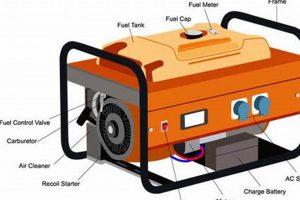
Safe and effective generator operation involves careful planning and execution. This includes understanding the generator’s power output, connecting appliances correctly, and adhering to essential safety precautions. For instance, a homeowner might use a portable generator to power essential appliances like a refrigerator and a few lights during a power outage, ensuring the total wattage drawn doesn’t exceed the generator’s capacity. Proper grounding and ventilation are also crucial for safe operation.
Backup power provided by these units offers significant advantages during emergencies, ensuring the continuity of essential services and enhancing safety and comfort. Historically, generators have evolved from bulky, noisy machines to the more compact and quieter models available today, making them a practical solution for residential power needs during outages or in off-grid locations. Reliable backup power can prevent food spoilage, maintain comfortable temperatures, and enable communication during critical events.
The following sections will delve into the crucial aspects of generator operation, covering topics such as selecting the right generator size, safe connection procedures, proper grounding techniques, essential safety measures, and recommended maintenance practices. This information empowers homeowners to utilize their generators effectively and safely.
Safe and Effective Generator Operation Tips
These tips provide crucial guidance for the safe and effective use of portable generators, ensuring optimal performance and preventing accidents.
Tip 1: Calculate Power Needs: Determine the wattage requirements of appliances intended for connection to the generator. Add these wattages to ensure the total load doesn’t exceed the generator’s capacity. Overloading can damage both the generator and connected appliances.
Tip 2: Proper Ventilation: Operate generators outdoors in well-ventilated areas, far from windows, doors, and vents. Carbon monoxide emissions pose a serious health risk. Never operate a generator indoors or in enclosed spaces.
Tip 3: Safe Connections: Utilize heavy-duty, outdoor-rated extension cords specifically designed for generator use. Ensure cords are in good condition and rated for the wattage being drawn. Avoid overloading extension cords.
Tip 4: Grounding: Properly ground the generator according to manufacturer instructions. This essential safety step protects against electrical shock.
Tip 5: Fuel Handling: Allow the generator to cool completely before refueling. Store fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Never refuel a running generator.
Tip 6: Regular Maintenance: Follow the manufacturers recommended maintenance schedule, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement. Regular maintenance ensures reliable operation and prolongs the generator’s lifespan.
Tip 7: Dry Operation: Never run a generator without adding the required fluids, specifically oil. This can severely damage the engine and lead to costly repairs. Check oil levels before each use.
Adherence to these guidelines ensures safe and efficient generator operation, providing reliable power during outages while minimizing risks.
By following these safety and operational guidelines, homeowners can confidently utilize portable generators as a reliable power source during emergencies, ensuring safety and peace of mind.
1. Safety First
Operating a portable gas generator requires careful attention to safety procedures. Overlooking these precautions can lead to significant hazards, including carbon monoxide poisoning, fire, and electrical shock. Prioritizing safety is paramount for protecting individuals and property.
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Prevention
Generators produce carbon monoxide, an odorless, colorless, and lethal gas. Operating a generator indoors, in a garage, or near open windows poses a severe risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Fatal incidents underscore the importance of operating generators exclusively outdoors in well-ventilated areas, far from any structure.
- Fire Hazard Mitigation
Generators utilize flammable fuel. Spilled fuel combined with the generator’s heat creates a significant fire hazard. Allowing the generator to cool completely before refueling and storing fuel safely away from ignition sources mitigates this risk. Using appropriate fuel containers and avoiding overfilling further reduces fire hazards.
- Electrical Shock Prevention
Improper grounding and connection procedures can lead to electrical shock. Ensuring the generator is properly grounded and using heavy-duty, outdoor-rated extension cords in good condition minimizes this risk. Connecting appliances directly to the generator without appropriate transfer switches can also create electrical hazards within the home’s wiring.
- Safe Operation Practices
Safe operation encompasses several critical practices. Never refuel a running generator. Keep the generator dry and protected from the elements. Regularly inspect the generator for damage. Adhering to these practices and consulting the manufacturer’s instructions ensures safe and reliable operation.
Integrating these safety precautions into every step of generator operation, from setup and use to maintenance and storage, ensures user well-being and prevents accidents. Neglecting these precautions can have dire consequences. Responsible generator use necessitates a proactive and informed approach to safety.
2. Proper Connection
Safe and efficient generator operation hinges on proper connection procedures. Incorrect connections can damage appliances, overload the generator, and pose significant safety risks. Understanding these procedures is essential for effective power delivery during outages.
- Appliance Connection Methods
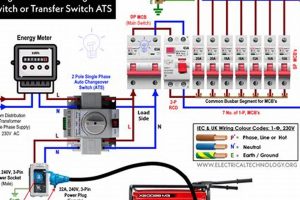
Connecting appliances directly to the generator’s outlets is suitable for smaller loads. However, for multiple appliances or larger loads, a power distribution panel or transfer switch offers safer and more organized power distribution. Transfer switches, professionally installed, prevent backfeeding into the utility grid, a dangerous condition that can harm utility workers and damage appliances.
- Extension Cord Selection and Usage
Using appropriately rated extension cords is crucial. Undersized cords can overheat, posing fire risks and damaging appliances. Outdoor-rated, heavy-duty extension cords designed for generator use are recommended. Inspecting cords for damage before each use ensures safe operation. Connecting multiple devices to a single cord may exceed its capacity; individual cords for high-wattage appliances are often safer.
- Transfer Switch Advantages
Transfer switches provide a safe and convenient method for connecting a generator to a home’s electrical system. They isolate the generator’s power from the utility grid, preventing backfeeding. This protects utility workers from electrocution and safeguards appliances from damage. While more complex to install, transfer switches offer significantly enhanced safety and convenience during prolonged outages.
- Avoiding Overloads
Calculating the total wattage of connected appliances and ensuring it remains within the generator’s capacity is critical. Overloading can damage both the generator and connected appliances. Prioritizing essential appliances during outages and staggering their use helps manage the load effectively. Monitoring the generator’s output meter aids in preventing overloads.
Proper connection procedures are integral to safe and effective generator operation. Understanding these procedures, from selecting the correct extension cords to utilizing transfer switches and managing loads, ensures efficient power delivery while mitigating risks and protecting both the generator and connected appliances. Failure to adhere to these guidelines can result in equipment damage, safety hazards, and inefficient power distribution during critical outages.
3. Adequate Ventilation
Adequate ventilation is paramount when operating a portable gas generator. Generators produce carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is lethal when inhaled. Insufficient ventilation traps CO, creating a hazardous environment. Consequences range from mild headaches and nausea to severe neurological damage and death. For example, operating a generator inside a garage, even with the door open, can lead to dangerous CO buildup. Another tragically common scenario involves placing a generator too close to a home’s windows or air intakes, inadvertently drawing CO indoors. The practical significance of understanding this connection lies in preventing potentially fatal CO poisoning.
Effective ventilation necessitates operating the generator outdoors, far from any enclosed spaces. A minimum distance of 20 feet from any structure, including windows, doors, and vents, is recommended. Wind direction must also be considered, ensuring exhaust fumes are directed away from occupied areas. Obstructions, such as fences or shrubbery, should not impede airflow around the generator. Furthermore, never operate a generator in an enclosed space, such as a basement, crawlspace, or shed, regardless of how well-ventilated it may seem. Even seemingly minor lapses in ventilation can result in dangerous CO accumulation.
Failure to provide adequate ventilation jeopardizes the safety of individuals and anyone nearby. CO poisoning symptoms can be subtle and easily mistaken for other ailments, delaying diagnosis and treatment. Portable CO detectors can provide an additional layer of protection, alerting individuals to dangerous CO levels. However, relying solely on detectors is insufficient; proper ventilation remains the primary defense against CO poisoning. Integrating a thorough understanding of ventilation principles into generator operation protocols is crucial for safe and responsible power generation.
4. Load Management
Load management is a critical aspect of safe and efficient portable generator operation. Generators have a defined wattage capacity, representing the maximum power they can safely deliver. Exceeding this capacity through excessive load leads to generator overload, potentially causing damage to the unit and connected appliances. Overloading manifests in various ways, including engine strain, overheating, and circuit breaker trips. In severe cases, it can lead to permanent generator damage or even electrical fires. Understanding load management principles is crucial for preventing these issues. For example, attempting to power a large air conditioner, a refrigerator, and multiple power tools simultaneously might exceed a typical portable generator’s capacity, resulting in an overload. Conversely, powering only essential appliances like a refrigerator, a few lights, and a small fan keeps the load within safe limits.
Effective load management involves calculating the wattage requirements of each appliance intended for connection to the generator. Wattage information is typically found on an appliance’s label or in its user manual. Summing these wattages provides the total load. This total load must remain below the generator’s rated wattage capacity. Prioritizing essential appliances during an outage is crucial for effective load management. Operating high-wattage appliances in sequence, rather than concurrently, avoids overloading the generator. For instance, running the washing machine followed by the microwave, rather than both simultaneously, distributes the load effectively over time. Monitoring the generator’s output meter provides real-time feedback on current load, enabling adjustments as needed. Furthermore, investing in a generator with a slightly higher wattage capacity than initially calculated offers a safety margin and accommodates future power needs.
Failure to implement proper load management strategies compromises generator longevity and safety. Repeated overloading reduces the generator’s lifespan and increases the risk of malfunctions. In addition to equipment damage, overloading can create electrical hazards, potentially damaging connected appliances or even causing fires. Practical application of load management principles ensures safe, efficient, and reliable power delivery during outages. It empowers individuals to maximize the benefits of portable generators while minimizing risks and prolonging the equipment’s lifespan. Effective load management is therefore an indispensable component of responsible generator ownership and operation.
5. Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for safe and reliable portable generator operation. Neglecting routine maintenance compromises performance, reduces lifespan, and increases the risk of malfunctions during critical power outages. A well-maintained generator provides consistent power when needed, while a neglected unit can fail unexpectedly, leading to inconvenience and potential safety hazards. Understanding and adhering to a regular maintenance schedule is therefore integral to effective generator ownership.
- Oil Changes
Regular oil changes are crucial for maintaining engine lubrication and preventing premature wear. Engine oil degrades over time, losing its lubricating properties and accumulating contaminants. Running a generator with degraded oil increases friction, leading to overheating and reduced engine life. Consulting the manufacturer’s recommendations for oil type and change intervals is crucial. For example, a typical recommendation might involve changing the oil every 50 hours of operation or annually, whichever comes first. Ignoring oil changes significantly shortens engine lifespan and increases the likelihood of malfunctions.
- Air Filter Cleaning/Replacement
Clean air filters ensure efficient combustion and optimal engine performance. Dirty air filters restrict airflow, reducing engine power and increasing fuel consumption. Dust, debris, and other airborne particles accumulate in the air filter, hindering proper air intake. Regularly inspecting and cleaning or replacing the air filter, as recommended by the manufacturer, maintains airflow and prevents performance degradation. In dusty environments, more frequent air filter maintenance may be necessary. Neglecting air filter maintenance can lead to reduced power output, increased fuel consumption, and potential engine damage.
- Spark Plug Inspection/Replacement
Spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mixture within the engine cylinder, initiating combustion. Worn or fouled spark plugs impede efficient combustion, reducing engine performance and increasing fuel consumption. Regular inspection and replacement of spark plugs, according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, ensures reliable ignition and optimal engine function. Signs of worn spark plugs include difficulty starting, rough engine running, and decreased power output. Ignoring spark plug maintenance can lead to performance issues, increased fuel consumption, and potential engine damage.
- Fuel System Maintenance
Proper fuel system maintenance prevents fuel-related issues that can hinder generator operation. Stale fuel, especially gasoline containing ethanol, can degrade over time, forming gums and varnishes that clog fuel lines and carburetor jets. Draining the fuel system before extended storage periods prevents these issues. Using a fuel stabilizer can extend fuel shelf life. Regularly inspecting and cleaning the fuel tank and lines helps maintain fuel system integrity. Neglecting fuel system maintenance can lead to starting difficulties, rough running, and reduced generator performance.
Integrating these maintenance tasks into a regular schedule ensures the generator’s reliability and longevity. A proactive approach to maintenance minimizes the risk of unexpected failures, particularly during critical power outages. Proper maintenance not only enhances performance and extends lifespan but also contributes to safer generator operation by mitigating the risk of malfunctions and associated hazards. Regular maintenance, therefore, represents a crucial aspect of responsible generator ownership and its effective utilization within a home environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding safe and effective portable generator operation in residential settings. Clarity on these points promotes proper usage and mitigates potential risks.
Question 1: How is the appropriate generator size determined for home use?
Generator size selection depends on the intended load. Calculate the total wattage of appliances planned for simultaneous operation during an outage. The generator’s running watts should exceed this total. Consulting an electrician can provide further guidance.
Question 2: What safety precautions are essential when operating a portable generator?
Operating a generator outdoors, far from structures, is crucial to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. Proper grounding and the use of heavy-duty extension cords prevent electrical hazards. Allowing the generator to cool before refueling mitigates fire risks.
Question 3: Can a portable generator be connected directly to a home’s electrical system?
Direct connection to a home’s electrical system requires a properly installed transfer switch. This prevents backfeeding, protecting utility workers and appliances. Direct connection without a transfer switch is unsafe and can damage the electrical system.
Question 4: What type of fuel is recommended for portable generators?
Consult the manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate fuel type. Using the incorrect fuel can damage the generator. Store fuel in approved containers in a well-ventilated area away from ignition sources.
Question 5: How frequently should generator maintenance be performed?
Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule is crucial. This typically includes regular oil changes, air filter cleaning or replacement, and spark plug inspection. Regular maintenance ensures reliable operation and prolongs generator lifespan.
Question 6: What steps should be taken to prepare a generator for an extended period of non-use?
For long-term storage, drain the fuel system or add a fuel stabilizer to prevent fuel degradation. Disconnect the spark plug and store the generator in a dry, protected location. Consult the manufacturer’s instructions for specific storage recommendations.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of generator operation ensures safe and efficient power delivery during outages. Prioritizing safety and adhering to manufacturer guidelines optimizes performance and prolongs the generator’s lifespan.
Further sections will delve into specific maintenance procedures, troubleshooting common issues, and exploring advanced generator features.
Conclusion
Safe and effective portable generator operation necessitates a comprehensive understanding of key principles. From meticulous load calculations and proper connection procedures to unwavering adherence to safety precautions and diligent maintenance practices, each step plays a vital role in ensuring reliable power delivery during outages. Adequate ventilation is paramount in mitigating the risks of carbon monoxide poisoning, while proper fuel handling and storage prevent fire hazards. Regular maintenance, including oil changes, air filter cleaning, and spark plug replacement, ensures optimal performance and prolongs the generator’s lifespan. Prioritizing these practices safeguards both individuals and property.
Portable generators offer invaluable support during power disruptions, providing essential power for critical appliances and enhancing safety and comfort. However, realizing these benefits requires responsible operation grounded in a thorough understanding of safety procedures and operational best practices. Continuous learning and adherence to manufacturer guidelines remain crucial for maximizing the benefits of portable generators while minimizing potential risks. Investing time in understanding these aspects empowers individuals to utilize portable generators safely and effectively, ensuring preparedness and resilience during unforeseen power outages.