator’s capacity, preventing potential electrical fires or equipment damage. For example, if a homeowner attempts to connect too many appliances to the generator, exceeding its wattage rating, the overload protection will activate, preventing damage and potential fire hazards.
- Proper Grounding and Electrical Outlets
Proper grounding and appropriately designed electrical outlets are crucial for preventing electrical shocks. Generators should be equipped with grounding ports and outlets designed to prevent accidental contact with live wires. These features minimize the risk of electrical shock during operation and connection of appliances. For example, GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets protect against electrical shocks by detecting imbalances in current flow and quickly interrupting the circuit. These safety features are particularly important when operating generators in wet or damp conditions.
- Safe Refueling Practices
Safe refueling procedures are essential for preventing fires and burns. Generators should be allowed to cool completely before refueling to minimize the risk of fuel ignition. Using approved fuel containers and avoiding spills further reduces fire hazards. Proper ventilation during refueling is also crucial for dispersing flammable fumes. For example, refueling a hot generator can ignite spilled fuel vapors, causing a serious fire. Adhering to safe refueling practices, including allowing the generator to cool and refueling in a well-ventilated area, significantly reduces fire risks.
Selecting a portable generator based solely on power output and cost, without careful consideration of essential safety features, significantly increases the risk of accidents and injuries. Integrating safety features into the selection process, alongside calculations provided by a portable generator calculator, ensures a comprehensive approach to emergency preparedness. Prioritizing safety features like CO detection, overload protection, proper grounding, and adherence to safe refueling practices safeguards households and minimizes potential hazards associated with generator operation. A holistic approach, balancing power needs with safety considerations, is crucial for responsible generator ownership.
Frequently Asked Questions
This FAQ section addresses common inquiries regarding portable generator calculators and their application in determining appropriate generator size for home use.
Question 1: How does a portable generator calculator determine the necessary generator size?
Calculators utilize input regarding anticipated electrical loads, typically expressed in watts. By summing the wattage requirements of appliances and devices planned for backup power, the calculator determines the minimum generator output capacity necessary to meet these demands. Some calculators also incorporate starting wattage requirements and safety margins to ensure reliable performance.
Question 2: Are starting watts important when using the calculator?
Starting watts, or surge watts, represent the initial power surge required to start electric motors, which are frequently found in appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners. These surge watts can be significantly higher than running watts. Failing to account for starting watts can lead to generator overload and potential damage. Accurate inclusion of both running and starting wattage ensures appropriate generator selection.
Question 3: Can a portable generator calculator account for future power needs?
While calculators primarily focus on current power requirements, anticipating future needs is advisable. Overestimating current needs, within reason, provides a buffer for potential future appliance additions or increased power demands. However, significantly oversizing a generator can lead to unnecessary fuel consumption and higher purchase costs.
Question 4: What are the limitations of portable generator calculators?
Calculators provide estimates based on user-provided data. Accuracy depends on the precision of this input. Furthermore, calculators may not account for complex electrical systems or specific local regulations. Consulting a qualified electrician can address complex scenarios and ensure compliance with applicable codes. Calculators offer valuable guidance but should not replace professional electrical advice when needed.
Question 5: How do fuel type and consumption relate to generator selection?
Fuel type influences runtime, operating costs, and storage considerations. Gasoline, propane, and diesel each possess unique characteristics. Calculators may incorporate fuel consumption data to provide runtime estimates based on fuel type and generator load. Understanding fuel considerations ensures selection of a generator that aligns with both power needs and logistical preferences.
Question 6: Are there safety considerations beyond generator sizing?
Generator sizing is only one aspect of safe operation. Proper ventilation, carbon monoxide detection, appropriate grounding, and adherence to safe refueling procedures are essential safety practices. While calculators address sizing requirements, comprehensive safety awareness is crucial for mitigating potential hazards associated with generator use.
Understanding the capabilities and limitations of portable generator calculators enables informed generator selection and safe operation. Careful consideration of power requirements, fuel considerations, and safety practices ensures reliable backup power during outages.
Further research into specific generator models, fuel types, and local regulations is recommended before making a purchase decision.
Conclusion
Careful evaluation of power needs, budget constraints, and safety considerations remains paramount in selecting an appropriate portable generator. Utilizing a portable generator calculator facilitates informed decision-making by providing a structured framework for assessing power requirements, estimating fuel consumption, and understanding runtime estimations. Accurately sizing a generator ensures sufficient power for essential appliances during outages without unnecessary overspending on excessive capacity. Prioritizing safety features, such as carbon monoxide detectors and overload protection, safeguards households from potential hazards associated with generator operation.
Investing in a portable generator represents a significant step towards enhancing household resilience during power disruptions. Thorough planning, informed by accurate calculations and a comprehensive understanding of generator operation, ensures reliable backup power when needed most. Proactive preparation, combined with responsible generator usage, empowers homeowners to navigate power outages safely and effectively, minimizing disruption and maintaining essential services. A well-chosen generator, paired with a robust emergency plan, provides peace of mind and safeguards households against the unpredictable nature of power outages.