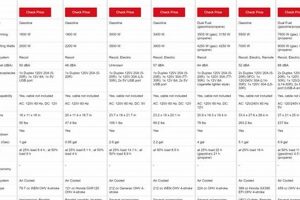
A tabular representation facilitates the evaluation of sound levels produced by various mobile power sources. This typically involves comparing decibel ratings across different models and brands, often alongside other relevant specifications like... Read more »

Compact, muted power sources are essential for a variety of applications where traditional generators are impractical due to their noise output. These devices provide electricity without the disruptive hum or roar often... Read more »

Portable generators manufactured by Generac Power Systems produce sound during operation, measured in decibels (dB). This sound output varies depending on the model’s size, load, and operating mode. For example, a smaller... Read more »
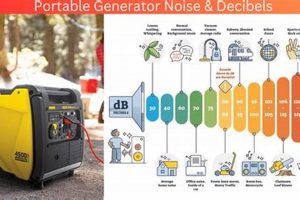
The acoustic output of compact, mobile power sources is a critical factor for users and the surrounding environment. This output is typically measured in decibels (dB), a logarithmic unit expressing the intensity... Read more »
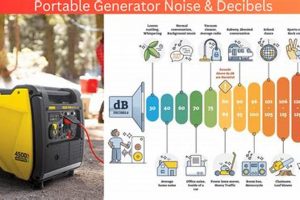
The sound produced by compact, mobile power sources typically involves a mix of frequencies emanating from the engine, exhaust, and cooling fan. A small engine operating under load, coupled with airflow and... Read more »

Compact, independent power sources designed for minimal sound output are increasingly popular for various applications. These units offer a practical solution for powering devices and appliances in noise-sensitive environments, such as campsites,... Read more »

A compact electronic device produces a consistent sound containing all audible frequencies at equal intensity. This sound often masks other noises, creating a more peaceful auditory environment. Examples include handheld devices using... Read more »

A compact, battery-powered device capable of producing a specific type of sound signal characterized by equal energy per octave is now readily available. This signal type is often utilized for sound masking,... Read more »

The acoustic output of compact, mobile power sources is typically measured in decibels (dB). A typical gasoline-powered unit might produce sound levels ranging from 60 dB to over 90 dB, depending on... Read more »

Minimizing the sound output of compact, transportable power sources involves a range of techniques and technologies. For instance, specialized enclosures can dampen acoustic emissions, while strategically chosen mufflers disrupt the flow of... Read more »


