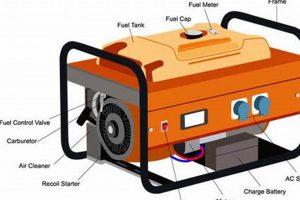
Compact, fuel-powered devices capable of generating electricity independently of the primary power grid offer a crucial safety net for residences during outages. These units can power essential appliances and devices, maintaining a degree of normalcy and safety until grid power is restored. A typical example might power refrigerators, lighting, and essential medical equipment during a severe storm.
Power disruptions can stem from various events, from natural disasters like hurricanes and ice storms to infrastructure failures and grid overloads. Loss of electricity can pose significant risks, disrupting communication, compromising food safety, and hindering necessary medical treatments. Backup power solutions ensure continued access to critical functionalities, protecting homeowners from the dangers and inconveniences of extended blackouts. Historically, reliance on candles and wood-burning stoves during outages posed substantial safety risks. The development and refinement of portable generator technology provides a far safer and more convenient method for maintaining essential services during power disruptions.
This discussion will further explore the various types available, key selection criteria, safe operation practices, and essential maintenance requirements for ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Essential Tips for Portable Generator Use
Safe and effective operation of portable generators requires careful planning and adherence to established safety guidelines. These tips offer crucial insights into responsible generator use, maximizing benefits while mitigating potential hazards.
Tip 1: Proper Sizing is Crucial: Accurately assess power requirements before purchasing a unit. Consider the wattage demands of essential appliances intended for backup power. Undersized generators risk overload and damage, while oversized units represent unnecessary expense and fuel consumption.
Tip 2: Safe Placement is Paramount: Operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas, away from windows, doors, and vents. Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious hazard associated with improper generator placement.
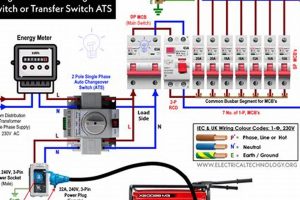
Tip 3: Connection Methods Matter: Never directly connect a generator to household wiring. Utilize a transfer switch installed by a qualified electrician to safely isolate the generator’s power from the utility grid, preventing backfeeding and protecting utility workers.
Tip 4: Fuel Safety First: Store fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated location away from ignition sources. Allow the generator to cool completely before refueling to prevent fire hazards.
Tip 5: Regular Maintenance is Key: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule. Regular oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacements ensure reliable performance and extend the generator’s lifespan.
Tip 6: Dry Run Testing is Essential: Periodically test the generator under load to verify proper operation. This ensures readiness during an actual outage and identifies any potential issues requiring attention.
Tip 7: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs): Employ GFCI-protected extension cords for added safety against electrical shocks, particularly in damp or wet conditions.
Adherence to these safety precautions and operational guidelines ensures effective use of portable generators, offering a reliable power source during emergencies while safeguarding against potential hazards.
By understanding the importance of preparation, safe operation, and regular maintenance, homeowners can effectively leverage the benefits of portable generators, mitigating the impact of power disruptions on daily life and safety.
1. Power Output
A critical factor in selecting a suitable portable generator is its power output, measured in watts. This specification directly dictates which appliances and devices the generator can effectively power during an outage. Understanding power output and its relationship to household energy demands is essential for informed generator selection and successful backup power implementation.
- Starting vs. Running Watts
Appliances have two wattage requirements: starting and running. Starting watts, significantly higher than running watts, represent the power surge required to initiate operation. For example, a refrigerator might require 1,200 starting watts but only 250 running watts. Generators must accommodate both, or they may stall when starting high-demand appliances.
- Calculating Total Power Needs
Accurately assessing household power needs is crucial for proper generator sizing. This involves identifying essential appliances and devices requiring backup power and summing their wattage requirements. Online calculators and resources can assist with this assessment. Overestimating ensures sufficient power, while underestimation risks overload and generator damage.
- Generator Wattage Options
Portable generators span a wide range of power outputs, from small units suitable for powering a few lights and essential electronics to larger models capable of running multiple appliances simultaneously. Selection depends entirely on individual backup power requirements, balancing necessary capacity with cost and fuel efficiency.
- Impact on Runtime
Power output influences runtime. Higher wattage generators consume more fuel, reducing the duration of operation on a single tank. Balancing power needs with desired runtime is a key consideration in generator selection, particularly for extended outages.
Careful consideration of power output, alongside other factors like fuel type and runtime, ensures selection of a generator that effectively meets household backup power needs. Accurately assessing wattage requirements and understanding the nuances of starting and running watts prevents generator overload, ensuring reliable operation during critical power outages.
2. Fuel Type
Fuel type significantly influences the practicality and effectiveness of portable generators for home use. Choosing the appropriate fuel depends on factors such as availability, storage capacity, cost, and the specific requirements of the intended application during a power outage. Understanding the characteristics of common fuel types empowers informed decisions and ensures reliable backup power when needed.
- Gasoline
Gasoline is readily available and offers high energy density. However, it has a limited shelf life, degrading over time and potentially causing carburetor issues. Gasoline generators require more frequent maintenance compared to other fuel types and pose flammability risks during storage and handling. While gasoline generators might be suitable for shorter outages, long-term storage necessitates fuel stabilizers and periodic replacement.
- Propane
Propane offers extended shelf life and cleaner burning compared to gasoline. Propane generators typically require less maintenance and pose reduced risks of fuel-related engine problems. Propane tanks can be easily stored and refilled, although they require dedicated storage space. The availability of propane refills might be a concern during widespread or prolonged emergencies.
- Diesel
Diesel generators provide excellent fuel efficiency and long runtimes. Diesel fuel is relatively stable, offering a longer shelf life than gasoline. However, diesel generators tend to be more expensive initially and can be noisier than gasoline or propane models. Diesel emissions contain particulates, requiring careful consideration of exhaust placement and ventilation.
- Dual Fuel/Tri-Fuel
Dual or tri-fuel generators offer flexibility, operating on gasoline, propane, or sometimes natural gas. This versatility provides options depending on fuel availability during an outage. However, these generators may require specific conversion kits or adjustments for switching between fuel types. Output power may also vary based on the fuel used.
Careful consideration of fuel type is crucial in selecting a portable generator that aligns with individual needs and circumstances. Balancing factors such as fuel availability, storage practicality, runtime requirements, and potential environmental impact ensures a reliable and effective backup power solution during emergencies.
3. Runtime
Runtime, a crucial factor in selecting a portable generator, signifies the duration a generator can operate continuously on a full tank of fuel. This duration directly impacts the practical utility of the generator during a power outage, influencing decisions regarding fuel storage, refueling frequency, and overall preparedness. A thorough understanding of runtime and its influencing factors is essential for ensuring uninterrupted power supply to critical systems during emergencies.
- Fuel Tank Capacity
The size of the generator’s fuel tank directly correlates with potential runtime. Larger tanks hold more fuel, enabling longer operation before refueling becomes necessary. However, larger tanks also increase the generator’s overall size and weight, influencing portability and storage considerations. A balance between desired runtime and practical tank size must be struck based on individual needs and anticipated outage durations.
- Load Size
The power demand placed on the generator directly affects runtime. Higher loads consume fuel more rapidly, shortening the operational duration. Accurately assessing power requirements for essential appliances and devices during an outage is crucial for estimating runtime and ensuring adequate fuel reserves. Operating the generator at lower loads can extend runtime, conserving fuel and minimizing refueling needs.
- Generator Efficiency
Generator efficiency, often expressed as a percentage, reflects how effectively the generator converts fuel into usable power. More efficient generators extract more energy from the same amount of fuel, leading to longer runtimes. Engine design, fuel type, and maintenance practices all influence generator efficiency and, consequently, runtime.
- Fuel Type
The type of fuel used influences both runtime and overall generator operation. Diesel generators generally offer longer runtimes compared to gasoline generators due to higher energy density. Propane, while offering a cleaner burn and longer shelf life, may necessitate more frequent refueling depending on tank size and load. Understanding the runtime characteristics of various fuel types is essential in selecting the appropriate generator for specific needs and outage scenarios.
Careful consideration of runtime in relation to fuel tank capacity, anticipated load, generator efficiency, and fuel type ensures selection of a generator capable of providing reliable power throughout the duration of an outage. Understanding these factors allows for informed decisions regarding fuel storage, refueling logistics, and overall preparedness, maximizing the effectiveness of the generator as a backup power solution in emergency situations.
4. Safety Features
Safety features are paramount in portable generator design, mitigating inherent risks associated with fuel-powered equipment and electricity generation. These features protect users, connected appliances, and the broader power grid from potential hazards during operation. Understanding these safety mechanisms and their functions is crucial for responsible generator use and preventing accidents.
A critical safety feature is the automatic shutoff system triggered by low oil levels. This mechanism prevents engine damage caused by insufficient lubrication during operation, extending the generator’s lifespan and preventing costly repairs. Overload protection prevents damage to the generator and connected appliances by automatically shutting down the unit when electrical loads exceed its capacity. This safeguard prevents fires and electrical hazards arising from excessive current draw. Furthermore, carbon monoxide (CO) sensors and alarms are essential safety components, detecting dangerous levels of CO buildup and alerting users to the potential for poisoning. This feature is crucial for preventing fatalities and serious health issues resulting from improper ventilation during generator operation. Properly grounded outlets prevent electric shocks by providing a safe path for fault currents, protecting users from electrocution.
Absence or malfunction of these safety features can lead to severe consequences, including fires, electrocution, carbon monoxide poisoning, and equipment damage. Regular inspection and maintenance of safety features, such as testing the CO alarm and ensuring proper grounding, are essential for reliable operation and accident prevention. Understanding and prioritizing these safety aspects ensures responsible and safe generator use, protecting lives and property during emergency power outages.
5. Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for reliable and safe operation of emergency portable generators. Neglecting routine upkeep can lead to malfunctions, reduced efficiency, and potentially hazardous situations during power outages. A well-maintained generator ensures consistent performance when needed most, while neglected units may fail to start or operate safely, exacerbating the challenges posed by a power disruption. For example, failing to change engine oil can lead to engine seizure, rendering the generator useless during an emergency. Similarly, neglecting air filter maintenance can restrict airflow, reducing power output and increasing fuel consumption.
A comprehensive maintenance schedule should include regular checks and procedures. Oil changes, at intervals specified by the manufacturer, maintain proper lubrication and prevent engine damage. Air filter cleaning or replacement ensures optimal airflow for efficient combustion. Spark plug inspection and replacement maintain consistent ignition and prevent engine misfires. Fuel system maintenance, including fuel stabilizer addition for gasoline generators and periodic draining of stale fuel, prevents fuel-related issues that can hinder generator operation. Beyond these routine tasks, periodic inspections of wiring, connections, and safety features like the automatic shutoff and carbon monoxide detector are crucial for safe and reliable operation.
Maintaining a detailed maintenance log, recording dates and specific procedures performed, aids in tracking service history and anticipating future maintenance needs. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and maximizes the lifespan of the generator. Ultimately, diligent maintenance transforms an emergency portable generator from a simple appliance into a dependable lifeline during critical power outages. It ensures readiness, mitigates potential hazards, and provides peace of mind during unpredictable events. Ignoring necessary maintenance, conversely, jeopardizes the generator’s functionality and potentially compromises safety, negating its intended purpose as a reliable backup power source.
Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common inquiries regarding emergency portable generators for home use clarifies key considerations for safe and effective utilization during power outages.
Question 1: How is the correct generator size determined for individual needs?
Determining the appropriate generator size involves calculating the total wattage required to power essential appliances and devices during an outage. Consider both running watts and starting watts, as starting watts are significantly higher. Online resources and wattage calculators can assist in this assessment.
Question 2: What are the primary safety precautions for generator operation?
Operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas away from structures. Never connect a generator directly to household wiring; utilize a transfer switch installed by a qualified electrician. Store fuel safely and allow the generator to cool before refueling.
Question 3: What fuels can be used in portable generators?
Common fuel types include gasoline, propane, and diesel. Each fuel has advantages and disadvantages related to cost, availability, storage, and environmental impact. Dual-fuel or tri-fuel generators offer flexibility by running on multiple fuel types.
Question 4: What maintenance is required for optimal generator performance?
Regular maintenance, as outlined in the manufacturer’s instructions, is crucial. Essential tasks include oil changes, air filter cleaning or replacement, spark plug checks, and fuel system maintenance.
Question 5: What is the significance of a transfer switch?
A transfer switch safely connects the generator to household circuits while isolating them from the utility grid. This prevents backfeeding, which poses significant risks to utility workers and can damage appliances.
Question 6: How frequently should a generator be tested?
Regularly testing the generator, ideally monthly, under a typical load ensures it functions correctly when needed. This proactive approach identifies potential issues before an actual outage occurs, allowing time for repairs or maintenance.
Prioritizing safety and understanding operational requirements ensures effective utilization of emergency portable generators, providing reliable power during outages. Consult manufacturer instructions and qualified professionals for specific guidance tailored to individual circumstances.
Further sections will delve into specific generator models, comparisons, and advanced operational considerations.
Emergency Portable Generators for Home Use
Careful consideration of factors such as power output, fuel type, runtime, safety features, and required maintenance ensures selection of an emergency portable generator suited to individual needs. Understanding safe operation and adhering to established guidelines mitigates potential hazards associated with generator use. Proper generator sizing, coupled with adherence to safety protocols, ensures effective backup power during outages, safeguarding households from disruptions to essential services.
Investing in an emergency portable generator represents a significant step towards household preparedness. Proactive planning, combined with informed generator selection and diligent maintenance, empowers homeowners to navigate unforeseen power disruptions with confidence, ensuring safety and maintaining essential functionalities during critical situations. Reliable backup power provides not merely convenience but also a crucial layer of security in an increasingly unpredictable world.