High-quality, mobile power sources designed for residential applications offer a crucial backup solution during power outages. These units, ranging in power output and fuel type, can operate essential appliances and devices, ensuring safety and comfort. For example, a homeowner might employ such a device to power a refrigerator, sump pump, and several lights during a storm-related outage.
Reliable backup power is paramount for maintaining a functional and safe household during unforeseen events. Power disruptions can lead to food spoilage, security system failures, and discomfort, particularly for individuals with medical needs or those relying on electrically powered equipment. The advent of increasingly compact and efficient models has broadened accessibility to reliable backup power, providing peace of mind and enhanced preparedness. Historically, homeowners relied on less convenient and often more hazardous solutions, underscoring the significance of this modern approach.
Factors influencing the selection of an appropriate mobile power source include power requirements, runtime, fuel type, noise levels, and budget. The following sections will explore these considerations in detail, providing guidance for consumers seeking the optimal solution for their individual circumstances.
Tips for Selecting and Operating a Portable Generator
Choosing and using a portable generator requires careful consideration to ensure safety and effectiveness. The following tips offer guidance for maximizing the benefits of these devices.
Tip 1: Calculate Power Requirements: Accurately assess the wattage required to operate essential appliances and devices. Sum the wattage of intended loads to determine the minimum generator output needed. Consider starting wattage, which can be significantly higher than running wattage for some appliances, such as refrigerators.
Tip 2: Choose the Right Fuel Type: Gasoline, propane, and inverter generators offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. Gasoline offers widespread availability but requires regular refueling and proper storage. Propane provides longer shelf life and cleaner emissions. Inverter generators offer quieter operation and greater fuel efficiency, particularly for smaller loads.
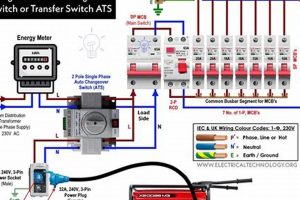
Tip 3: Prioritize Safety: Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces due to the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Place the generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from windows and doors. Utilize a properly rated transfer switch for safe connection to the home’s electrical system.
Tip 4: Consider Runtime: Evaluate how long the generator can operate on a single tank of fuel. Longer runtimes minimize refueling frequency, especially during extended outages. Fuel efficiency varies significantly between models and fuel types.
Tip 5: Factor in Noise Levels: Generators produce varying noise levels. Consider noise output, especially if operating in close proximity to neighbors or during nighttime hours. Inverter generators generally offer quieter operation compared to conventional models.
Tip 6: Maintain the Generator: Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring reliable performance. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for oil changes, air filter cleaning, and other routine maintenance tasks. Store fuel properly to prevent degradation and maintain generator functionality.
Tip 7: Adhere to Local Regulations: Familiarize oneself with local regulations regarding generator use. Some areas may have restrictions on noise levels or operating hours. Ensure compliance with applicable ordinances and safety guidelines.
Careful planning and informed decision-making are crucial for maximizing the benefits of a portable generator. These tips offer a starting point for consumers seeking reliable backup power solutions.
By understanding power needs, fuel options, safety procedures, and maintenance requirements, consumers can confidently select and operate a portable generator, ensuring preparedness for unexpected power interruptions.
1. Power Output
Power output, measured in watts, stands as a critical determinant in selecting a suitable portable generator for residential applications. This specification directly dictates the number and type of appliances and devices a generator can power concurrently. Insufficient power output can lead to overloading and potential damage to both the generator and connected equipment. Conversely, an excessively high power output results in unnecessary fuel consumption and increased operating costs. A precise understanding of household power requirements is therefore essential. For example, a homeowner intending to power a refrigerator, sump pump, and several lights during an outage must calculate the combined wattage of these items to determine the minimum required generator output.
Matching power output to specific needs represents a crucial balance between functionality and efficiency. Determining essential appliances and calculating their combined running wattage, along with considering the higher starting wattage of certain devices like refrigerators and air conditioners, enables informed generator selection. Overestimating power needs results in increased purchase and operating costs, while underestimation risks insufficient power supply during critical situations. Practical applications include calculating the necessary wattage to operate essential medical equipment during a power outage or ensuring sufficient power for sump pumps to prevent basement flooding during heavy rainfall. Evaluating peak power demands and potential future needs ensures the selected generator provides adequate power for current and anticipated requirements.
Accurate assessment of power requirements facilitates informed generator selection, maximizing functionality while optimizing efficiency. Careful consideration of both running and starting wattage of intended loads ensures the chosen generator provides adequate power without unnecessary excess. This understanding translates directly into effective and cost-efficient operation, enabling homeowners to maintain essential services and enhance safety during power disruptions. Understanding the nuances of power output empowers consumers to navigate the complexities of generator selection and ensure the chosen unit aligns precisely with individual needs and circumstances. Further research into specific appliance wattages and generator models is recommended to refine this understanding and make informed purchasing decisions.
2. Fuel Efficiency
Fuel efficiency plays a pivotal role in the selection and operation of portable generators for home use. A fuel-efficient generator reduces operating costs, minimizes refueling frequency, and lessens environmental impact. This efficiency is typically measured in gallons per hour (GPH) at various load levels. Lower GPH values indicate higher fuel efficiency. Factors influencing fuel efficiency include engine design, load size, and generator type. For example, inverter generators generally exhibit higher fuel efficiency compared to conventional generators, particularly at lower loads, due to their variable engine speed capability. Choosing a fuel-efficient model becomes increasingly significant during extended power outages, where minimizing fuel consumption is paramount.
The practical implications of fuel efficiency are substantial. Reduced fuel consumption translates directly into lower operating costs, a particularly relevant factor in scenarios with fluctuating fuel prices. Less frequent refueling enhances convenience, especially during prolonged outages or in situations where fuel availability may be limited. Improved fuel efficiency also contributes to reduced emissions, aligning with environmentally conscious practices. Real-world examples include the ability to power essential household appliances for extended periods without frequent refueling stops or the potential cost savings achieved over the lifespan of the generator due to lower fuel consumption. Furthermore, fuel-efficient models often operate more quietly, contributing to reduced noise pollution.
In conclusion, prioritizing fuel efficiency in the selection of a portable generator offers significant advantages. Lower operating costs, reduced refueling needs, and decreased environmental impact contribute to a more sustainable and cost-effective approach to backup power. Understanding the connection between fuel efficiency and generator performance allows consumers to make informed decisions that align with both practical needs and budgetary constraints. This consideration ultimately enhances the overall value and utility of the generator as a reliable power source during outages. Additional factors, such as fuel type and storage capacity, should be considered in conjunction with fuel efficiency to arrive at a comprehensive assessment of a generator’s suitability for individual needs.
3. Runtime Capacity
Runtime capacity represents a crucial factor in selecting a portable generator for home use. This metric, typically measured in hours, indicates the duration a generator can operate continuously on a single tank of fuel at a given load. Sufficient runtime capacity is essential for ensuring uninterrupted power during extended outages. Understanding the interplay between runtime, fuel capacity, and load requirements is crucial for effective generator selection and utilization.
- Fuel Tank Size and Consumption Rate:
Runtime is directly influenced by the generator’s fuel tank size and its fuel consumption rate. Larger fuel tanks generally provide longer runtimes, but actual operating duration depends on the engine’s efficiency and the load applied. A generator with a higher fuel consumption rate will deplete its fuel tank more quickly, resulting in a shorter runtime, even with a larger tank. For instance, a generator with a large fuel tank but a high consumption rate may offer a similar runtime to a generator with a smaller tank and a lower consumption rate.
- Load Size and Power Output:
The load placed on the generator significantly impacts its runtime. Higher power demands result in increased fuel consumption and consequently, a shorter runtime. Operating the generator at a lower percentage of its maximum power output extends the runtime. Practical examples include powering essential appliances only during extended outages to conserve fuel and maximize runtime or selecting a generator with sufficient power output to avoid running it near its maximum capacity, thereby optimizing runtime.
- Fuel Type and Efficiency:
The type of fuel used also affects runtime. Different fuels have varying energy densities, influencing how long the generator can operate on a given volume. Furthermore, the generator’s engine design and efficiency play a significant role in fuel consumption and therefore, runtime. For example, propane generators often offer longer runtimes compared to gasoline generators of similar size due to propane’s higher energy density and cleaner combustion characteristics.
- Inverter Technology and Variable Speed:
Inverter generators utilize advanced technology to adjust engine speed based on the load, leading to improved fuel efficiency and extended runtime, especially at lower loads. Compared to conventional generators that operate at a fixed speed, inverter generators can significantly reduce fuel consumption and extend runtime when powering smaller loads. This makes them particularly well-suited for applications where fluctuating power demands are common.
Selecting a generator with appropriate runtime capacity requires careful consideration of fuel tank size, fuel consumption rate, anticipated load requirements, and fuel type. Balancing these factors ensures the generator can provide adequate power for the desired duration during outages. Consumers should assess their specific needs and usage scenarios, considering factors like the frequency and duration of typical power outages, to determine the optimal runtime capacity for their individual circumstances. This comprehensive understanding of runtime capacity contributes significantly to informed decision-making and ensures the selected generator effectively fulfills its intended purpose as a reliable backup power source.
4. Noise Levels
Noise levels represent a critical consideration when selecting a portable generator for home use. Measured in decibels (dB), generator noise can range from a quiet hum to a loud roar, impacting both user comfort and neighborhood relations. Excessive noise can be disruptive, especially during extended operation or nighttime use. Various factors contribute to generator noise, including engine design, exhaust system, and overall construction. Understanding these factors allows for informed decisions that prioritize noise reduction without compromising performance.
The practical implications of generator noise are significant. Operating a loud generator can lead to strained relationships with neighbors, particularly in densely populated areas. Local ordinances often regulate permissible noise levels, and exceeding these limits can result in fines or other penalties. High noise levels can also disrupt sleep and create an uncomfortable living environment for generator users and their families. Conversely, quieter generators offer a more peaceful experience, minimizing disturbance and promoting harmonious coexistence. Real-world examples include selecting a quieter inverter generator for use in a suburban setting or utilizing noise-reducing enclosures and baffles to minimize operational noise impact.
Minimizing noise pollution is a key aspect of responsible generator ownership. Selecting models with lower decibel ratings, utilizing sound-dampening enclosures, and strategically positioning the generator away from living spaces and neighboring properties contribute significantly to noise reduction. Technological advancements, such as inverter technology, have led to the development of quieter generators that prioritize both performance and noise reduction. Ultimately, considering noise levels during the selection process enhances both user experience and community harmony, demonstrating a commitment to considerate and responsible generator operation.
5. Portability & Size
Portability and size are integral considerations when selecting a portable generator for home use. The ideal unit balances power output and runtime with manageable dimensions and weight. Practicality dictates that the generator should be easily transportable and storable. Overly large or heavy units can present challenges for maneuvering and storage, particularly for individuals with physical limitations or limited storage space. Conversely, excessively small units may lack the necessary power output and runtime to meet household needs. The optimal balance depends on individual circumstances, including power requirements, storage solutions, and physical capabilities.
The interplay between portability, size, and functionality influences the overall effectiveness of a portable generator. A compact, lightweight unit simplifies transport and storage, allowing for quick deployment during outages. However, smaller size often correlates with lower power output and runtime. Larger, more powerful generators offer increased capacity but compromise portability. Real-world scenarios highlight this trade-off: a homeowner with limited storage space might prioritize a compact inverter generator despite its lower power output, while a homeowner with greater power demands and ample storage might opt for a larger, more powerful conventional generator. Understanding these trade-offs empowers consumers to select the most suitable unit for their specific needs.
In conclusion, the ideal portable generator for home use effectively balances portability, size, and performance. Careful consideration of individual power requirements, storage limitations, and physical capabilities informs the selection process. Prioritizing maneuverability and compact design ensures ease of use and storage, while adequate power output and runtime guarantee functionality during outages. Striking the optimal balance between these factors maximizes the generator’s practical value and ensures it serves as a reliable and convenient power source when needed. This understanding empowers consumers to make informed purchasing decisions, selecting a generator that seamlessly integrates into their specific living environment and effectively meets their backup power needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common inquiries regarding portable generators for residential applications provides clarity and facilitates informed decision-making. The following questions and answers offer valuable insights for consumers considering the acquisition of a portable generator.
Question 1: What size portable generator is needed for a typical home?
Generator sizing depends on specific power requirements. Calculating the wattage of essential appliances and devices determines the necessary generator output. Consulting a qualified electrician is recommended for complex electrical systems or specialized equipment.
Question 2: What are the different fuel types available for portable generators, and what are their respective advantages and disadvantages?
Common fuel types include gasoline, propane, and diesel. Gasoline offers widespread availability but requires regular refueling and proper storage. Propane provides longer shelf life and cleaner emissions but may require larger tanks for extended runtimes. Diesel offers high efficiency and long runtimes but can be more expensive and noisy.
Question 3: How are portable generators safely connected to a home’s electrical system?
Safe connection requires a properly installed transfer switch. Direct connection to household wiring is unsafe and can cause electrocution or damage to appliances. Consulting a qualified electrician is crucial for safe transfer switch installation and generator integration.
Question 4: What safety precautions are essential when operating a portable generator?
Operating a generator outdoors in a well-ventilated area, away from windows and doors, is paramount due to carbon monoxide risks. Proper grounding and dry operation are essential for preventing electrical hazards. Adequate fuel storage and handling procedures minimize fire risks.
Question 5: How often should a portable generator undergo maintenance?
Regular maintenance, as outlined in the manufacturer’s guidelines, ensures reliable performance. Routine maintenance typically includes oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement. Adhering to a maintenance schedule prolongs generator lifespan and optimizes performance.
Question 6: What are the typical noise levels of portable generators, and how can noise be minimized?
Noise levels vary depending on generator size, type, and load. Inverter generators generally operate more quietly than conventional models. Positioning the generator on a stable, level surface away from reflective surfaces can minimize noise. Specialized enclosures or sound-dampening materials can further reduce noise levels.
Careful consideration of these frequently asked questions empowers informed decision-making regarding the selection, installation, and operation of portable generators. Further research and consultation with qualified professionals are encouraged to address specific requirements and ensure safe and effective generator utilization.
Navigating the various aspects of portable generator selection and operation requires a comprehensive understanding of power needs, fuel options, safety procedures, and maintenance requirements. This knowledge ensures the chosen generator aligns with specific circumstances and serves as a reliable power source during outages. The following sections delve deeper into specific generator types and their respective applications, further refining the selection process.
Conclusion
Optimal portable generator selection for residential applications necessitates careful evaluation of several critical factors. Power output, fuel efficiency, runtime capacity, noise levels, portability, and size significantly influence performance, cost-effectiveness, and overall suitability. Balancing these factors ensures the chosen generator effectively meets individual needs and provides reliable backup power during outages. Thorough research and consideration of specific circumstances, including anticipated load requirements, budget constraints, and local regulations, empower informed purchasing decisions. Understanding the nuances of each factor optimizes the selection process and contributes to long-term satisfaction with the chosen unit. Furthermore, prioritizing safety and adhering to proper operating and maintenance procedures ensures safe and effective generator utilization, maximizing its value as a dependable backup power solution.
Reliable backup power assumes increasing importance in a world facing increasingly frequent and unpredictable power disruptions. Investing in a high-quality portable generator provides peace of mind and ensures preparedness for unforeseen events. Careful consideration of the factors outlined herein empowers consumers to navigate the complexities of generator selection and secure a reliable power source capable of safeguarding essential household functions during critical situations. Proactive planning and informed decision-making transform a portable generator from a simple appliance into a crucial component of household resilience and safety. The ability to maintain essential services, preserve comfort, and ensure safety during power outages underscores the enduring value and significance of a well-chosen portable generator in modern homes.